
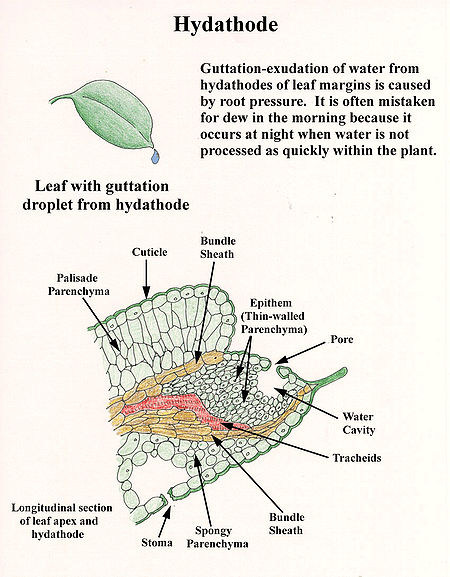
Hydathode
Encyclopedia
Secretion
Secretion is the process of elaborating, releasing, and oozing chemicals, or a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast to excretion, the substance may have a certain function, rather than being a waste product...
tissue
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
in leaves
Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
, usually of Angiosperms, that secretes water through pore
Pore
- Animal biology and microbiology :* Sweat pore, an anatomical structure of the skin of humans used for secretion of sweat* Canal pore, an anatomical structure that is part of the lateral line sense system of some aquatic organisms...
s in the epidermis
Epidermis (botany)
The epidermis is a single-layered group of cells that covers plants' leaves, flowers, roots and stems. It forms a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The epidermis serves several functions, it protects against water loss, regulates gas exchange, secretes metabolic compounds,...
or margin of leaves, typically at the tip of a marginal tooth or serration. They probably evolved from modified stomata. It is involved in guttation
Guttation
Guttation is the appearance of drops of xylem sap on the tips or edges of leaves of some vascular plants, such as grasses. Guttation is not to be confused with dew, which condenses from the atmosphere onto the plant surface.- Process :...
, where water is released from the top in order to transport the nutrients in the water from the root
Root
In vascular plants, the root is the organ of a plant that typically lies below the surface of the soil. This is not always the case, however, since a root can also be aerial or aerating . Furthermore, a stem normally occurring below ground is not exceptional either...
s to the leaves. Hydathodes are connected to the plant vascular system by a vascular bundle.
Since the liquid being extruded is from the xylem it also contains salts, sugars, and organic compounds dissolved in water and this is sometimes seen to crystallize on evaporation, forming a white powdery substance on the leafs edge. This crystallisation is very obvious in halophyte
Halophyte
A halophyte is a plant that grows where it is affected by salinity in the root area or by salt spray, such as in saline semi-deserts, mangrove swamps, marshes and sloughs, and seashores. An example of a halophyte is the salt marsh grass Spartina alterniflora . Relatively few plant species are...
s, plants adapted to live in high salt environments, and consequently the hydathodes are known as salt glands in those species.
Hydathodes are special structures through which exudation of water takes place in liquid form.They are mainly found in aquatic plants and in some herbaceous plants growing in moist places. They occur at the apices of the veins at the tips of the leaves or on their margins. Hydathodes are made of a group of living cells with numerous intercellular spaces filled with water, but few or no chloroplasts. They represents modified bundle-ends. These cells called EPITHEM cells open out into one or more sub-epidermal chambers. These, in turn, сommunicate with the exterior through an open water stomata or open pore. The water stoma structurally resembles an ordinary stoma, but is usually larger and has lost the power of movement. Hydathodes are commonly seen in water lettuce, water hyacinth, rose, balsam, and many other species.

