Honokiol
Encyclopedia
Honokiol is a biphenolic compound present in the cones, bark, and leaves of Magnolia grandiflora that has been used in the traditional Japanese medicine Saiboku-to as an anxiolytic
, antithrombotic
, anti-depressant, anti-emetic, and anti-bacterial. While early research on the effective compounds in traditional remedies have simply used whole magnolia bark extracts, known as houpu magnolia
, recent work has identified honokiol and its structural isomer
magnolol
as the active compounds in magnolia bark. In the late 1990s, honokiol saw a revival in western countries as a potent and highly tolerable anti-tumorigenic and neurotrophic compound.
, sarcoma
, myeloma, leukemia
, bladder
, lung
, prostate
, oral squamous cell carcinomaand colon cancer cell lines. Honokiol inhibits phosphorylation of Akt
, p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase
(MAPK), and src
. Additionally, honokiol modulates the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation pathway, an upstream effector of vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF), cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and MCL1
, all significant pro-angiogenic and survival factors. Honokiol induces caspase-dependent apoptosis
in a TRAIL-mediated manner, and potentiates the pro-apoptotic effects of doxorubicin
and other etoposide
s. So potent is honokiol's pro-apoptotic effects that it overcomes even notoriously drug resistant neoplasms such as multiple myeloma and chronic B-cell leukemia
.
outgrowth and have neuroprotective effects in rat
cortical neurons. Additionally, honokiol increases free cytoplasmic Ca2+
in rat cortical neurons.. Honokiol is a weak cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand but the naturally occuring derivative 4-O-methylhonokiol was shown to be a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor inverse agonist and to possess antioscteoclastic effects. Schuehly W, Paredes JM, Kleyer J, Huefner A, Anavi-Goffer S, Raduner S, Altmann KH, Gertsch J. Mechanisms of osteoclastogenesis inhibition by a novel class of biphenyl-type cannabinoid CB(2) receptor inverse agonists.Chem Biol. 2011 Aug 26;18(8):1053-64.
injury. Honokiol significantly increases the prostacyclin
metabolite 6-keto-PGF1alpha, potentially the key factor in honokiol's anti-thrombotic activity.
, which differs from honokiol only by the position of one hydroxyl group, purification has often been limited to a HPLC
or electromigration
. However, methods developed in 2006 by workers in the lab of Jack L. Arbiser, took advantage of the proximity of the phenolic hydroxyl groups in magnolol, which form a protectable diol
, to generate a magnolol
acetonide (Figure 1), with a subsequent simple purification via flash chromatography over silica.
Figure 1
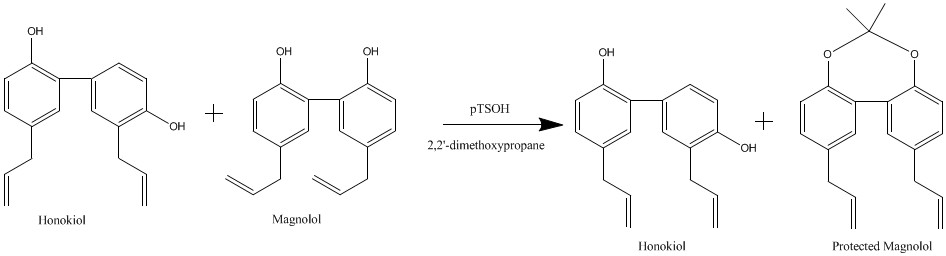
Magnolol and Honokiol are normally inseparable. Honokiol is easily separable from the protected magnolol acetonide.
Anxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
, antithrombotic
Antithrombotic
A antithrombotic is a drug which reduces thrombus formation.Different antithrombotics affect different processes:* Antiplatelet drugs limit the migration or aggregation of platelets.* Anticoagulants limit the ability of the blood to clot....
, anti-depressant, anti-emetic, and anti-bacterial. While early research on the effective compounds in traditional remedies have simply used whole magnolia bark extracts, known as houpu magnolia
Houpu magnolia
Magnolia officinalis is a species of Magnolia native to the mountains and valleys of China at altitudes of 300-1500 m.- Identification :...
, recent work has identified honokiol and its structural isomer
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers do not necessarily share similar properties, unless they also have the same functional groups. There are many different classes of isomers, like stereoisomers, enantiomers, geometrical...
magnolol
Magnolol
Magnolol is a bioactive compound found in the bark of the Houpu magnolia . It is known to act on the GABAA receptors in rats, as well as having antifungal properties.-References:*...
as the active compounds in magnolia bark. In the late 1990s, honokiol saw a revival in western countries as a potent and highly tolerable anti-tumorigenic and neurotrophic compound.
Anti-tumorigenic activities
Honokiol has shown pro-apoptotic effects in melanomaMelanoma
Melanoma is a malignant tumor of melanocytes. Melanocytes are cells that produce the dark pigment, melanin, which is responsible for the color of skin. They predominantly occur in skin, but are also found in other parts of the body, including the bowel and the eye...
, sarcoma
Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a cancer that arises from transformed cells in one of a number of tissues that develop from embryonic mesoderm. Thus, sarcomas include tumors of bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, vascular, and hematopoietic tissues...
, myeloma, leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
, bladder
Urinary bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow muscular, and distensible organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor...
, lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
, prostate
Prostate
The prostate is a compound tubuloalveolar exocrine gland of the male reproductive system in most mammals....
, oral squamous cell carcinomaand colon cancer cell lines. Honokiol inhibits phosphorylation of Akt
AKT
Akt, also known as Protein Kinase B , is a serine/threonine protein kinase that plays a key role in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, cell proliferation, apoptosis, transcription and cell migration.-Family members:...
, p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
Mitogen-activated protein kinases are serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that respond to extracellular stimuli and regulate various cellular activities, such as gene expression, mitosis, differentiation, proliferation, and cell survival/apoptosis.-Activation:MAP kinases are activated...
(MAPK), and src
Src
Src may refer to:* Src , a family of proto-oncogenic tyrosine kinases* In computer programming, a common abbreviation for source codeSee also*SRC...
. Additionally, honokiol modulates the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation pathway, an upstream effector of vascular endothelial growth factor
Vascular endothelial growth factor
Vascular endothelial growth factor is a signal protein produced by cells that stimulates vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. It is part of the system that restores the oxygen supply to tissues when blood circulation is inadequate....
(VEGF), cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), and MCL1
MCL1
Induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MCL1 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Bcl-2 family. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and two transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been...
, all significant pro-angiogenic and survival factors. Honokiol induces caspase-dependent apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
in a TRAIL-mediated manner, and potentiates the pro-apoptotic effects of doxorubicin
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin INN is a drug used in cancer chemotherapy. It is an anthracycline antibiotic, closely related to the natural product daunomycin, and like all anthracyclines, it works by intercalating DNA....
and other etoposide
Etoposide
Etoposide phosphate is an anti-cancer agent. It is known in the laboratory as a topoisomerase poison. Etoposide is often incorrectly referred to as a topoisomerase inhibitor in order to avoid using the term "poison" in a clinical setting...
s. So potent is honokiol's pro-apoptotic effects that it overcomes even notoriously drug resistant neoplasms such as multiple myeloma and chronic B-cell leukemia
B-cell leukemia
B-cell leukemia describes several different types of lymphoid leukemia which affect B cells.Types include :* 9823/3 - B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma* 9826/3 - Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, mature B-cell type...
.
Neurotrophic activity
Honokiol has been shown to promote neuriteNeurite
A neurite refers to any projection from the cell body of a neuron. This projection can be either an axon or a dendrite. The term is frequently used when speaking of immature or developing neurons, especially of cells in culture, because it can be difficult to tell axons from dendrites before...
outgrowth and have neuroprotective effects in rat
Rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents of the superfamily Muroidea. "True rats" are members of the genus Rattus, the most important of which to humans are the black rat, Rattus rattus, and the brown rat, Rattus norvegicus...
cortical neurons. Additionally, honokiol increases free cytoplasmic Ca2+
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
in rat cortical neurons.. Honokiol is a weak cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand but the naturally occuring derivative 4-O-methylhonokiol was shown to be a potent and selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor inverse agonist and to possess antioscteoclastic effects. Schuehly W, Paredes JM, Kleyer J, Huefner A, Anavi-Goffer S, Raduner S, Altmann KH, Gertsch J. Mechanisms of osteoclastogenesis inhibition by a novel class of biphenyl-type cannabinoid CB(2) receptor inverse agonists.Chem Biol. 2011 Aug 26;18(8):1053-64.
Anti-thrombotic activity
Honokiol inhibits platelet aggregation in rabbits in a dose-dependent manner, and protects cultured RAEC against oxidized low density lipoproteinLipoprotein
A lipoprotein is a biochemical assembly that contains both proteins and lipids water-bound to the proteins. Many enzymes, transporters, structural proteins, antigens, adhesins, and toxins are lipoproteins...
injury. Honokiol significantly increases the prostacyclin
Prostacyclin
Prostacyclin is a member of the family of lipid molecules known as eicosanoids.As a drug, it is also known as "epoprostenol". The terms are sometimes used interchangeably.-History:...
metabolite 6-keto-PGF1alpha, potentially the key factor in honokiol's anti-thrombotic activity.
Purification
Several methods for purifying honokiol have been utilized. As honokiol exists naturally with its structural isomer magnololMagnolol
Magnolol is a bioactive compound found in the bark of the Houpu magnolia . It is known to act on the GABAA receptors in rats, as well as having antifungal properties.-References:*...
, which differs from honokiol only by the position of one hydroxyl group, purification has often been limited to a HPLC
High-performance liquid chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography , HPLC, is a chromatographic technique that can separate a mixture of compounds and is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify and purify the individual components of the mixture.HPLC typically utilizes different types of stationary...
or electromigration
Electromigration
Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direct current densities are used, such as in...
. However, methods developed in 2006 by workers in the lab of Jack L. Arbiser, took advantage of the proximity of the phenolic hydroxyl groups in magnolol, which form a protectable diol
Diol
A diol or glycol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom...
, to generate a magnolol
Magnolol
Magnolol is a bioactive compound found in the bark of the Houpu magnolia . It is known to act on the GABAA receptors in rats, as well as having antifungal properties.-References:*...
acetonide (Figure 1), with a subsequent simple purification via flash chromatography over silica.
Figure 1

Magnolol and Honokiol are normally inseparable. Honokiol is easily separable from the protected magnolol acetonide.

