Ideo motor response
Encyclopedia
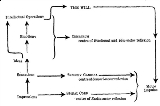
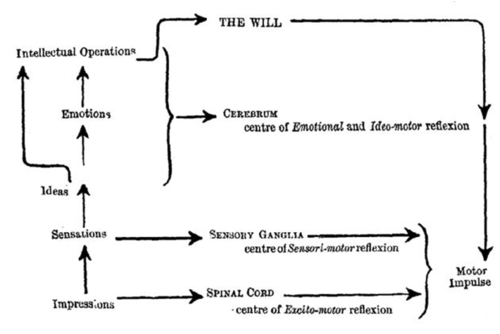
The ideo-motor response (or "ideo-motor reflex"), often abbreviated to IMR, is a concept in hypnosis
and psychological research. It is derived from the terms 'ideo' (idea, or mental representation
) and 'motor' (muscular action). The phrase is most commonly used in reference to the process whereby a thought or mental image brings about a seemingly "reflexive" or automatic muscular reaction, often of minuscule degree, and potentially outside of the awareness of the subject. The cognate term "ideo-dynamic response" (or "reflex") extends to the description of all bodily reactions caused in a similar manner by certain ideas, e.g., the salivation often caused by imagining sucking a lemon, which is a secretory response. Here, "ideo-dynamic" means "the power of an idea (over the body)". In the Victorian psychological terminology from which this concept derives, an "idea" may include any mental representation, e.g., a mental image or memory, etc. The ideo-dynamic response became the original neuro-psychological theory of suggestion
in hypnotism.
. Carpenter was a friend and collaborator of James Braid, the founder of hypnotism.
Braid soon assimilated the ideo-motor theory into hypnotism and it became the central theory of hypnotic suggestion. In The Physiology of Fascination (1855), Braid writes,
Braid coined the term "monoideo-dynamic" to express his theory that hypnotism functioned primarily by concentrating attention upon a single (mono) "dominant idea", which he believed amplified the ideo-dynamic or ideo-motor response.
, whereby 'yes' or 'no' answers may be given by indication of a physical manifestation rather than a verbal one; such results are produced by 'pre-suggesting' the correct response and attaching it to either the left or right hand side of the subject's body.
In hypnosis, this may be circumvented by dissociating the particular thought-process-response-abort of a digit or entire limb; and therefore give control to the unconscious mind
to enable (by suggestion) the route of conscious thought-unconscious process-conscious process (of the fact)-conscious response (do not act)- unconscious response (dissociate from conscious)- ignore abortive conscious attempt- unconscious unabort... Which would then display a reaction or response in a physical manner or behavioral context.
Body language may be considered the most commonly visible aspect of IMR, but may also include such unconscious activities as doodling or art - as the conscious thought is sublimated into a different type of activity in unconscious expression.
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is "a trance state characterized by extreme suggestibility, relaxation and heightened imagination."It is a mental state or imaginative role-enactment . It is usually induced by a procedure known as a hypnotic induction, which is commonly composed of a long series of preliminary...
and psychological research. It is derived from the terms 'ideo' (idea, or mental representation
Mental representation
A representation, in philosophy of mind, cognitive psychology, neuroscience, and cognitive science, is a hypothetical internal cognitive symbol that represents external reality, or else a mental process that makes use of such a symbol; "a formal system for making explicit certain entities or types...
) and 'motor' (muscular action). The phrase is most commonly used in reference to the process whereby a thought or mental image brings about a seemingly "reflexive" or automatic muscular reaction, often of minuscule degree, and potentially outside of the awareness of the subject. The cognate term "ideo-dynamic response" (or "reflex") extends to the description of all bodily reactions caused in a similar manner by certain ideas, e.g., the salivation often caused by imagining sucking a lemon, which is a secretory response. Here, "ideo-dynamic" means "the power of an idea (over the body)". In the Victorian psychological terminology from which this concept derives, an "idea" may include any mental representation, e.g., a mental image or memory, etc. The ideo-dynamic response became the original neuro-psychological theory of suggestion
Suggestion
Suggestion is the psychological process by which one person guides the thoughts, feelings, or behaviour of another. Nineteenth century writers on psychology such as William James used the words "suggest" and "suggestion" in senses close to those they have in common speech—one idea was said to...
in hypnotism.
History
The term "ideo-motor reflex" or "ideo-motor response" was introduced in the 1840s by the eminent Victorian physiologist and psychologist William Benjamin CarpenterWilliam Benjamin Carpenter
William Benjamin Carpenter MD CB FRS was an English physician, invertebrate zoologist and physiologist. He was instrumental in the early stages of the unified University of London.-Life:...
. Carpenter was a friend and collaborator of James Braid, the founder of hypnotism.
Braid soon assimilated the ideo-motor theory into hypnotism and it became the central theory of hypnotic suggestion. In The Physiology of Fascination (1855), Braid writes,
Braid coined the term "monoideo-dynamic" to express his theory that hypnotism functioned primarily by concentrating attention upon a single (mono) "dominant idea", which he believed amplified the ideo-dynamic or ideo-motor response.

Questioning
It is strongly associated with the practice of hypnosisHypnosis
Hypnosis is "a trance state characterized by extreme suggestibility, relaxation and heightened imagination."It is a mental state or imaginative role-enactment . It is usually induced by a procedure known as a hypnotic induction, which is commonly composed of a long series of preliminary...
, whereby 'yes' or 'no' answers may be given by indication of a physical manifestation rather than a verbal one; such results are produced by 'pre-suggesting' the correct response and attaching it to either the left or right hand side of the subject's body.
An example of IMR
If you were to be asked to imagine doing up your shoelaces as vividly as possible, your brain would consciously fixate on the task and work through it as vividly and as logically as possible. The theory of IMR would imply that your muscular memory associated with your hands, would then attempt the task physically, but abort the process unless it was truly necessary and curtail the events that would unfold if you were actually willing to send the complete information along your nervous system to your hands. This may therefore involve an involuntary 'twitch' or movement of the associated digits are placed into preparation of function, processed against reality and then given the signal to not actually act.In hypnosis, this may be circumvented by dissociating the particular thought-process-response-abort of a digit or entire limb; and therefore give control to the unconscious mind
Unconscious mind
The unconscious mind is a term coined by the 18th century German romantic philosopher Friedrich Schelling and later introduced into English by the poet and essayist Samuel Taylor Coleridge...
to enable (by suggestion) the route of conscious thought-unconscious process-conscious process (of the fact)-conscious response (do not act)- unconscious response (dissociate from conscious)- ignore abortive conscious attempt- unconscious unabort... Which would then display a reaction or response in a physical manner or behavioral context.
Body language may be considered the most commonly visible aspect of IMR, but may also include such unconscious activities as doodling or art - as the conscious thought is sublimated into a different type of activity in unconscious expression.

