
Glutathione-ascorbate cycle
Encyclopedia
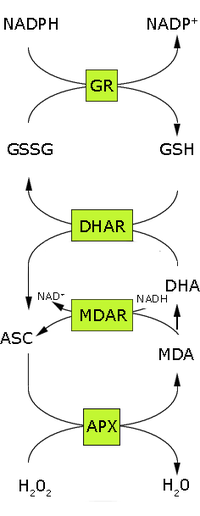
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
that detoxifies hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
(H2O2), which is a reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen. Examples include oxygen ions and peroxides. Reactive oxygen species are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired valence shell electrons....
that is produced as a waste product in metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
. The cycle involves the antioxidant metabolites: ascorbate, glutathione and NADPH and the enzymes linking these metabolites.
In the first step of this pathway, H2O2 is reduced to water by ascorbate peroxidase
Ascorbate peroxidase
Ascorbate peroxidases are enzymes that detoxify peroxides such as hydrogen peroxide using ascorbate as a substrate. The reaction they catalyse is the transfer of electrons from ascorbate to a peroxide, producing dehydroascorbate and water as products.Ascorbate + Hydrogen peroxide →...
(APX) using ascorbate as the electron donor. The oxidized ascorbate (monodehydroascorbate) is regenerated by monodehydroascorbate reductase
Monodehydroascorbate reductase (NADH)
In enzymology, a monodehydroascorbate reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThe 3 substrates of this enzyme are NADH, H+, and monodehydroascorbate, whereas its two products are NAD+ and ascorbate....
(MDAR). However, monodehydroascorbate is a radical and if not rapidly reduced it disproportionates into ascorbate and dehydroascorbate. Dehydroascorbate is reduced to ascorbate by dehydroascorbate reductase at the expense of GSH
Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide that contains an unusual peptide linkage between the amine group of cysteine and the carboxyl group of the glutamate side-chain...
, yielding oxidized glutathione (GSSG). Finally GSSG is reduced by glutathione reductase
Glutathione reductase
Glutathione reductase, also known as GSR or GR, is an enzyme that reduces glutathione disulfide to the sulfhydryl form GSH, which is an important cellular antioxidant....
(GR) using NADPH as electron donor. Thus ascorbate and glutathione
Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide that contains an unusual peptide linkage between the amine group of cysteine and the carboxyl group of the glutamate side-chain...
are not consumed; the net electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
flow is from NADPH to H2
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
O2
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. The reduction of dehydroascorbate may be non-enzymatic or catalysed by proteins with dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR) activity, such as glutathione S-transferase omega 1
GSTO1
Glutathione S-transferase omega-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GSTO1 gene.-Further reading:...
or glutaredoxins.
In plants, the glutathione-ascorbate cycle operates in the cytosol
Cytosol
The cytosol or intracellular fluid is the liquid found inside cells, that is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into compartments....
, mitochondria, plastids and peroxisomes. Since glutathione, ascorbate and NADPH are present in high concentrations in plant cells it is assumed that the glutathione-ascorbate cycle plays a key role for H2O2 detoxification. Nevertheless, other enzymes (peroxidases) including peroxiredoxins and glutathione peroxidase
Glutathione peroxidase
Glutathione peroxidase is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage...
s, which use thioredoxin
Thioredoxin
Thioredoxin is a class of small redox proteins known to be present in all organisms. It plays a role in many important biological processes. In humans, it is encoded by the TXN gene. Loss-of-function mutation of either of the two human thioredoxin genes is lethal at the four-cell stage of the...
s or glutaredoxins as reducing substrates, also contribute to H2O2 removal in plants.

