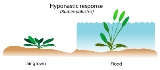
Hyponastic response
Encyclopedia
The hyponastic response is an upward bending of leaves
or other plant
parts, resulting from growth of the lower side. This can be observed in many terrestrial plants and is thought to be linked to the plant hormone
ethylene
.
Submerged plants often show the hyponastic response, where the upward bending of the leaves and the elongation of the petiole
s might help the plant to restore normal gas exchange with the atmosphere.
Plants produce ethylene, and normally this dissolves in the air quite easily. But when the plant is submerged ethylene is trapped in the plant. Plants that are exposed to elevated ethylene levels in experimental set-ups also show the hyponastic response.

Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
or other plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
parts, resulting from growth of the lower side. This can be observed in many terrestrial plants and is thought to be linked to the plant hormone
Plant hormone
Plant hormones are chemicals that regulate plant growth, which, in the UK, are termed 'plant growth substances'. Plant hormones are signal molecules produced within the plant, and occur in extremely low concentrations. Hormones regulate cellular processes in targeted cells locally and, when moved...
ethylene
Ethylene
Ethylene is a gaseous organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest alkene . Because it contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Ethylene is widely used in industry and is also a plant hormone...
.
Submerged plants often show the hyponastic response, where the upward bending of the leaves and the elongation of the petiole
Petiole (botany)
In botany, the petiole is the stalk attaching the leaf blade to the stem. The petiole usually has the same internal structure as the stem. Outgrowths appearing on each side of the petiole are called stipules. Leaves lacking a petiole are called sessile, or clasping when they partly surround the...
s might help the plant to restore normal gas exchange with the atmosphere.
Plants produce ethylene, and normally this dissolves in the air quite easily. But when the plant is submerged ethylene is trapped in the plant. Plants that are exposed to elevated ethylene levels in experimental set-ups also show the hyponastic response.


