
Hollomon-Jaffe parameter
Encyclopedia
The Hollomon-Jaffe parameter, or HP, describes the effect of a heat treatment
at a temperature
for a certain time.
. The same effect can be achieved with a low temperature and a long holding time, or with a higher temperature and a short holding time.
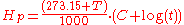
This formula is not consistent concerning the units; the parameters must be entered in a certain manner. T is in degrees Celsius. The argument of the logarithmic function
has the unit hour
s. C is a parameter unique to the material used. The Hollomon parameter itself is unitless
and realistic numeric values vary between 15 and 21.
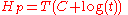
where T is in kilokelvins, t is in hours, and C is the same as above.
Heat treatment
Heat treating is a group of industrial and metalworking processes used to alter the physical, and sometimes chemical, properties of a material. The most common application is metallurgical. Heat treatments are also used in the manufacture of many other materials, such as glass...
at a temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
for a certain time.
Effect
The effect of the heat treatment depends on its temperature and its timeTime
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
. The same effect can be achieved with a low temperature and a long holding time, or with a higher temperature and a short holding time.
Formula
In the Hollomon-Jaffe parameter, This exchangeability of time and temperature can be described by the following formula: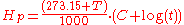
This formula is not consistent concerning the units; the parameters must be entered in a certain manner. T is in degrees Celsius. The argument of the logarithmic function
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
has the unit hour
Hour
The hour is a unit of measurement of time. In modern usage, an hour comprises 60 minutes, or 3,600 seconds...
s. C is a parameter unique to the material used. The Hollomon parameter itself is unitless
Dimensionless quantity
In dimensional analysis, a dimensionless quantity or quantity of dimension one is a quantity without an associated physical dimension. It is thus a "pure" number, and as such always has a dimension of 1. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and...
and realistic numeric values vary between 15 and 21.

where T is in kilokelvins, t is in hours, and C is the same as above.

