Hyperlysinemia
Encyclopedia
Hyperlysinemia is an autosomal
recessive metabolic disorder characterized by an abnormal increase of lysine
in the blood
, but appears to be benign. It can be associated with saccharopine dehydrogenase
.

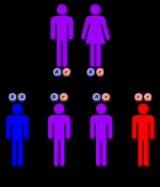
Hyperlysinemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive metabolic disorder characterized by an abnormal increase of lysine
Lysine
Lysine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH4NH2. It is an essential amino acid, which means that the human body cannot synthesize it. Its codons are AAA and AAG....
in the blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
, but appears to be benign. It can be associated with saccharopine dehydrogenase
Saccharopine dehydrogenase
Saccharopine dehydrogenase is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of lysine, via saccharopine.It can be classified under , , , and ....
.
Genetics

Hyperlysinemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry
Genetic carrier
A genetic carrier , is a person or other organism that has inherited a genetic trait or mutation, but who does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. They are, however, able to pass the gene onto their offspring, who may then express the gene...
one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.

