
Gibbs-Thomson effect
Encyclopedia
The Gibbs–Thomson effect (also called the Gibbs–Kelvin effect or Kelvin effect) relates surface curvature
to vapor pressure
and chemical potential
and is a consequence of surface tension
. It is named after Josiah Willard Gibbs
and William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
. (It is not to be confused with the thermoelectric Thomson effect.)
It leads to the fact that small liquid droplets (i.e. particles with a high surface curvature) exhibit a higher effective vapor pressure
, since the surface is larger in comparison to the volume. The Gibbs–Thomson effect can cause strong depression of the freezing point of liquids dispersed within fine porous materials.
Another notable example of the Gibbs–Thomson effect is Ostwald ripening
, in which concentration gradients cause small precipitates to dissolve and larger ones to grow.
The Gibbs–Thomson equation for a precipitate with radius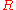 is:
is:


Ostwald ripening is thought to occur in the formation of orthoclase
megacrysts in granites as a consequence of subsolidus growth. See rock microstructure
for more.
Curvature
In mathematics, curvature refers to any of a number of loosely related concepts in different areas of geometry. Intuitively, curvature is the amount by which a geometric object deviates from being flat, or straight in the case of a line, but this is defined in different ways depending on the context...
to vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
and chemical potential
Chemical potential
Chemical potential, symbolized by μ, is a measure first described by the American engineer, chemist and mathematical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs. It is the potential that a substance has to produce in order to alter a system...
and is a consequence of surface tension
Surface tension
Surface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
. It is named after Josiah Willard Gibbs
Josiah Willard Gibbs
Josiah Willard Gibbs was an American theoretical physicist, chemist, and mathematician. He devised much of the theoretical foundation for chemical thermodynamics as well as physical chemistry. As a mathematician, he invented vector analysis . Yale University awarded Gibbs the first American Ph.D...
and William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin OM, GCVO, PC, PRS, PRSE, was a mathematical physicist and engineer. At the University of Glasgow he did important work in the mathematical analysis of electricity and formulation of the first and second laws of thermodynamics, and did much to unify the emerging...
. (It is not to be confused with the thermoelectric Thomson effect.)
It leads to the fact that small liquid droplets (i.e. particles with a high surface curvature) exhibit a higher effective vapor pressure
Vapor pressure
Vapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
, since the surface is larger in comparison to the volume. The Gibbs–Thomson effect can cause strong depression of the freezing point of liquids dispersed within fine porous materials.
Another notable example of the Gibbs–Thomson effect is Ostwald ripening
Ostwald ripening
right|thumb|300px|Basic schematic of the Ostwald ripening process Ostwald ripening is an observed phenomenon in solid solutions or liquid sols which describes the change of an inhomogeneous structure over time...
, in which concentration gradients cause small precipitates to dissolve and larger ones to grow.
The Gibbs–Thomson equation for a precipitate with radius
 is:
is:

-
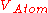 : Atomic volume
: Atomic volume -
 : Boltzmann constant
: Boltzmann constant -
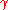 : Surface tensionSurface tensionSurface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
: Surface tensionSurface tensionSurface tension is a property of the surface of a liquid that allows it to resist an external force. It is revealed, for example, in floating of some objects on the surface of water, even though they are denser than water, and in the ability of some insects to run on the water surface...
(J m
m )
) -
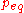 : Equilibrium partial pressure (or chemical potential or concentration)
: Equilibrium partial pressure (or chemical potential or concentration) -
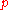 : Partial pressure (or chemical potential or concentration)
: Partial pressure (or chemical potential or concentration) -
 : Absolute temperature
: Absolute temperature
Ostwald ripening is thought to occur in the formation of orthoclase
Orthoclase
Orthoclase is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Greek for "straight fracture," because its two cleavage planes are at right angles to each other. Alternate names are alkali feldspar and potassium feldspar...
megacrysts in granites as a consequence of subsolidus growth. See rock microstructure
Rock microstructure
Rock microstructure includes the texture of a rock and the small scale rock structures. The words "texture" and "microstructure" are interchangeable, with the latter preferred in modern geological literature...
for more.

