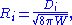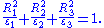Index ellipsoid
Encyclopedia
In optics
, an index ellipsoid is a diagram of an ellipsoid that depicts the orientation and relative magnitude of refractive indices
in a crystal
.
The equation for the ellipsoid is constructed using the electric displacement vector D and the dielectric constant
s. Defining the field energy W as
and the reduced displacement as
then the index ellipsoid is defined by the equation
The semiaxes of this ellipsoid are dielectric constants of the crystal.
This ellipsoid can be used to determine the polarization of an incoming wave with wave vector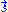 by taking the intersection of the plane
by taking the intersection of the plane 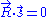 with the index ellipsoid. The axes of the resulting ellipse are the resulting polarization directions.
with the index ellipsoid. The axes of the resulting ellipse are the resulting polarization directions.
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, an index ellipsoid is a diagram of an ellipsoid that depicts the orientation and relative magnitude of refractive indices
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
in a crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
.
The equation for the ellipsoid is constructed using the electric displacement vector D and the dielectric constant
Dielectric constant
The relative permittivity of a material under given conditions reflects the extent to which it concentrates electrostatic lines of flux. In technical terms, it is the ratio of the amount of electrical energy stored in a material by an applied voltage, relative to that stored in a vacuum...
s. Defining the field energy W as
and the reduced displacement as
then the index ellipsoid is defined by the equation
The semiaxes of this ellipsoid are dielectric constants of the crystal.
This ellipsoid can be used to determine the polarization of an incoming wave with wave vector
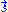 by taking the intersection of the plane
by taking the intersection of the plane 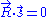 with the index ellipsoid. The axes of the resulting ellipse are the resulting polarization directions.
with the index ellipsoid. The axes of the resulting ellipse are the resulting polarization directions.