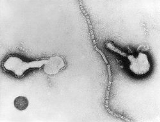
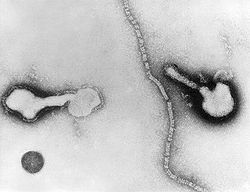
Human parainfluenza viruses
Encyclopedia
Serotype
Serotype or serovar refers to distinct variations within a subspecies of bacteria or viruses. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their cell surface antigens...
s of enveloped single-stranded RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
viruses belonging to the paramyxovirus
Paramyxovirus
Paramyxoviruses are viruses of the Paramyxoviridae family of the Mononegavirales order; they are negative-sense single-stranded RNA viruses responsible for a number of human and animal diseases.-Genera:*Subfamily Paramyxovirinae**Genus Avulavirus Paramyxoviruses (from Greek para-, beyond, -myxo-,...
family.
Parainfluenza viruses can be detected via cell culture
Cell culture
Cell culture is the complex process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions. In practice, the term "cell culture" has come to refer to the culturing of cells derived from singlecellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells. However, there are also cultures of plants, fungi and microbes,...
, immunofluorescent
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on biological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows...
microscopy
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view samples and objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye...
, and PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction is a scientific technique in molecular biology to amplify a single or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence....
.
Clinical significance
They are the second most common cause of lower respiratory tract infectionLower respiratory tract infection
Lower respiratory tract infection while often used as a synonym for pneumonia, can also be applied to other types of infection including lung abscess and acute bronchitis...
in younger children. Together, the parainfluenza viruses cause ~75% of the cases of Croup
Croup
Croup is a respiratory condition that is usually triggered by an acute viral infection of the upper airway. The infection leads to swelling inside the throat, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classical symptoms of a "barking" cough, stridor, and hoarseness...
.
Repeated infection throughout the life of the host is not uncommon. Symptoms of later breakouts include upper respiratory tract
Upper respiratory tract
The upper respiratory tract or upper airway primarily refers to the parts of the respiratory system lying outside of the thorax or above the sternal angle. Another definition commomly used in medicine is the airway above the glottis or vocal cords...
illness as in a cold
Common cold
The common cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory system, caused primarily by rhinoviruses and coronaviruses. Common symptoms include a cough, sore throat, runny nose, and fever...
and sore throat. The incubation period
Incubation period
Incubation period is the time elapsed between exposure to a pathogenic organism, a chemical or radiation, and when symptoms and signs are first apparent...
of all four serotypes is 1 to 7 days. In immunosuppressed
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression involves an act that reduces the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immuno-suppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reaction to treatment of other...
people, such as transplant patients, parainfluenza virus infections can cause severe pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
, which can be fatal.
Prevention
Though no vaccines currently exist, research is underway.Parainfluenza viruses last only a few hours in the environment and are inactivated by soap and water.
Types
There are four serotypes. These include:- HPIV-1 (most common cause of croupCroupCroup is a respiratory condition that is usually triggered by an acute viral infection of the upper airway. The infection leads to swelling inside the throat, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classical symptoms of a "barking" cough, stridor, and hoarseness...
; also other upper and lower respiratory tract illnesses typical) - HPIV-2 (causes croupCroupCroup is a respiratory condition that is usually triggered by an acute viral infection of the upper airway. The infection leads to swelling inside the throat, which interferes with normal breathing and produces the classical symptoms of a "barking" cough, stridor, and hoarseness...
and other upper and lower respiratory tract illnesses) - HPIV-3 (associated with bronchiolitisBronchiolitisBronchiolitis is inflammation of the bronchioles, the smallest air passages of the lungs. It usually occurs in children less than two years of age and presents with coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. This inflammation is usually caused by viruses...
and pneumoniaPneumoniaPneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
) - HPIV-4 (includes subtypes 4a and 4b)

