Helix angle
Encyclopedia

Mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is a discipline of engineering that applies the principles of physics and materials science for analysis, design, manufacturing, and maintenance of mechanical systems. It is the branch of engineering that involves the production and usage of heat and mechanical power for the...
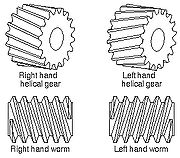
, a helix angle is the angle between any helix and an axial line on its right, circular cylinder or cone. Common applications are screw
Screw
A screw, or bolt, is a type of fastener characterized by a helical ridge, known as an external thread or just thread, wrapped around a cylinder. Some screw threads are designed to mate with a complementary thread, known as an internal thread, often in the form of a nut or an object that has the...
s, helical gears, and worm gears.
The helix angle references the axis of the cylinder, distinguishing it from the lead angle, which references a line perpendicular to the axis. Naturally, the helix angle is the geometric complement
Complementary angles
In geometry, complementary angles are angles whose measures sum to 90°. If the two complementary angles are adjacent their non-shared sides form a right angle....
of the lead angle. The helix angle is measured in degrees.
Concept
In terms specific to screws, the helix angle can be found by unraveling the helix from the screw, representing the section as a right triangle, and calculating the angle that is formed. Note that while the terminology directly refers to screws, these concepts are analogous to most mechanical applications of the helix angle.
The helix angle can be expressed as:
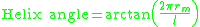
where
- l is lead of the screw or gear
- rm is mean radius of the screw thread or gear tooth
Applications
The helix angle is crucial in mechanical engineering applications that involve power transferMechanical energy
In physics, mechanical energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy present in the components of a mechanical system. It is the energy associated with the motion and position of an object. The law of conservation of energy states that in an isolated system that is only subject to...
and motion
Motion (physics)
In physics, motion is a change in position of an object with respect to time. Change in action is the result of an unbalanced force. Motion is typically described in terms of velocity, acceleration, displacement and time . An object's velocity cannot change unless it is acted upon by a force, as...
conversion. Some examples are outlined below, though its use is much more widely spread.
Screw
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
in power screw applications.
The maximum efficiency for a screw is defined by the following equations:
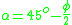
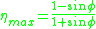
Where
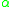 is the helix angle,
is the helix angle, 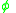 is the friction angle, and
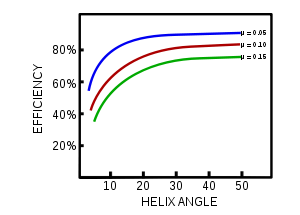
is the friction angle, and 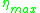 is the maximum efficiency. The friction value is dependent on the materials of the screw and interacting nut, but ultimately the efficiency is controlled by the helix angle. The efficiency can be plotted versus the helix angle for a constant friction, as shown in the diagram to the right. The maximum efficiency is a helix angle between 40 and 45 degrees, however a reasonable efficiency is achieved above 15°. Due to difficulties in forming the thread, helix angle greater than 30° are rarely used. Moreover, above 30° the friction angle becomes greater than the helix angle and the nut is no longer self locking and the mechanical advantage disappears.
is the maximum efficiency. The friction value is dependent on the materials of the screw and interacting nut, but ultimately the efficiency is controlled by the helix angle. The efficiency can be plotted versus the helix angle for a constant friction, as shown in the diagram to the right. The maximum efficiency is a helix angle between 40 and 45 degrees, however a reasonable efficiency is achieved above 15°. Due to difficulties in forming the thread, helix angle greater than 30° are rarely used. Moreover, above 30° the friction angle becomes greater than the helix angle and the nut is no longer self locking and the mechanical advantage disappears.Helical gear