Internal iliac artery
Encyclopedia
The internal iliac artery (formerly known as the hypogastric artery) is the main artery
of the pelvis
.
, the buttock, the reproductive organs, and the medial compartment of the thigh
. The vesicular branches of the internal iliac arteries supply the bladder
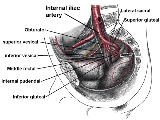
It is a short, thick vessel, smaller than the external iliac artery
, and about 3 to 4 cm in length.
, opposite the lumbosacral articulation, and, passing downward to the upper margin of the greater sciatic foramen
, divides into two large trunks, an anterior and a posterior.
The following are relations of the artery at various points: it is posterior to the ureter
, anterior to the internal iliac vein
, the lumbosacral trunk
, and the piriformis muscle
; near its origin, it is medial to the external iliac vein
, which lies between it and the psoas major muscle
; it is above the obturator nerve
.
The following are the branches of internal iliac artery. Because it is variable, a listed artery may not be a direct branch, but instead might arise off a direct branch.
, the internal iliac artery is twice as large as the external iliac, and is the direct continuation of the common iliac.
It ascends along the side of the bladder
, and runs upward on the back of the anterior wall of the abdomen to the umbilicus
, converging toward its fellow of the opposite side.
Having passed through the umbilical opening, the two arteries, now termed umbilical, enter the umbilical cord
, where they are coiled around the umbilical vein, and ultimately ramify in the placenta
.
At birth, when the placental circulation ceases, the pelvic portion only of the umbilical artery remains patent gives rise to the superior vesical artery (or arteries) of the adult; the remainder of the vessel is converted into a solid fibrous cord, the medial umbilical ligament
(otherwise known as the obliterated hypogastric artery) which extends from the pelvis to the umbilicus.
The lengths of the common iliac and internal iliac arteries bear an inverse proportion to each other, the internal iliac artery being long when the common iliac is short, and vice versa.
The place of division of the internal iliac artery varies between the upper margin of the sacrum
and the upper border of the greater sciatic foramen
.
The right and left hypogastric arteries in a series of cases often differed in length, but neither seemed constantly to exceed the other.
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
of the pelvis
Pelvis
In human anatomy, the pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the lower limbs .The pelvis includes several structures:...
.
Structure
The internal iliac artery supplies the walls and viscera of the pelvisPelvis
In human anatomy, the pelvis is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the lower limbs .The pelvis includes several structures:...
, the buttock, the reproductive organs, and the medial compartment of the thigh
Thigh
In humans the thigh is the area between the pelvis and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.The single bone in the thigh is called the femur...
. The vesicular branches of the internal iliac arteries supply the bladder
It is a short, thick vessel, smaller than the external iliac artery
External iliac artery
The external iliac arteries are two major arteries which bifurcate off the common iliac arteries anterior to the sacroiliac joint of the pelvis. They proceed anterior and inferior along the medial border of the psoas major muscles...
, and about 3 to 4 cm in length.
Course
It arises at the bifurcation of the common iliac arteryCommon iliac artery
The common iliac arteries are two large arteries that originate from the aortic bifurcation at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra. They bifurcate into the external iliac artery and internal iliac artery ....
, opposite the lumbosacral articulation, and, passing downward to the upper margin of the greater sciatic foramen
Greater sciatic foramen
-Boundaries:It is bounded as follows:* anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the illium* posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament* inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine* superiorly by the anterior sacroilliac ligament...
, divides into two large trunks, an anterior and a posterior.
The following are relations of the artery at various points: it is posterior to the ureter
Ureter
In human anatomy, the ureters are muscular tubes that propel urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In the adult, the ureters are usually long and ~3-4 mm in diameter....
, anterior to the internal iliac vein
Internal iliac vein
The internal iliac vein begins near the upper part of the greater sciatic foramen, passes upward behind and slightly medial to the Internal iliac artery and, at the brim of the pelvis, joins with the external iliac vein to form the common iliac vein.-Tributaries:With the exception of the fetal...
, the lumbosacral trunk
Lumbosacral trunk
The lumbosacral trunk is nervous tissue that connects the lumbar plexus with the sacral plexus.-Structure:The lumbosacral trunk comprises the whole of the anterior division of the fifth and a part of that of the fourth lumbar nerve; it appears at the medial margin of the psoas major and runs...
, and the piriformis muscle
Piriformis muscle
The piriformis is a muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limb. It was first named by Spigelius, a professor from the University of Padua in the 16th century.- Origin and insertion :...
; near its origin, it is medial to the external iliac vein
External iliac vein
The external iliac veins are large veins that connect the femoral veins to the common iliac veins. Their origin is at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligaments and they terminate when they join the internal iliac veins ....
, which lies between it and the psoas major muscle
Psoas major muscle
-External links: - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Muscles of the Posterior Abdominal Wall"* *...
; it is above the obturator nerve
Obturator nerve
The obturator nerve in human anatomy arises from the ventral divisions of the second, third, and fourth lumbar nerves; the branch from the third is the largest, while that from the second is often very small.-Path:...
.
Branches
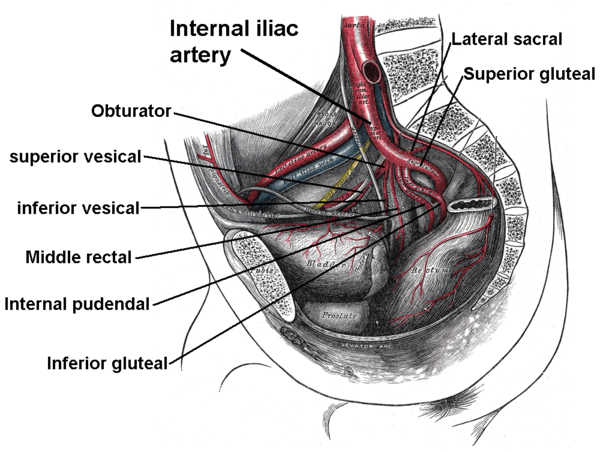
The exact arrangement of branches of the internal iliac artery is variable. Generally, the artery divides into an anterior division and a posterior division, with the posterior division giving rise to the superior gluteal, iliolumbar, and lateral sacral arteries. The rest usually arise from the anterior division.The following are the branches of internal iliac artery. Because it is variable, a listed artery may not be a direct branch, but instead might arise off a direct branch.

| Division | Branch | Sub-branches | To/through >- | Posterior |
Iliolumbar artery Iliolumbar artery The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.-Course:The iliolumbar artery turns upward behind the obturator nerve and the external iliac artery and vein, to the medial border of the psoas major, behind which it divides into:* Lumbar branch of... |
lumbar and iliac branches | psoas major muscle Psoas major muscle -External links: - "Posterior Abdominal Wall: Muscles of the Posterior Abdominal Wall"* *... , quadratus lumborum muscle Quadratus lumborum muscle The Quadratus lumborum is irregular and quadrilateral in shape, and broader below than above.-Origin and insertion:It arises by aponeurotic fibers from the iliolumbar ligament and the adjacent portion of the iliac crest for about 5 cm., and is inserted into the lower border of the last rib for... , iliacus muscle Iliacus muscle The iliacus is a flat, triangular muscle which fills the iliac fossa.- Course :The iliacus arises from the iliac fossa on the interior side of the hip bone, and also from the region of the anterior inferior iliac spine... >- | Posterior |
Lateral sacral arteries | superior and inferior branches | anterior sacral foramina Anterior sacral foramina At the ends of the transverse ridges of the pelvic surface of the sacrum are seen the anterior sacral foramina , four in number on either side, somewhat rounded in form, diminishing in size from above downward, and directed lateralward and forward.They give exit to the anterior divisions of the... >- | Posterior |
Superior gluteal artery Superior gluteal artery The superior gluteal artery is the largest branch of the internal iliac artery, and appears to be the continuation of the posterior division of that vessel.... |
- | greater sciatic foramen Greater sciatic foramen -Boundaries:It is bounded as follows:* anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the illium* posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament* inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine* superiorly by the anterior sacroilliac ligament... >- | Anterior |
Obturator artery Obturator artery The obturator artery is a branch of the internal iliac artery that passes antero-inferiorly on the lateral wall of the pelvis, to the upper part of the obturator foramen, and, escaping from the pelvic cavity through the obturator canal, it divides into both an anterior and a posterior... (occasionally from inferior epigastric artery Inferior epigastric artery In human anatomy, inferior epigastric artery refers to the artery that arises from the external iliac artery and anastomoses with the superior epigastric artery... ) |
- | obturator canal Obturator canal The obturator canal is a passageway formed in the obturator foramen by part of the obturator membrane. It connects the pelvis to the thigh.The obturator artery, obturator vein, and obturator nerve all travel through the canal.-Pathology:... >- | Anterior |
Inferior gluteal artery Inferior gluteal artery The inferior gluteal artery , the larger of the two terminal branches of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery, is distributed chiefly to the buttock and back of the thigh.... |
- | greater sciatic foramen Greater sciatic foramen -Boundaries:It is bounded as follows:* anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the illium* posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament* inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine* superiorly by the anterior sacroilliac ligament... >- | Anterior |
Umbilical artery Umbilical artery The umbilical artery is a paired artery that is found in the abdominal and pelvic regions. In the fetus, it extends into the umbilical cord.-Umbilical arteries in the fetus:... |
superior vesical artery Superior vesical artery The superior vesical artery supplies numerous branches to the upper part of the bladder.From one of these a slender vessel, the artery to the ductus deferens, takes origin and accompanies the duct in its course to the testis, where it anastomoses with the internal spermatic artery.Other branches... (usually, but sometimes it branches directly from anterior trunk) |
medial umbilical ligament Medial umbilical ligament The medial umbilical ligament is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds .... >- | Anterior |
Uterine artery Uterine artery -Structure:The uterine artery usually arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It travels to the uterus, crossing the ureter anteriorly, reaching the uterus by traveling in the cardinal ligament.... (females) or deferential artery (males) |
superior and vaginal branches | uterus Uterus The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species... , vas deferens Vas deferens The vas deferens , also called ductus deferens, , is part of the male anatomy of many vertebrates; they transport sperm from the epididymis in anticipation of ejaculation.... >- | Anterior |
Vaginal artery Vaginal artery -Terminology:The vaginal artery is usually defined as a branch of the internal iliac artery.Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the internal iliac artery or the uterine artery... (females, can also arise from uterine artery Uterine artery -Structure:The uterine artery usually arises from the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It travels to the uterus, crossing the ureter anteriorly, reaching the uterus by traveling in the cardinal ligament.... ) |
- | vagina Vagina The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the... >- | Anterior |
inferior vesical artery Inferior vesical artery The inferior vesical artery is an artery in the pelvis that supplies the lower part of the bladder.-Structure:The inferior vesical artery is a branch of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery. It frequently arises in common with the middle rectal artery, and is distributed to the... |
- | urinary bladder Urinary bladder The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor... >- | Anterior |
Middle rectal artery Middle rectal artery The middle rectal artery is an artery in the pelvis that supplies blood to the rectum.-Structure:The middle rectal artery usually arises with the inferior vesical artery, a branch of the internal iliac artery... |
- | rectum Rectum The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in some mammals, and the gut in others, terminating in the anus. The human rectum is about 12 cm long... >- | Anterior |
Internal pudendal artery Internal pudendal artery The internal pudendal artery is an artery that branches off the internal iliac artery, providing blood to the external genitalia.The internal pudendal artery is the terminal branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery... |
many branches - see article for details | greater sciatic foramen Greater sciatic foramen -Boundaries:It is bounded as follows:* anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the illium* posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament* inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine* superiorly by the anterior sacroilliac ligament... |
Structure in fetus
In the fetusFetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
, the internal iliac artery is twice as large as the external iliac, and is the direct continuation of the common iliac.
It ascends along the side of the bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
, and runs upward on the back of the anterior wall of the abdomen to the umbilicus
Navel
The navel is a scar on the abdomen caused when the umbilical cord is removed from a newborn baby...
, converging toward its fellow of the opposite side.
Having passed through the umbilical opening, the two arteries, now termed umbilical, enter the umbilical cord
Umbilical cord
In placental mammals, the umbilical cord is the connecting cord from the developing embryo or fetus to the placenta...
, where they are coiled around the umbilical vein, and ultimately ramify in the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
.
At birth, when the placental circulation ceases, the pelvic portion only of the umbilical artery remains patent gives rise to the superior vesical artery (or arteries) of the adult; the remainder of the vessel is converted into a solid fibrous cord, the medial umbilical ligament
Medial umbilical ligament
The medial umbilical ligament is a paired structure found in human anatomy. It is on the deep surface of the anterior abdominal wall, and is covered by the medial umbilical folds ....
(otherwise known as the obliterated hypogastric artery) which extends from the pelvis to the umbilicus.
Variation
In two-thirds of a large number of cases, the length of the internal iliac varied between 2.25 and 3.4 cm.; in the remaining third it was more frequently longer than shorter, the maximum length being about 7 cm. the minimum about 1 cm.The lengths of the common iliac and internal iliac arteries bear an inverse proportion to each other, the internal iliac artery being long when the common iliac is short, and vice versa.
The place of division of the internal iliac artery varies between the upper margin of the sacrum
Sacrum
In vertebrate anatomy the sacrum is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine and at the upper and back part of the pelvic cavity, where it is inserted like a wedge between the two hip bones. Its upper part connects with the last lumbar vertebra, and bottom part with the coccyx...
and the upper border of the greater sciatic foramen
Greater sciatic foramen
-Boundaries:It is bounded as follows:* anterolaterally by the greater sciatic notch of the illium* posteromedially by the sacrotuberous ligament* inferiorly by the sacrospinous ligament and the ischial spine* superiorly by the anterior sacroilliac ligament...
.
The right and left hypogastric arteries in a series of cases often differed in length, but neither seemed constantly to exceed the other.
Collateral Circulation
The circulation after ligature of the internal iliac artery is carried on by the anastomoses of:- the middle rectal arteryMiddle rectal arteryThe middle rectal artery is an artery in the pelvis that supplies blood to the rectum.-Structure:The middle rectal artery usually arises with the inferior vesical artery, a branch of the internal iliac artery...
and the superior rectal arterySuperior rectal arteryThe superior rectal artery is an artery that descends into the pelvis to supply blood to the rectum.-Structure:The superior rectal artery is the continuation of the inferior mesenteric artery... - the iliolumbar arteryIliolumbar arteryThe iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery.-Course:The iliolumbar artery turns upward behind the obturator nerve and the external iliac artery and vein, to the medial border of the psoas major, behind which it divides into:* Lumbar branch of...
with the last lumbar artery - the lateral sacral arteries with the median sacral arteryMedian sacral arteryThe median sacral artery is a small vessel, which arises from the back of the aorta, a little above its bifurcation....

