
Integrated urban water management in Aracaju, Brazil
Encyclopedia
Integrated urban water management
in Aracaju
, the capital city of the Brazilian State of Sergipe (SSE) has been and still is a challenging prospect. Home to half a million people, Aracaju is located in a tropical coastal zone within a semi-arid state and receives below average rainfall of 1,200 mm/year where average rainfall in Latin America is higher at 1,556 mm/yr. (Source:FAO 2000) Most of the residents do have access to the potable water supply and non-revenue water
losses are nearly 50%.
The watersheds and rivers feeding the capital city are drought prone; therefore, water scarcity is an ongoing challenge for Aracaju. Aracaju does not have significant groundwater resources, has conflicts between urban and agricultural demand, struggles with a weak institutional framework, and discharges untreated wastewater the São Francisco River running through the city. In an attempt to address these water-related challenges, the SSE has initiated a multi-stakeholder planning process as part of their economic development plan for the years 2008-2011. The city, with assistance from multinational development banks and organizations is also in the planning stages of a water project that will support institutional improvement and development of the irrigation sector.
(SSE) is one of the smallest, least populated, and poorest states in Brazil. It is located in the northeast region, with an area of 21,910 km2 and a population of about 1.94 million inhabitants, 81.2% of which live in urban areas. The coastal zone of Sergipe
, which includes the Metropolitan Region of Aracaju
(MRA), concentrates 43.7% (500k) of the state’s population and produces about 56% of the state’s GDP. Sergipe has the highest per capita annual income in the northeast region at $4,378 (R$7,560), but this represents only about 60 percent of the average national per capita income, and some 52 percent of the population earns less than two minimum salaries a month at around $269 (R$465), indicating a high level of poverty. The economy of Aracaju is based on services, industry and tourism. The GDP as of 2005 for the capital city in the SSE was $2.9 billion (R$ 5 billion).
and Agreste
regions represent 82% of the territory and have an average annual rainfall from 400 to 800 mm/year, while the coastal zone of Aracaju has an average annual rainfall of 1,200 mm/year. This is not much rain when compared to the Amazon basin average rainfall at 8,700mm/yr; however, more in line with the Latin America average of 1556 mm/yr.(Source:FAO 2000) Aracaju has a typical tropical climate, with warm temperatures and high relative humidity throughout the year. January is the warmest month, with an average temperature between 32°C (89.6°F) and 22°C (71.6°F). July experiences the coolest temperatures and most rainfall, with average temperatures between 27°C (80.6°F) and 17°C (62.6°F).
The State of Sergipe (SSE) engaged in a participatory planning process with a priority on water that involved public consultations with civil society and identified priority areas of intervention. This participatory planning process served as a key input to SSE’s 2008-2011 economic development and government action plan, which selected integrated management of natural and water resources, solid waste and sanitation services as one of the SSE’s key priorities.
Integrated urban water management
Integrated urban water management is a philosophy of varying definitions and interpretations. According to the authors of the book entitled, "Integrated Urban Water Management: Humid Tropics", IUWM is described as the practice of managing freshwater, wastewater, and storm water as components of a...
in Aracaju
Aracaju
-Vegetation:Aracaju lies in tropical forest. Rainforests are characterized by high rainfall, with minimum normal annual rainfall between 2,000 mm and 1,700 mm...
, the capital city of the Brazilian State of Sergipe (SSE) has been and still is a challenging prospect. Home to half a million people, Aracaju is located in a tropical coastal zone within a semi-arid state and receives below average rainfall of 1,200 mm/year where average rainfall in Latin America is higher at 1,556 mm/yr. (Source:FAO 2000) Most of the residents do have access to the potable water supply and non-revenue water
Non-revenue water
Non revenue water is water that has been produced and is “lost” before it reaches the customer. Losses can be real losses or apparent losses . High levels of NRW are detrimental to the financial viability of water utilities, as well to the quality of water itself...
losses are nearly 50%.
The watersheds and rivers feeding the capital city are drought prone; therefore, water scarcity is an ongoing challenge for Aracaju. Aracaju does not have significant groundwater resources, has conflicts between urban and agricultural demand, struggles with a weak institutional framework, and discharges untreated wastewater the São Francisco River running through the city. In an attempt to address these water-related challenges, the SSE has initiated a multi-stakeholder planning process as part of their economic development plan for the years 2008-2011. The city, with assistance from multinational development banks and organizations is also in the planning stages of a water project that will support institutional improvement and development of the irrigation sector.
Economic aspects
The State of SergipeSergipe
Sergipe , is the smallest state of the Brazilian Federation, located on the northeastern Atlantic coast of the country. It borders on two other states, Bahia to the south and west and Alagoas to the north, and to the east is the Atlantic Ocean...
(SSE) is one of the smallest, least populated, and poorest states in Brazil. It is located in the northeast region, with an area of 21,910 km2 and a population of about 1.94 million inhabitants, 81.2% of which live in urban areas. The coastal zone of Sergipe
Sergipe
Sergipe , is the smallest state of the Brazilian Federation, located on the northeastern Atlantic coast of the country. It borders on two other states, Bahia to the south and west and Alagoas to the north, and to the east is the Atlantic Ocean...
, which includes the Metropolitan Region of Aracaju
Aracaju
-Vegetation:Aracaju lies in tropical forest. Rainforests are characterized by high rainfall, with minimum normal annual rainfall between 2,000 mm and 1,700 mm...
(MRA), concentrates 43.7% (500k) of the state’s population and produces about 56% of the state’s GDP. Sergipe has the highest per capita annual income in the northeast region at $4,378 (R$7,560), but this represents only about 60 percent of the average national per capita income, and some 52 percent of the population earns less than two minimum salaries a month at around $269 (R$465), indicating a high level of poverty. The economy of Aracaju is based on services, industry and tourism. The GDP as of 2005 for the capital city in the SSE was $2.9 billion (R$ 5 billion).
Geography and climate
The state’s semi-arid SertãoSertão
In Portuguese, the word sertão first referred to the vast hinterlands of Asia that Lusitanian explorers encountered. In Brazil, the geographical term referred to backlands away from the Atlantic coastal regions where the Portuguese first settled in South America in the early sixteenth century...
and Agreste
Agreste
In Brazil, the agreste is a narrow zone in the states of Paraíba, Pernambuco, Alagoas, Sergipe and Bahia between the coastal forest zona da mata and the semiarid sertão...
regions represent 82% of the territory and have an average annual rainfall from 400 to 800 mm/year, while the coastal zone of Aracaju has an average annual rainfall of 1,200 mm/year. This is not much rain when compared to the Amazon basin average rainfall at 8,700mm/yr; however, more in line with the Latin America average of 1556 mm/yr.(Source:FAO 2000) Aracaju has a typical tropical climate, with warm temperatures and high relative humidity throughout the year. January is the warmest month, with an average temperature between 32°C (89.6°F) and 22°C (71.6°F). July experiences the coolest temperatures and most rainfall, with average temperatures between 27°C (80.6°F) and 17°C (62.6°F).
Water supply
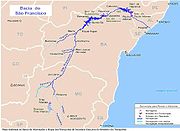
Surface water is the main source of supply, with limited use of groundwater, which is still an unknown and uncertain resource for the area. Aracaju is supplied by the Sergipe and Vazza Barris watersheds making up 6,232 km2 or 28% of the landmass in the state. Together, these two basins convey a flow of water measured at approximately 30 m3/s.(still need the complete reference from "Carta Consulta")
Irrigation
Development of irrigation potential in the basin is limited by water scarcity, pollution and conflicts for water allocation especially for urban supply. However, existing irrigation infrastructure could generate a more effective and efficient use if infrastructure is modernized, service delivery is improved and modern irrigation techniques are made available to farmers. Inefficient management of the irrigation perimeters is also a constraint that needs to be addressed to guarantee their sustainability and optimize positive social and economic results.Water usage & coverage
The total demand for water in the Sergipe river basin is estimated to be of 260,000 m3/day; however, the volume of water provided by the basin itself only amounts to 55,000 m3/day. Transfers from the São Francisco river basin to the MRA cover some of the deficit in availability; however, there are high investment and operating costs associated with these water transfers. The Water supply is available to about 85.2% of the population in the basin; however, access is uneven in social and territorial aspects. The level of water losses in the State Water Supply and Sanitation Utility (DESO) is at 48%, therefore a portion of the population is subject to rationing. As the population of the Sergipe river basin continues to grow at a higher rate than the state average, it is important to maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of the existing and planned infrastructure and the management of water resources and services.Water challenges
The SSE’s and the capital city of Aracaju’s primary water resources challenges are related to scarcity, water pollution, lack of institutional capacity and framework, and recurrent droughts and floods (which may be exacerbated by climate change and increased hydrological variability). The SSE and Aracaju are currently struggling to confront these challenges in the context of rising urbanization, informality, and pollution.Water scarcity
Encompassing almost half the State’s population, including most of The Metropolitan Region of Aracaju (Região Metropolitana de Aracaju-RMA), the Sergipe river basin entirely includes eight municipalities and partially includes another eighteen. A water use/availability study found that overall water demand is 260,000 cubic meters per day while the total volume of water provided by the basin itself is only 55,000 cubic meters per day. This indicates a water deficit of over 80 percent. The shortfall is covered in part by transfers from the São Francisco River. Water scarcity is further exacerbated by the contamination of water resources in urban areas in and around the RMA due to ongoing urbanization and informal occupants.Water Pollution
Pollution of water resources further aggravates scarcity. The main sources of pollution are the discharge of untreated wastewater and inadequate disposal of solid waste. Only an average of 38.7% of the population has access to sewerage, and untreated sewer discharged into water bodies contributes to the basin’s downstream pollution. With regards to solid waste, even though 80% of the population is covered by solid waste removal services, adequate disposal of this waste does not exist. Solid waste is disposed of in open air dumps along highways, in mangroves, or in areas close to water causing severe urban and environmental impacts.Weak Institutional Capacity
Currently, the State of Sergipe (SSE) does not have an adequate institutional framework and set of tools in order to plan, manage, and regulate water resources and water service provision in an integrated manner. The state has several agencies for water management, environmental policies, irrigation, and agricultural development, but the institutional capacity of these agencies is limited and roles and responsibilities are not well clarified.Response to challenges
The World Family Summit program has created the "Sergipe Practical Plan of Action 2006-2015" that has set goals in line with the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) to ensure access to adequate drinking water and sanitation. Furthermore this plan defines and investment strategy for the management of freshwater resources and great control of water pollution.The State of Sergipe (SSE) engaged in a participatory planning process with a priority on water that involved public consultations with civil society and identified priority areas of intervention. This participatory planning process served as a key input to SSE’s 2008-2011 economic development and government action plan, which selected integrated management of natural and water resources, solid waste and sanitation services as one of the SSE’s key priorities.
Key Institutions
Sergipe is a small and poor state, with several agencies in charge of environment, water resources, irrigation management, water supply, and wastewater regulation. Theses institutions share responsibilities within some projects and what follows provides some explanation of this; however, this is by no means a clear definition as the SSE remains mired in institutional incapacity. For example, and with regards to integrated water resources management (IWRM) and institutional development, SEMARH may handle technical and safeguards issues while UAPAS deals with procurement and financial management. Water and irrigation initiatives appear to be the domain of COHIDRO and UAPAS. DESO takes on all components (safeguards, technical, procurement, financial management) when dealing with water and cities projects.- DESO (Companhia de Saneamento de Sergipe) is the State water supply and sanitation utility responsible for hydrological studies and projects, water supply services, sewer and sanitation in the state of Sergipe. DESO handles dissemination of concessions and service contracts for all of the municipal districts in Sergipe.
- SEMARH (Secretaria de Estado do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Hídricos) is the State Secretariat of Environment and Water Resources. Responsibilities include: planning of inter-sectoral water resource management instruments, consolidate and grow and data base of water management data, provide regulatory action and incentives for the improvement of the water quality in the Sergipe River, urban infrastructures, and control of water pollution.
- UAPAS, the Sergipe Water Project Technical Administration Unit – (Unidade de Técnica de Administração do Projeto Águas de Sergipe) is a unit that has been created by state decree within SEMARH. The unit will be composed of a project coordinator and staff assigned from SEMARH and other participating secretariats, including the State Secretariat of Infrastructure (Secretaria de Estado da Infraestrutura - SEINFRA), the State Secretariat of Economic Development, Science, Technology and Tourism (Secretaria de Estado do Desenvolvimento Econômico, da Ciência e Tecnologia e do Turismo - SEDETEC) and SEAGRI. With Regards to a forthcoming state water project to be funded by the World Bank, the UAPAS will be responsible for the day-to-day implementation of Integrated Water Resources Management (IRWM), institutional development, and irrigation. The UAPAS is also responsible for compiling the reports and financial records of all project components.
- PROAGUA is a program that aims to strengthen the institutions and actors involved in water resources management in Brazil. The objective is of promoting the rational and sustainable use of water resources within a participatory approach.
- COHIDRO (Companhia de Desenvolvimento de Recursos Hídricos e Irrigação de Sergipe) is the Water Resources and Irrigation development company of Sergipe and components of the company include: a) Development of resources hídricos; b) Irrigation; c) Provisioning of water; d) basic sanitation for rural communities; e) Promote water resource studies and research; f) and perforation of water boreholes.
Legal Framework
As with the institutional framework, the legal framework within the SSE needs further clarification. There have been advances in the legal framework of water resources management, information systems, and planning efforts at state and river basin levels, but implementation of governance instruments for modern water management and services regulation is only just emerging.See also
- Water resources management in BrazilWater resources management in BrazilWater resources management is a key element of Brazil’s strategy to promote sustainable growth and a more equitable and inclusive society. Brazil’s achievements over the past 70 years have been closely linked to the development of hydraulic infrastructure for hydroelectric power generation and...
- Irrigation in BrazilIrrigation in BrazilIrrigation in Brazil has been developed through the use of different models. Public involvement in irrigation is relatively new while private investment has traditionally been responsible for irrigation development. Private irrigation predominates in the populated South, Southeast, and Center-West...
- Water management in Greater Mexico CityWater management in Greater Mexico CityGreater Mexico City , a metropolitan area with more than 19 million inhabitants including Mexico's capital with about 9 million inhabitants, faces tremendous water challenges...
- Water management in the Metropolitan Region of São PauloWater management in the Metropolitan Region of São PauloWater management in the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo faces several challenges, including pollution of drinking water reservoirs that are surrounded by slums, water scarcity leading to conflicts with the Campinas Metropolitan area to the north, inefficient water use, and flooding...
- Urban water management in Monterrey, MexicoUrban water management in Monterrey, MexicoBeginning early in the 20th century, Monterrey, Mexico began a successful economic metamorphosis and growth pattern that remains an exception in Mexico. This all began with increased investments in irrigation that fueled a boom in agriculture and ranching for this northern Mexican city...
- Integrated urban water management in Medellín, ColombiaIntegrated urban water management in Medellín, ColombiaIntegrated urban water management ' in Medellín, Colombia is considered to be an overall success and a good example of how a large metropolitan area with moderate income disparity can adequately operate and maintain quality water supply to its many citizens...
- Urban water management in Bogotá, ColombiaUrban water management in Bogotá, ColombiaWater management in Bogotá, Colombia, a city of more than 7 million inhabitants, faces three main challenges: improving the quality of the highly polluted Bogotá river, controlling floods and revitalizing riparian areas along the river....
- Integrated urban water management in Buenos Aires, ArgentinaIntegrated urban water management in Buenos Aires, ArgentinaIntegrated urban water management ' in Buenos Aires is not unlike many large urban areas in Latin America where in past decades, more focus was placed on just a few sectors or only one sector...
- Water management in greater TegucigalpaWater management in greater TegucigalpaTegucigalpa, the capital city of Honduras, is located in a central mountainous region having a tropical climate within the Choluteca River Basin. Major rivers supplying the capital city are the Choluteca and Guacerique rivers which then fill the Concepción and Laureles storage reservoirs...

