
Graded bedding
Encyclopedia
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
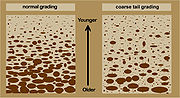
, a graded bed is one characterized by a systematic change in grain or clast size from the base of the bed to the top. Most commonly this takes the form of normal grading, with coarser sediments at the base, which grade upward into progressively finer ones. Normally graded beds generally represent depositional environments
Sedimentary depositional environment
In geology, sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment and, therefore, the rock types that will be formed after lithification, if the sediment is preserved in the rock...
which decrease in transport energy as time passes, but also form during rapid depositional events. They are perhaps best represented in turbidite
Turbidite
Turbidite geological formations have their origins in turbidity current deposits, which are deposits from a form of underwater avalanche that are responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.-The ideal turbidite sequence:...
strata
Stratum
In geology and related fields, a stratum is a layer of sedimentary rock or soil with internally consistent characteristics that distinguish it from other layers...
, where they indicate a sudden strong current that deposits heavy, coarse sediments first, with finer ones following as the current weakens. They can also form in terrestrial stream
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
deposits.
In reverse or inverse grading the bed coarsens upwards. This type of grading is relatively uncommon but is characteristic of sediments deposited by grain flow and debris flow
Debris flow
A debris flow is a fast moving, liquefied landslide of unconsolidated, saturated debris that looks like flowing concrete. It is differentiated from a mudflow in terms of the viscosity and textural properties of the flow. Flows can carry material ranging in size from clay to boulders, and may...
. It is also observed in eolian ripples.

