
Holdover in synchronization applications
Encyclopedia
“Synchronization is as important as power at the cell site.”
The quote above suggests that we can think of holdover in synchronization applications as analogous to running on backup power.
Modern wireless communication systems require at least knowledge of frequency and often knowledge of phase as well in order to work correctly. Base stations need to know what time it is, and they usually get this knowledge from the outside world somehow (from a GPS Time and Frequency receiver, or from a synchronization source somewhere in the network they are connected to).
But if the connection to the reference is lost then the base station will be on its own to establish what time it is. The base station needs a way to establish accurate frequency and phase (to know what time it is) using internal (or local) resources, and that’s where the function of holdover becomes important.
Two independent clocks once synchronized will walk away from one another without limit. To have them display the same time it would be necessary to re-synchronize them at regular intervals. The periods between synchronizations is referred to as Holdover and performance under Holdover relies on the quality of the reference oscillator (usually an OCXO), the PLL design and the correction mechanisms employed.
Some of the most stringent requirements come from the newer generation of wireless base stations, where phase accuracy targets as low as 1μs need to be maintained for correct operation. However the need for accurate timing has been an integral part of the history of wireless communication systems, and it has been suggested that the search for reliable and cost effective timing soluctions was spurred on by the need for CDMA to compete with lower cost solutions.
Within the base station, besides standard functions, accurate timing and the means to maintain it through holdover is vitally important for services such as E911
GPS as a source of timing is a key component in not just Synchronization in telecommunications
but to critical infrastructure in general. Of the 18 Critical Resource and Key infrastructure (CIKR)sectors, 15 use GPS derived timing to function correctly. One notable application where highly accurate timing accuracy (and the means to maintain it through holdover) is of importance is in the use of Synchrophasor
s in the power industry to detect line faults. Another is in Low latency
trading applications in capital markets.
effects, making GPS only available to some locations at certain times of the day, for example.
A GPS outage however is not initially an issue because clocks can go into holdover, allowing the interference to be alleviated as much as the stability of the oscillator providing holdover will allow. The more stable the oscillator, the longer the system can operate without GPS.
applications holdover is defined by ETSI
as:
We can regard Holdover then as a measure of accuracy or error acquired by a clock when there is no controlling external reference to correct for any errors.
MIL-PRF-55310 defines Clock Accuracy as:
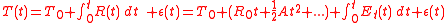
Where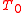 is the synchronization error at
is the synchronization error at  ;
; 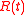 is the fractional frequency difference between two clocks under comparison;
is the fractional frequency difference between two clocks under comparison; 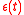 is the error due to random noise;
is the error due to random noise; 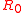 is
is 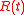 at
at  ;
;  is the linear aging rate and
is the linear aging rate and 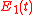 is the frequency difference due to environmental effects.
is the frequency difference due to environmental effects.
Similarly ITU G.810 defines Time Error as:
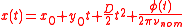
Where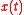 is the time error;
is the time error; 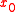 is the time error at
is the time error at  ;
; 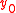 is the fractional frequency error at
is the fractional frequency error at  ;
; 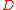 is the linear fractional frequency drift rate;
is the linear fractional frequency drift rate; 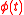 is the random phase deviation component and
is the random phase deviation component and  is the nominal frequency.
is the nominal frequency.
NIST defines a Disciplined Oscillator as:
In a GPSDO a GPS or GNSS signal is used as the exernal reference that steers an internal oscillator. In a modern GPSDO the GPS processing and steering function are both implemented in a Microprocessor allowing a direct comparison between the GPS reference signal and the oscillator output.
Amongst the building blocks of a GPS Time and Frequency solution the oscillator is a key component and typically they are built around an Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator (OCXO
) or a Rubidium based clock
. The dominant factors influencing the quality of the reference oscillator are taken to be aging and temperature stability. An addition of a Microprocessor to the reference oscillator can improve temperature stability and aging performance During Holdover any remaining clock error caused by aging and temperature instability can be corrected by control mechanisms. A combination of quartz based reference oscillator (such as an OCXO
) and modern correction algorithms can get good results in Holdover applications.
The Holdover capability then is provided by either by a free running local oscillator, or a local oscillator that is steered with software that retains knowledge of its past performance. The basic aim of a steering mechanism is to improve the stability of a clock or oscillator while minimizing the number of times it needs calibration In Holdover the learned behaviour of the OCXO
is used to anticipate and correct for future behavior Effective aging and temperature compensation can be provided by such a mechanism and the system designer is faced with a range of choices for algorithms and techniques to do this correction including extrapolation, interpolation and predictive filters (including Kalman filter
s).
Once the barriers of aging and environmental effects are removed the only theoretical limitation to holdover performance in such a GPSDO is irregularity or noise in the drift rate, which is detected using a metric like Allan deviation or Time deviation
.
The complexity in trying to predict the effects on Holdover due to systematic effects like Aging and Temperature Stability and stochastic influences like Random Walk
noise has resulted in tailor made Holdover Oscillator solutions being introduced in the market.
The quote above suggests that we can think of holdover in synchronization applications as analogous to running on backup power.
Modern wireless communication systems require at least knowledge of frequency and often knowledge of phase as well in order to work correctly. Base stations need to know what time it is, and they usually get this knowledge from the outside world somehow (from a GPS Time and Frequency receiver, or from a synchronization source somewhere in the network they are connected to).
But if the connection to the reference is lost then the base station will be on its own to establish what time it is. The base station needs a way to establish accurate frequency and phase (to know what time it is) using internal (or local) resources, and that’s where the function of holdover becomes important.
Two independent clocks once synchronized will walk away from one another without limit. To have them display the same time it would be necessary to re-synchronize them at regular intervals. The periods between synchronizations is referred to as Holdover and performance under Holdover relies on the quality of the reference oscillator (usually an OCXO), the PLL design and the correction mechanisms employed.
The Importance of GPS Derived Timing
A key application for GPS in telecommunications is to provide synchronization in wireless basestations. Base stations depend on timing to operate correctly, particularly for the handoff that occurs when a user moves from one cell to another. In these applications holdover is used in base stations to ensure continued operation while GPS is unavailable and to reduce the costs associated with emergency repairs, since holdover allows the site to continue to function correctly until maintenance can be performed at a convenient time.Some of the most stringent requirements come from the newer generation of wireless base stations, where phase accuracy targets as low as 1μs need to be maintained for correct operation. However the need for accurate timing has been an integral part of the history of wireless communication systems, and it has been suggested that the search for reliable and cost effective timing soluctions was spurred on by the need for CDMA to compete with lower cost solutions.
Within the base station, besides standard functions, accurate timing and the means to maintain it through holdover is vitally important for services such as E911
GPS as a source of timing is a key component in not just Synchronization in telecommunications
Synchronization in telecommunications
Many services running on modern digital telecommunications networks require accurate synchronization for correct operation. For example, if switches do not operate with the same clock rates, then slips will occur and degrade performance...
but to critical infrastructure in general. Of the 18 Critical Resource and Key infrastructure (CIKR)sectors, 15 use GPS derived timing to function correctly. One notable application where highly accurate timing accuracy (and the means to maintain it through holdover) is of importance is in the use of Synchrophasor
Synchrophasor
A phasor measurement unit is a device which measures the electrical waves on an electricity grid, using a common time source for synchronization. Time synchronization allows synchronized real-time measurements of multiple remote measurement points on the grid...
s in the power industry to detect line faults. Another is in Low latency
Low latency (capital markets)
Low latency is a topic within capital markets, where the proliferation of algorithmic trading requires firms to react to market events faster than the competition to increase profitability of trades. For example, when executing arbitrage strategies the opportunity to “arb” the market may only...
trading applications in capital markets.
How GPS Derived Timing Can Fail
GPS is sensitive to jamming and interferance because the signal levels the system levels are so low and can easily be swamped by other sources, that can be accidental or deliberate. Also since GPS depends on line of sight signals it can be disrupted by Urban canyonUrban canyon
An urban canyon is an artefact of an urban environment similar to a natural canyon. It is manifested by streets cutting through dense blocks of structures, especially skyscrapers, which causes a canyon effect...
effects, making GPS only available to some locations at certain times of the day, for example.
A GPS outage however is not initially an issue because clocks can go into holdover, allowing the interference to be alleviated as much as the stability of the oscillator providing holdover will allow. The more stable the oscillator, the longer the system can operate without GPS.
Defining Holdover
In Synchronization in telecommunicationsSynchronization in telecommunications
Many services running on modern digital telecommunications networks require accurate synchronization for correct operation. For example, if switches do not operate with the same clock rates, then slips will occur and degrade performance...
applications holdover is defined by ETSI
European Telecommunications Standards Institute
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute is an independent, non-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, with worldwide projection...
as:
An operating condition of a clock which has lost its controlling input and is using stored data, acquired while in locked operation, to control its output. The stored data are used to control phase and frequency variations, allowing the locked condition to be reproduced within specifications. Holdover begins when the clock output no longer reflects the influence of a connected external reference, or transition from it. Holdover terminates when the output of the clock reverts to locked mode condition.
We can regard Holdover then as a measure of accuracy or error acquired by a clock when there is no controlling external reference to correct for any errors.
MIL-PRF-55310 defines Clock Accuracy as:
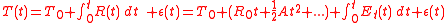
Where
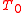 is the synchronization error at
is the synchronization error at  ;
; 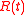 is the fractional frequency difference between two clocks under comparison;
is the fractional frequency difference between two clocks under comparison; 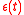 is the error due to random noise;
is the error due to random noise; 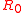 is
is 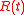 at
at  ;
;  is the linear aging rate and
is the linear aging rate and 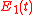 is the frequency difference due to environmental effects.
is the frequency difference due to environmental effects.Similarly ITU G.810 defines Time Error as:
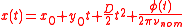
Where
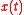 is the time error;
is the time error; 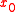 is the time error at
is the time error at  ;
; 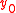 is the fractional frequency error at
is the fractional frequency error at  ;
;  is the linear fractional frequency drift rate;
is the linear fractional frequency drift rate; 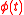 is the random phase deviation component and
is the random phase deviation component and  is the nominal frequency.
is the nominal frequency.Implementing Holdover
In applications that require Synchronization (such as wireless base stations) GPS Clocks are often used and in this context are often known as a GPSDO (GPS Disciplined Oscillator) or GPS TFS (GPS Time and Frequency Source).NIST defines a Disciplined Oscillator as:
An oscillator whose output frequency is continuously steered (often through the use of a phase locked loop) to agree with an external reference. For example, a GPS disciplined oscillator (GPSDO) usually consists of a quartz or rubidium oscillator whose output frequency is continuously steered to agree with signals broadcast by the GPS satellites.
In a GPSDO a GPS or GNSS signal is used as the exernal reference that steers an internal oscillator. In a modern GPSDO the GPS processing and steering function are both implemented in a Microprocessor allowing a direct comparison between the GPS reference signal and the oscillator output.
Amongst the building blocks of a GPS Time and Frequency solution the oscillator is a key component and typically they are built around an Oven Controlled Crystal Oscillator (OCXO
Crystal oven
A crystal oven is a temperature-controlled chamber used to maintain the quartz crystal in electronic crystal oscillators at a constant temperature, in order to prevent changes in the frequency due to variations in ambient temperature...
) or a Rubidium based clock
Rubidium standard
A rubidium standard or rubidium atomic clock is a frequency standard in which a specified hyperfine transition of electrons in rubidium-87 atoms is used to control the output frequency...
. The dominant factors influencing the quality of the reference oscillator are taken to be aging and temperature stability. An addition of a Microprocessor to the reference oscillator can improve temperature stability and aging performance During Holdover any remaining clock error caused by aging and temperature instability can be corrected by control mechanisms. A combination of quartz based reference oscillator (such as an OCXO
Crystal oven
A crystal oven is a temperature-controlled chamber used to maintain the quartz crystal in electronic crystal oscillators at a constant temperature, in order to prevent changes in the frequency due to variations in ambient temperature...
) and modern correction algorithms can get good results in Holdover applications.
The Holdover capability then is provided by either by a free running local oscillator, or a local oscillator that is steered with software that retains knowledge of its past performance. The basic aim of a steering mechanism is to improve the stability of a clock or oscillator while minimizing the number of times it needs calibration In Holdover the learned behaviour of the OCXO
Crystal oven
A crystal oven is a temperature-controlled chamber used to maintain the quartz crystal in electronic crystal oscillators at a constant temperature, in order to prevent changes in the frequency due to variations in ambient temperature...
is used to anticipate and correct for future behavior Effective aging and temperature compensation can be provided by such a mechanism and the system designer is faced with a range of choices for algorithms and techniques to do this correction including extrapolation, interpolation and predictive filters (including Kalman filter
Kalman filter
In statistics, the Kalman filter is a mathematical method named after Rudolf E. Kálmán. Its purpose is to use measurements observed over time, containing noise and other inaccuracies, and produce values that tend to be closer to the true values of the measurements and their associated calculated...
s).
Once the barriers of aging and environmental effects are removed the only theoretical limitation to holdover performance in such a GPSDO is irregularity or noise in the drift rate, which is detected using a metric like Allan deviation or Time deviation
Time deviation
TDEV is a metric often used to determine an aspect of the quality of timing signals in telecommunication applications and is a statistical analysis of the phase stability of a signal over a given period of time...
.
The complexity in trying to predict the effects on Holdover due to systematic effects like Aging and Temperature Stability and stochastic influences like Random Walk
Random walk
A random walk, sometimes denoted RW, is a mathematical formalisation of a trajectory that consists of taking successive random steps. For example, the path traced by a molecule as it travels in a liquid or a gas, the search path of a foraging animal, the price of a fluctuating stock and the...
noise has resulted in tailor made Holdover Oscillator solutions being introduced in the market.
See also
- SynchronizationSynchronizationSynchronization is timekeeping which requires the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. The familiar conductor of an orchestra serves to keep the orchestra in time....
- Synchronization in Synchronous optical networking
- Time transferTime transferTime transfer is a scheme where multiple sites share a precise reference time. Time transfer solves problems such as astronomical observatories correlating observed flashes or other phenomenon with each other, as well as cell phone towers coordinating handoffs as a phone moves from one cell to...
- Timekeeping in Global Positioning System
- Precision Time ProtocolPrecision Time ProtocolThe Precision Time Protocol is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems....

