
Interlocking interval topology
Encyclopedia
In mathematics, and especially general topology
, the interlocking interval topology is an example of a topology
on the set , i.e. the set of all positive real number
s that are not positive whole numbers. To give the set S a topology means to say which subset
s of S are "open", and to do so in a way that the following axiom
s are met:
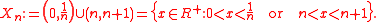
The sets generated by Xn will be formed by all possible unions of finite intersections of the Xn.
General topology
In mathematics, general topology or point-set topology is the branch of topology which studies properties of topological spaces and structures defined on them...
, the interlocking interval topology is an example of a topology
Topology
Topology is a major area of mathematics concerned with properties that are preserved under continuous deformations of objects, such as deformations that involve stretching, but no tearing or gluing...
on the set , i.e. the set of all positive real number
Real number
In mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
s that are not positive whole numbers. To give the set S a topology means to say which subset
Subset
In mathematics, especially in set theory, a set A is a subset of a set B if A is "contained" inside B. A and B may coincide. The relationship of one set being a subset of another is called inclusion or sometimes containment...
s of S are "open", and to do so in a way that the following axiom
Axiom
In traditional logic, an axiom or postulate is a proposition that is not proven or demonstrated but considered either to be self-evident or to define and delimit the realm of analysis. In other words, an axiom is a logical statement that is assumed to be true...
s are met:
- The union of open sets is an open set.
- The finite intersection of open sets is an open set.
- S and the empty setEmpty setIn mathematics, and more specifically set theory, the empty set is the unique set having no elements; its size or cardinality is zero. Some axiomatic set theories assure that the empty set exists by including an axiom of empty set; in other theories, its existence can be deduced...
∅ are open sets.
Construction
The open sets in this topology are taken to be the whole set S, the empty set ∅, and the sets generated by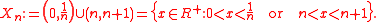
The sets generated by Xn will be formed by all possible unions of finite intersections of the Xn.

