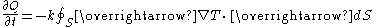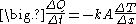Heat current
Encyclopedia
A heat current is a kinetic exchange rate between molecule
s, relative to the material in which the kinesis
occurs. It is defined as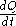 , where
, where 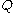 is heat
is heat
and is time
is time
.
For conduction, heat current is defined by Fourier's law as
where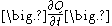 is the amount of heat transferred per unit time [W] and
is the amount of heat transferred per unit time [W] and
The above differential equation
, when integrated
for a homogeneous material of 1-D geometry between two endpoints at constant temperature, gives the heat flow rate as:
where
For thermal radiation
, heat current is defined as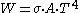
where the constant of proportionality is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant,
is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, 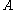 is the radiating surface area, and
is the radiating surface area, and 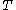 is temperature.
is temperature.
Heat current can also be thought of as the total phonon
distribution multiplied by the energy of one phonon, times the group velocity
of the phonon
s. The phonon distribution of a particular phonon mode is given by the Bose-Einstein
factor, which is dependent on temperature and phonon
energy.
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s, relative to the material in which the kinesis
Kinematics
Kinematics is the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies and systems without consideration of the forces that cause the motion....
occurs. It is defined as
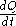 , where
, where 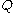 is heat
is heatHeat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
and
 is time
is timeTime
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
.
For conduction, heat current is defined by Fourier's law as
where
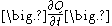 is the amount of heat transferred per unit time [W] and
is the amount of heat transferred per unit time [W] and
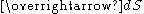 is an oriented surface area element [m2]
is an oriented surface area element [m2]
The above differential equation
Differential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
, when integrated
Integral
Integration is an important concept in mathematics and, together with its inverse, differentiation, is one of the two main operations in calculus...
for a homogeneous material of 1-D geometry between two endpoints at constant temperature, gives the heat flow rate as:
where
- A is the cross-sectional surface area,
-
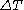 is the temperature difference between the ends,
is the temperature difference between the ends, -
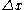 is the distance between the ends.
is the distance between the ends.
For thermal radiation
Thermal radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation generated by the thermal motion of charged particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation....
, heat current is defined as
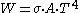
where the constant of proportionality
 is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant,
is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, 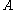 is the radiating surface area, and
is the radiating surface area, and 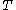 is temperature.
is temperature.Heat current can also be thought of as the total phonon
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
distribution multiplied by the energy of one phonon, times the group velocity
Group velocity
The group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall shape of the wave's amplitudes — known as the modulation or envelope of the wave — propagates through space....
of the phonon
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
s. The phonon distribution of a particular phonon mode is given by the Bose-Einstein
Bose–Einstein statistics
In statistical mechanics, Bose–Einstein statistics determines the statistical distribution of identical indistinguishable bosons over the energy states in thermal equilibrium.-Concept:...
factor, which is dependent on temperature and phonon
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
energy.