Gardner's syndrome
Encyclopedia
Gardner syndrome, also known as familial colorectal polyposis, is an autosomal
dominant form of polyposis characterized by the presence of multiple polyps
in the colon
together with tumors outside the colon. The extracolonic tumors may include osteoma
s of the skull, thyroid cancer
, epidermoid cyst
s, fibroma
s and
sebaceous cyst
s, as well as the occurrence of desmoid tumors in approximately 15% of affected individuals. The countless polyps in the colon predispose to the development of colon cancer; if the colon is not removed, the chance of colon cancer is considered to be very significant. Polyps may also grow in the stomach, duodenum, spleen, kidneys, liver, mesentery and small bowel. In a small number of cases, polyps have also appeared in the cerebellum. Cancers related to GS commonly appear in the thyroid, liver and kidneys.
At this time, there is no cure, and in its more advanced forms, it is considered a terminal diagnosis with a life expectancy of 35–45 years; treatments are surgery and palliative care, although some chemotherapy has been tried with limited success.
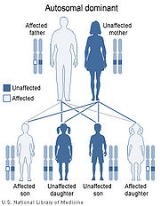
 Gardner syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Typically, one parent has Gardner syndrome. Each of their children, male and female alike, are at 50% risk of inheriting the gene for Gardner syndrome. The risk increases in each succeeding generation, as affected occurs (cluster studies appear by registry).
Gardner syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Typically, one parent has Gardner syndrome. Each of their children, male and female alike, are at 50% risk of inheriting the gene for Gardner syndrome. The risk increases in each succeeding generation, as affected occurs (cluster studies appear by registry).
in the APC gene located in chromosome
5q21 (band q21 on chromosome 5). This is the same gene as is mutant in familial adenomatous polyposis
(FAP), a more common disease that also predisposes to colon cancer. New genetic and molecular information has caused some genetic disorders to be split into multiple entities while other genetic disorders merge into one condition. After existing for most of the second half of the 20th century, Gardner syndrome has vanished as a separate entity. It has been merged into familial adenomatous polyposis
(FAP) and is now considered simply a phenotypic variant
of FAP.
s, congenital
hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), in addition to multiple adenomatous polyps of the colon. Gardner syndrome is also associated with FAP (Familial Adenomatous Polyposis) and may manifest as aggressive fibromatosis (desmoid tumors) of the retroperitoneum.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
dominant form of polyposis characterized by the presence of multiple polyps
Polyp (medicine)
A polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated. If no stalk is present, it is said to be sessile. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, sinus, urinary bladder...
in the colon
Colon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
together with tumors outside the colon. The extracolonic tumors may include osteoma
Osteoma
An osteoma is a new piece of bone usually growing on another piece of bone, typically the skull. It is a benign tumor.When the bone tumor grows on other bone it is known as "homoplastic osteoma"; when it grows on other tissue it is called "heteroplastic osteoma".Osteoma represents the most common...
s of the skull, thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer
Thyroid neoplasm is a neoplasm or tumor of the thyroid. It can be a benign tumor such as thyroid adenoma, or it can be a malignant neoplasm , such as papillary, follicular, medullary or anaplastic thyroid cancer. Most patients are 25 to 65 years of age when first diagnosed; women are more affected...
, epidermoid cyst
Epidermoid cyst
An epidermoid cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium.-Terminology:...
s, fibroma
Fibroma
Fibromas are benign tumors that are composed of fibrous or connective tissue. They can grow in all organs, arising from mesenchyme tissue. The term "fibroblastic" or "fibromatous" is used to describe tumors of the fibrous connective tissue...
s and
sebaceous cyst
Sebaceous cyst
A sebaceous cyst is a term that loosely refers to either epidermoid cysts or pilar cysts . Because an epidermoid cyst originates in the epidermis and a pilar cyst originates from hair follicles, by definition, neither type of cyst is strictly a sebaceous cyst...
s, as well as the occurrence of desmoid tumors in approximately 15% of affected individuals. The countless polyps in the colon predispose to the development of colon cancer; if the colon is not removed, the chance of colon cancer is considered to be very significant. Polyps may also grow in the stomach, duodenum, spleen, kidneys, liver, mesentery and small bowel. In a small number of cases, polyps have also appeared in the cerebellum. Cancers related to GS commonly appear in the thyroid, liver and kidneys.
At this time, there is no cure, and in its more advanced forms, it is considered a terminal diagnosis with a life expectancy of 35–45 years; treatments are surgery and palliative care, although some chemotherapy has been tried with limited success.
Genetics

Cause
Gardner syndrome is now known to be caused by mutationMutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
in the APC gene located in chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
5q21 (band q21 on chromosome 5). This is the same gene as is mutant in familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
(FAP), a more common disease that also predisposes to colon cancer. New genetic and molecular information has caused some genetic disorders to be split into multiple entities while other genetic disorders merge into one condition. After existing for most of the second half of the 20th century, Gardner syndrome has vanished as a separate entity. It has been merged into familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
(FAP) and is now considered simply a phenotypic variant
Variant
Variant is a free cultural magazine based in Glasgow, Scotland, and founded in 1984. Available in both print and internet editions, it is distributed mainly though arts and cultural institutions through Britain and Ireland. Although nominally an arts and cultural bulletin, the magazine also deals...
of FAP.
Diagnosis
Gardner syndrome can be identified based on oral findings, including multiple impacted and supernumerary teeth, multiple jaw osteomas which give a "cotton-wool" appearance to the jaws, as well as multiple odontomaOdontoma
The odontoma is a hamartoma of odontogenic origin.The average age of people found with an odontoma is 14, and the condition is frequently associated with an unerupted tooth....
s, congenital
hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), in addition to multiple adenomatous polyps of the colon. Gardner syndrome is also associated with FAP (Familial Adenomatous Polyposis) and may manifest as aggressive fibromatosis (desmoid tumors) of the retroperitoneum.

