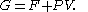Isothermal-isobaric ensemble
Encyclopedia
The isothermal–isobaric ensemble (constant temperature and constant pressure ensemble) is a statistical mechanical ensemble that maintains constant temperature 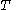 and constant pressure
and constant pressure 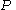 applied. It is also called the
applied. It is also called the 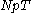 -ensemble, where the number of particles
-ensemble, where the number of particles 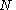 is also kept as a constant. This ensemble plays an important role in chemistry as chemical reactions are usually carried out under constant pressure condition. The partition function can be written as the weighted sum of the partition function of canonical ensemble
is also kept as a constant. This ensemble plays an important role in chemistry as chemical reactions are usually carried out under constant pressure condition. The partition function can be written as the weighted sum of the partition function of canonical ensemble
,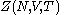 .
.
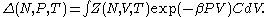
where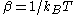 (
(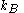 is the Boltzmann constant), and
is the Boltzmann constant), and 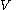 is volume of the system.
is volume of the system.
There are several candidates for the normalization factor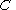 , e.g.,
, e.g., 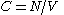 , or
, or 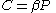 . These choices make the partition function a nondimensional
. These choices make the partition function a nondimensional
quantity. The differences vanish in the thermodynamic limit
, i.e., in the limit of infinite number of particles.
The characteristic state function of this ensemble is the Gibbs free energy
,
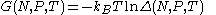
This thermodynamic potential is related to the Helmholtz free energy
(logarithm of the canonical partition function),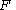 , in the following way:
, in the following way:
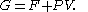
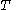 and constant pressure
and constant pressure 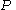 applied. It is also called the
applied. It is also called the 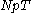 -ensemble, where the number of particles
-ensemble, where the number of particles 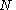 is also kept as a constant. This ensemble plays an important role in chemistry as chemical reactions are usually carried out under constant pressure condition. The partition function can be written as the weighted sum of the partition function of canonical ensemble
is also kept as a constant. This ensemble plays an important role in chemistry as chemical reactions are usually carried out under constant pressure condition. The partition function can be written as the weighted sum of the partition function of canonical ensembleCanonical ensemble
The canonical ensemble in statistical mechanics is a statistical ensemble representing a probability distribution of microscopic states of the system...
,
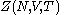 .
.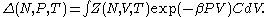
where
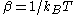 (
(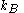 is the Boltzmann constant), and
is the Boltzmann constant), and 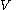 is volume of the system.
is volume of the system.There are several candidates for the normalization factor
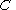 , e.g.,
, e.g., 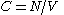 , or
, or 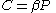 . These choices make the partition function a nondimensional
. These choices make the partition function a nondimensionalNondimensionalization
Nondimensionalization is the partial or full removal of units from an equation involving physical quantities by a suitable substitution of variables. This technique can simplify and parameterize problems where measured units are involved. It is closely related to dimensional analysis...
quantity. The differences vanish in the thermodynamic limit
Thermodynamic limit
In thermodynamics, particularly statistical mechanics, the thermodynamic limit is reached as the number of particles in a system, N, approaches infinity...
, i.e., in the limit of infinite number of particles.
The characteristic state function of this ensemble is the Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
,
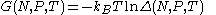
This thermodynamic potential is related to the Helmholtz free energy
Helmholtz free energy
In thermodynamics, the Helmholtz free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the “useful” work obtainable from a closed thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and volume...
(logarithm of the canonical partition function),
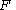 , in the following way:
, in the following way: