
George Smoot
Encyclopedia
George Fitzgerald Smoot III (born February 20, 1945) is an American
astrophysicist
, cosmologist
, Nobel laureate, and $1 million TV quiz show prize winner (Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader?
). He won the Nobel Prize in Physics
in 2006 for his work on COBE
with John C. Mather
that led to the measurement "of the black body
form and anisotropy
of the cosmic microwave background radiation
."
This work helped further the big-bang theory of the universe using the Cosmic Background Explorer Satellite (COBE
). According to the Nobel Prize committee, "the COBE project can also be regarded as the starting point for cosmology
as a precision science."
Smoot donated his share of the Nobel Prize money, less travel costs, to a charitable foundation.
Currently he is a professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley
, senior scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
, and since 2010, a professor of physics at the Paris Diderot University, France. In 2003, he was awarded the Einstein Medal.
. He graduated from Upper Arlington High School
in Upper Arlington, Ohio
, in 1962. He studied mathematics
before switching to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
where he obtained dual bachelor's degree
s in mathematics and physics in 1966 and a Ph.D.
in particle physics
in 1970.
Although Smoot attended MIT, he was not the same Smoot
who was laid end to end to measure the Harvard Bridge
between Cambridge
and Boston; this was his cousin Oliver R. Smoot
, an MIT alumnus who later served as the chairman of the American National Standards Institute
.
, collaborating with Luis Walter Alvarez on the HAPPE (High Altitude Particle Physics Experiment), a stratospheric
weather balloon
designed to detect antimatter
in Earth's upper atmosphere, the presence of which was predicted by the now obscure steady state theory
of cosmology
.
He then took up an interest in cosmic microwave background radiation
(CMB), previously discovered by Arno Allan Penzias
and Robert Woodrow Wilson
in 1964. There were, at that time, several open questions about this topic, relating directly to fundamental questions about the structure of the universe
. Certain models predicted the universe as a whole was rotating, which would have an effect on the CMB: its temperature
would depend on the direction of observation. With the help of Alvarez and Richard A. Muller
, Smoot developed a differential radiometer
which measured the difference in temperature of the CMB between two directions 60 degrees apart. The instrument, which was mounted on a Lockheed U-2
plane, made it possible to determine that the overall rotation of the universe was zero, which was within the limits of accuracy of the instrument. It did, however, detect a variation in the temperature of the CMB of a different sort. That the CMB appears to be at a higher temperature on one side of the sky than on the opposite side, referred to as a dipole pattern, has been explained as a Doppler effect
of the Earth's motion relative to the area of CMB emission, which is called the last scattering surface. Such a Doppler effect arises because the Sun
, and in fact the Milky Way
as a whole, is not stationary, but rather is moving at nearly 600 km/s with respect to the last scattering surface. This is probably due to the gravitational attraction between our galaxy and a concentration of mass like the Great Attractor
.
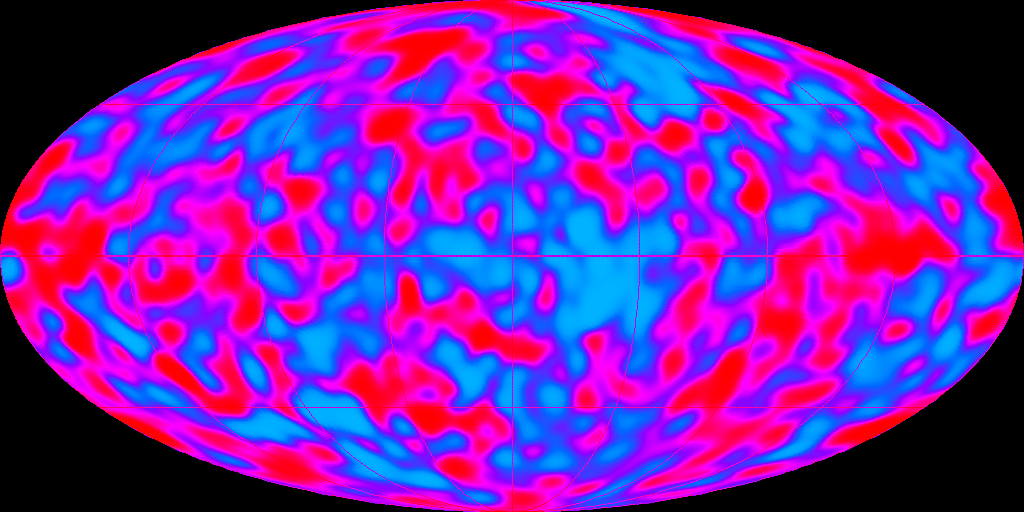 At that time, the CMB appeared to be perfectly uniform excluding the distortion caused by the Doppler effect as mentioned above. This result contradicted observations of the universe, with various structures such as galaxies
At that time, the CMB appeared to be perfectly uniform excluding the distortion caused by the Doppler effect as mentioned above. This result contradicted observations of the universe, with various structures such as galaxies
and galaxy cluster
s indicating that the universe was relatively heterogeneous on a small scale. However, these structures formed slowly. Thus, if the universe is heterogeneous today, it would have been heterogeneous at the time of the emission of the CMB as well, and observable today through weak variations in the temperature of the CMB. It was the detection of these anisotropies that Smoot was working on in the late 1970s. He then proposed to NASA
a project involving a satellite
equipped with a detector that was similar to the one mounted on the U-2 but was more sensitive and not influenced by air pollution
. The proposal was accepted and incorporated as one of the instruments of the satellite COBE
, which cost US$160 million. COBE was launched on November 18, 1989, after a delay owing to the destruction of the Space Shuttle Challenger
. After more than two years of observation and analysis, the COBE research team announced on 23 April 1992 that the satellite had detected tiny fluctuations in the CMB, a breakthrough in the study of the early universe. The observations were "evidence for the birth of the universe" and led Smoot to say regarding the importance of his discovery that "if you're religious, it's like looking at God."
 The success of COBE
The success of COBE
was the outcome of prodigious teamwork involving more than 1,000 researchers, engineers and other participants. John Mather coordinated the entire process and also had primary responsibility for the experiment that revealed the blackbody form of the CMB measured by COBE. George Smoot had main responsibility for measuring the small variations in the temperature of the radiation.
Smoot collaborated with San Francisco Chronicle
journalist Keay Davidson to write the general-audience book Wrinkles in Time, that chronicled his team's efforts. In the book The Very First Light, John Mather and John Boslough complement and broaden the COBE story, and suggest that George Smoot violated team policy by leaking news of COBE's discoveries to the press before NASA's formal announcement, a leak that, to Mather, smacked of self-promotion and betrayal. Smoot eventually apologized for not following the agreed publicity plan and Mather said tensions eventually eased. Mather acknowledged that "George had brought COBE worldwide publicity" the project might not normally have received.
, which had improved angular resolution compared to COBE, and refined the measurements of the anisotropies of the CMB. Smoot has continued CMB observations and analysis and is currently a collaborator on the third generation CMB anisotropy Planck satellite. He is also a collaborator of the design of the Supernova/Acceleration Probe (SNAP), a satellite which is proposed to measure the properties of dark energy
. He has also assisted in analyzing data from the Spitzer Space Telescope
in connection with measuring far infrared background radiation
.
as himself in "The Terminator Decoupling
", episode 17 of the second season of The Big Bang Theory
. He contacted the show as a fan of their often physics-based plots and was incorporated into an episode featuring him lecturing at a fictional physics symposium.
On September 18, 2009, Smoot appeared as the final contestant on the last episode of the Fox
television show "Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader?
". He reached the final question, "What U.S. state is home to Acadia National Park?", to which he gave the correct answer "Maine", becoming the first man to win the one million dollar prize.
On December 10, 2009, he appeared in a BBC
interview of Nobel
laureates, discussing the value science has to offer society.
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
astrophysicist
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is the branch of astronomy that deals with the physics of the universe, including the physical properties of celestial objects, as well as their interactions and behavior...
, cosmologist
Cosmology
Cosmology is the discipline that deals with the nature of the Universe as a whole. Cosmologists seek to understand the origin, evolution, structure, and ultimate fate of the Universe at large, as well as the natural laws that keep it in order...
, Nobel laureate, and $1 million TV quiz show prize winner (Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader?
Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader? (U.S. game show)
Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader? is an American quiz game show on Fox. It is produced by Mark Burnett and is hosted by Jeff Foxworthy. The show premiered as a three-day special which began on February 27, 2007 with the first two shows each a half-hour in length...
). He won the Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded once a year by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901; the others are the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and...
in 2006 for his work on COBE
COBE
The COsmic Background Explorer , also referred to as Explorer 66, was a satellite dedicated to cosmology. Its goals were to investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation of the universe and provide measurements that would help shape our understanding of the cosmos.This work provided...
with John C. Mather
John C. Mather
John Cromwell Mather is an American astrophysicist, cosmologist and Nobel Prize in Physics laureate for his work on the Cosmic Background Explorer Satellite with George Smoot. COBE was the first experiment to measure ".....
that led to the measurement "of the black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
form and anisotropy
Anisotropy
Anisotropy is the property of being directionally dependent, as opposed to isotropy, which implies identical properties in all directions. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physical or mechanical properties An example of anisotropy is the light...
of the cosmic microwave background radiation
Cosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
."
This work helped further the big-bang theory of the universe using the Cosmic Background Explorer Satellite (COBE
COBE
The COsmic Background Explorer , also referred to as Explorer 66, was a satellite dedicated to cosmology. Its goals were to investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation of the universe and provide measurements that would help shape our understanding of the cosmos.This work provided...
). According to the Nobel Prize committee, "the COBE project can also be regarded as the starting point for cosmology
Cosmology
Cosmology is the discipline that deals with the nature of the Universe as a whole. Cosmologists seek to understand the origin, evolution, structure, and ultimate fate of the Universe at large, as well as the natural laws that keep it in order...
as a precision science."
Smoot donated his share of the Nobel Prize money, less travel costs, to a charitable foundation.
Currently he is a professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley , is a teaching and research university established in 1868 and located in Berkeley, California, USA...
, senior scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
, and since 2010, a professor of physics at the Paris Diderot University, France. In 2003, he was awarded the Einstein Medal.
Early life and education
Smoot was born in Yukon, FloridaYukon, Florida
-External links:**...
. He graduated from Upper Arlington High School
Upper Arlington High School (Ohio)
Upper Arlington High School is the sole high school in the Upper Arlington City School District in Upper Arlington, Ohio, a northwest suburb of Columbus, Ohio. It receives students from Jones Middle School and Hastings Middle School. The principal of the high school is Mr. Kip Greenhill...
in Upper Arlington, Ohio
Upper Arlington, Ohio
Upper Arlington is a suburban city in Franklin County, Ohio, United States, on the northwest side of the Columbus metropolitan area. The population was 33,686 at the 2000 census.-Geography:...
, in 1962. He studied mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
before switching to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. MIT has five schools and one college, containing a total of 32 academic departments, with a strong emphasis on scientific and technological education and research.Founded in 1861 in...
where he obtained dual bachelor's degree
Bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree is usually an academic degree awarded for an undergraduate course or major that generally lasts for three or four years, but can range anywhere from two to six years depending on the region of the world...
s in mathematics and physics in 1966 and a Ph.D.
Ph.D.
A Ph.D. is a Doctor of Philosophy, an academic degree.Ph.D. may also refer to:* Ph.D. , a 1980s British group*Piled Higher and Deeper, a web comic strip*PhD: Phantasy Degree, a Korean comic series* PhD Docbook renderer, an XML renderer...
in particle physics
Particle physics
Particle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
in 1970.
Although Smoot attended MIT, he was not the same Smoot
Smoot
The smoot is a nonstandard unit of length created as part of an MIT fraternity prank. It is named after Oliver R. Smoot, a fraternity pledge to Lambda Chi Alpha, who in October 1958 lay on the Harvard Bridge , and was used by his fraternity brothers to measure the length of the bridge.-Unit...
who was laid end to end to measure the Harvard Bridge
Harvard Bridge
The Harvard Bridge carries Massachusetts Avenue from Back Bay, Boston to Cambridge, Massachusetts. It is the longest bridge over the Charles River....
between Cambridge
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, in the Greater Boston area. It was named in honor of the University of Cambridge in England, an important center of the Puritan theology embraced by the town's founders. Cambridge is home to two of the world's most prominent...
and Boston; this was his cousin Oliver R. Smoot
Oliver R. Smoot
Oliver Reed Smoot, Jr. was Chairman of the American National Standards Institute from 2001 to 2002 and President of the International Organization for Standardization from 2003 to 2004...
, an MIT alumnus who later served as the chairman of the American National Standards Institute
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international...
.
Initial research
George Smoot switched to cosmology and began work at Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
, collaborating with Luis Walter Alvarez on the HAPPE (High Altitude Particle Physics Experiment), a stratospheric
Stratosphere
The stratosphere is the second major layer of Earth's atmosphere, just above the troposphere, and below the mesosphere. It is stratified in temperature, with warmer layers higher up and cooler layers farther down. This is in contrast to the troposphere near the Earth's surface, which is cooler...
weather balloon
Weather balloon
A weather or sounding balloon is a balloon which carries instruments aloft to send back information on atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity and wind speed by means of a small, expendable measuring device called a radiosonde...
designed to detect antimatter
Antimatter
In particle physics, antimatter is the extension of the concept of the antiparticle to matter, where antimatter is composed of antiparticles in the same way that normal matter is composed of particles...
in Earth's upper atmosphere, the presence of which was predicted by the now obscure steady state theory
Steady State theory
In cosmology, the Steady State theory is a model developed in 1948 by Fred Hoyle, Thomas Gold, Hermann Bondi and others as an alternative to the Big Bang theory...
of cosmology
Physical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
.
He then took up an interest in cosmic microwave background radiation
Cosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
(CMB), previously discovered by Arno Allan Penzias
Arno Allan Penzias
Arno Allan Penzias is an American physicist and Nobel laureate in physics.-Early life and education:Penzias was born in Munich, Germany. At age six he was among the Jewish children evacuated to Britain as part of the Kindertransport rescue operation...
and Robert Woodrow Wilson
Robert Woodrow Wilson
For the American President, see Woodrow Wilson.Robert Woodrow Wilson is an American astronomer, 1978 Nobel laureate in physics, who with Arno Allan Penzias discovered in 1964 the cosmic microwave background radiation...
in 1964. There were, at that time, several open questions about this topic, relating directly to fundamental questions about the structure of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
. Certain models predicted the universe as a whole was rotating, which would have an effect on the CMB: its temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
would depend on the direction of observation. With the help of Alvarez and Richard A. Muller
Richard A. Muller
Richard A. Muller is a noted American professor of physics at the University of California, Berkeley. He is also a faculty senior scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.-Career:...
, Smoot developed a differential radiometer
Radiometer
A radiometer is a device for measuring the radiant flux of electromagnetic radiation. Generally, the term radiometer denotes an infrared radiation detector, yet it also includes detectors operating on any electromagnetic wavelength....
which measured the difference in temperature of the CMB between two directions 60 degrees apart. The instrument, which was mounted on a Lockheed U-2
Lockheed U-2
The Lockheed U-2, nicknamed "Dragon Lady", is a single-engine, very high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft operated by the United States Air Force and previously flown by the Central Intelligence Agency . It provides day and night, very high-altitude , all-weather intelligence gathering...
plane, made it possible to determine that the overall rotation of the universe was zero, which was within the limits of accuracy of the instrument. It did, however, detect a variation in the temperature of the CMB of a different sort. That the CMB appears to be at a higher temperature on one side of the sky than on the opposite side, referred to as a dipole pattern, has been explained as a Doppler effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
of the Earth's motion relative to the area of CMB emission, which is called the last scattering surface. Such a Doppler effect arises because the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, and in fact the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
as a whole, is not stationary, but rather is moving at nearly 600 km/s with respect to the last scattering surface. This is probably due to the gravitational attraction between our galaxy and a concentration of mass like the Great Attractor
Great Attractor
The Great Attractor is a gravity anomaly in intergalactic space within the range of the Centaurus Supercluster that reveals the existence of a localised concentration of mass equivalent to tens of thousands of Milky Ways, observable by its effect on the motion of galaxies and their associated...
.
COBE

Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
and galaxy cluster
Galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster is a compact cluster of galaxies. Basic difference between a galaxy group and a galaxy cluster is that there are many more galaxies in a cluster than in a group. Also, galaxies in a cluster are more compact and have higher velocity dispersion. One of the key features of cluster is...
s indicating that the universe was relatively heterogeneous on a small scale. However, these structures formed slowly. Thus, if the universe is heterogeneous today, it would have been heterogeneous at the time of the emission of the CMB as well, and observable today through weak variations in the temperature of the CMB. It was the detection of these anisotropies that Smoot was working on in the late 1970s. He then proposed to NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
a project involving a satellite
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
equipped with a detector that was similar to the one mounted on the U-2 but was more sensitive and not influenced by air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
. The proposal was accepted and incorporated as one of the instruments of the satellite COBE
COBE
The COsmic Background Explorer , also referred to as Explorer 66, was a satellite dedicated to cosmology. Its goals were to investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation of the universe and provide measurements that would help shape our understanding of the cosmos.This work provided...
, which cost US$160 million. COBE was launched on November 18, 1989, after a delay owing to the destruction of the Space Shuttle Challenger
Space Shuttle Challenger
Space Shuttle Challenger was NASA's second Space Shuttle orbiter to be put into service, Columbia having been the first. The shuttle was built by Rockwell International's Space Transportation Systems Division in Downey, California...
. After more than two years of observation and analysis, the COBE research team announced on 23 April 1992 that the satellite had detected tiny fluctuations in the CMB, a breakthrough in the study of the early universe. The observations were "evidence for the birth of the universe" and led Smoot to say regarding the importance of his discovery that "if you're religious, it's like looking at God."

COBE
The COsmic Background Explorer , also referred to as Explorer 66, was a satellite dedicated to cosmology. Its goals were to investigate the cosmic microwave background radiation of the universe and provide measurements that would help shape our understanding of the cosmos.This work provided...
was the outcome of prodigious teamwork involving more than 1,000 researchers, engineers and other participants. John Mather coordinated the entire process and also had primary responsibility for the experiment that revealed the blackbody form of the CMB measured by COBE. George Smoot had main responsibility for measuring the small variations in the temperature of the radiation.
Smoot collaborated with San Francisco Chronicle
San Francisco Chronicle
thumb|right|upright|The Chronicle Building following the [[1906 San Francisco earthquake|1906 earthquake]] and fireThe San Francisco Chronicle is a newspaper serving primarily the San Francisco Bay Area of the U.S. state of California, but distributed throughout Northern and Central California,...
journalist Keay Davidson to write the general-audience book Wrinkles in Time, that chronicled his team's efforts. In the book The Very First Light, John Mather and John Boslough complement and broaden the COBE story, and suggest that George Smoot violated team policy by leaking news of COBE's discoveries to the press before NASA's formal announcement, a leak that, to Mather, smacked of self-promotion and betrayal. Smoot eventually apologized for not following the agreed publicity plan and Mather said tensions eventually eased. Mather acknowledged that "George had brought COBE worldwide publicity" the project might not normally have received.
Recent projects
After COBE, Smoot took part in another experiment involving a stratospheric balloon, MAXIMAMillimeter Anisotropy eXperiment IMaging Array
The Millimeter Anisotropy eXperiment IMaging Array experiment was a balloon-borne experiment funded by the U.S. NSF, NASA and Department of Energy, and operated by an international collaboration headed by the University of California, to measure the fluctuations of the cosmic microwave background....
, which had improved angular resolution compared to COBE, and refined the measurements of the anisotropies of the CMB. Smoot has continued CMB observations and analysis and is currently a collaborator on the third generation CMB anisotropy Planck satellite. He is also a collaborator of the design of the Supernova/Acceleration Probe (SNAP), a satellite which is proposed to measure the properties of dark energy
Dark energy
In physical cosmology, astronomy and celestial mechanics, dark energy is a hypothetical form of energy that permeates all of space and tends to accelerate the expansion of the universe. Dark energy is the most accepted theory to explain recent observations that the universe appears to be expanding...
. He has also assisted in analyzing data from the Spitzer Space Telescope
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope , formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003...
in connection with measuring far infrared background radiation
Infrared astronomy
Infrared astronomy is the branch of astronomy and astrophysics that studies astronomical objects visible in infrared radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 micrometers...
.
Public appearances
Shortly after being notified of his Nobel prize, Smoot appeared as the guest conductor of the University of California marching band as it presented a choreographed representation of the Big Bang at halftime of a football game. He followed his performance with a celebratory ramble through Memorial Stadium, greeted row by row and section by section with waves of applause. It was referred to as an "only in Berkeley" occasion. Smoot had a cameo appearanceCameo appearance
A cameo role or cameo appearance is a brief appearance of a known person in a work of the performing arts, such as plays, films, video games and television...
as himself in "The Terminator Decoupling
The Terminator Decoupling
"The Terminator Decoupling" is an episode of the television series The Big Bang Theory that first aired on CBS on March 9, 2009. It is the seventeenth episode of the second season of the series and the thirty-fourth episode overall...
", episode 17 of the second season of The Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang Theory
The Big Bang Theory is an American sitcom created by Chuck Lorre and Bill Prady, both of whom serve as executive producers on the show, along with Steven Molaro. All three also serve as head writers...
. He contacted the show as a fan of their often physics-based plots and was incorporated into an episode featuring him lecturing at a fictional physics symposium.
On September 18, 2009, Smoot appeared as the final contestant on the last episode of the Fox
Fox Broadcasting Company
Fox Broadcasting Company, commonly referred to as Fox Network or simply Fox , is an American commercial broadcasting television network owned by Fox Entertainment Group, part of Rupert Murdoch's News Corporation. Launched on October 9, 1986, Fox was the highest-rated broadcast network in the...
television show "Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader?
Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader?
Are You Smarter Than a 5th Grader? is a television game show format based on asking grade-school level questions to adults, hosted by Jeff Foxworthy...
". He reached the final question, "What U.S. state is home to Acadia National Park?", to which he gave the correct answer "Maine", becoming the first man to win the one million dollar prize.
On December 10, 2009, he appeared in a BBC
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation is a British public service broadcaster. Its headquarters is at Broadcasting House in the City of Westminster, London. It is the largest broadcaster in the world, with about 23,000 staff...
interview of Nobel
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
laureates, discussing the value science has to offer society.
Publications
- Lubin, P. M. & G. F. Smoot. "Search for Linear Polarization of the Cosmic Background Radiation", Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
(LBNL), United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
, (Oct. 1978). - Gorenstein, M. V.& G. F. Smoot. "Large-Angular-Scale Anisotropy in the Cosmic Background Radiation", Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
(LBNL), United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
, (May 1980). - Smoot, G. F., De Amici, G., Friedman, S. D., Witebsky, C., Mandolesi, N., Partridge, R. B., Sironi, G., Danese, L. & G. De Zotti. "Low Frequency Measurement of the Spectrum of the Cosmic Background Radiation", Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
(LBNL), United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
, (June 1983). - Smoot, G. F., De Amici, G., Levin, S. & C. Witebsky. "New Measurements of the Cosmic Background Radiation Spectrum", Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
(LBNL), United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
, (Dec. 1984). - Smoot, G., Levin, S. M., Witebsky, C., De Amici, G., Y. Rephaeli. "An Analysis of Recent Measurements of the Temperature of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation", Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
(LBNL), United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
, (July 1987). - Ade, P., Balbi, A., Bock, J., Borrill, J., Boscaleri, A., de Bernardis, P., Ferreira, P. G., Hanany, S., Hristov, V. V., Jaffe, A. H., Lange, A. E., Lee, A. T., Mauskopf, P. D., Netterfield, C. B., Oh, S., Pascale, E., Rabii, B., Richards, P. L., Smoot, G. F., Stompor, R., Winant, C. D. & J. H. P. Wu. "MAXIMA-1: A Measurement of the Cosmic Microwave Background Anisotropy on Angular Scales of 10' to 5 degrees", Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
(LBNL), United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material...
, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), National Science FoundationNational Science FoundationThe National Science Foundation is a United States government agency that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health...
(NSF), KDI Precision Products, Inc., Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council UK, (June 4, 2005).
External links
- George Smoot official website at UC Berkeley
- Biography and Bibliographic Resources, from the Office of Scientific and Technical InformationOffice of Scientific and Technical InformationThe Office of Scientific and Technical Information is a component of the Office of Science within the U.S. Department of Energy...
, United States Department of EnergyUnited States Department of EnergyThe United States Department of Energy is a Cabinet-level department of the United States government concerned with the United States' policies regarding energy and safety in handling nuclear material... - George Smoot biography at the Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
- George Smoot curriculum vitae at the Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
- Smoot Group Cosmology official website at the Lawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryLawrence Berkeley National LaboratoryThe Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory , is a U.S. Department of Energy national laboratory conducting unclassified scientific research. It is located on the grounds of the University of California, Berkeley, in the Berkeley Hills above the central campus...
- Low gravity phase separator U.S. Patent 4027494 at the United States Patent Office
- Nobel Prize announcement at the Nobel FoundationNobel FoundationThe Nobel Foundation is a private institution founded on 29 June 1900 to manage the finances and administration of the Nobel Prizes. The Foundation is based on the last will of Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite....
- Contemplating the birth of the universe
- George Smoot on the design of the universe
- George Smoot at the Internet Movie Database
- George Smoot chairs the prestigious Eutelsat Star Awards

