
Galley division
Encyclopedia
In arithmetic
, the galley method, also known as the batello or the scratch method, was the most widely used method of division
in use prior to 1600. The names galea and batello refer to a boat which the outline of the work was thought to resemble.
An earlier version of this method was used as early as 825 by Al-Khwarizmi. The Galley method is thought to be of Arab
origin and is most effective when used on a sand abacus
.However, Lam Lay Yong
's research pointed out that the Galley method of
division was originated in ancient China
The galley method writes fewer figures than long division
, and results in interesting shapes and pictures as it expands both above and below the initial lines. It was the preferred method of division for 17 centuries longer than long division's 4 centuries.

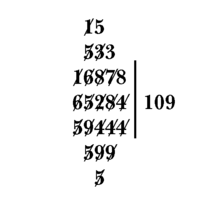
 Set up the problem by writing the dividend and then a bar. The quotient will be written after the bar. Steps: Write the divisor below the dividend. Align the divisor so that its leftmost digit is directly below the dividend's leftmost digit (if the divisor is 594, for instance, it would be written an additional space to the right, so that the "5" would appear below the "6", as shown in the illustration). Dividing 652 by 594 yields the quotient 1 which is written to the right of the bar.
Set up the problem by writing the dividend and then a bar. The quotient will be written after the bar. Steps: Write the divisor below the dividend. Align the divisor so that its leftmost digit is directly below the dividend's leftmost digit (if the divisor is 594, for instance, it would be written an additional space to the right, so that the "5" would appear below the "6", as shown in the illustration). Dividing 652 by 594 yields the quotient 1 which is written to the right of the bar.
Now multiply each digit of the divisor by the new digit of the quotient and subtract that from the left-hand segment of the dividend. Where the subtrahend and the dividend segment differ, cross out the dividend digit and write if necessary the subtrahend digit and next vertical empty space. Cross out the divisor digit used. Compute 6 − 5×1 = 1. Cross out the 6 of the divident and above it write a 1. Cross out the 5 of the divisor. The resulting dividend is now read off as the topmost un-crossed digits: 15284. Using the left-hand segment of the resulting dividend we get 15 − 9×1 = 6. Cross out the 1 and 5 and write 6 above. Cross out the 9. The resulting dividend is 6284. Compute 62 − 4×1 = 58. Cross out the 6 and 2 and write 5 and 8 above. Cross out the 4. The resulting dividend is 5884. Write the divisor one step to the right of where it was originally written using empty spaces below existing crossed out digits. Dividing 588 by 594 yields 0 which is written as the new digit of the quotient. As 0 times any digit of the divisor is 0, the dividend will remain unchanged. We therefore can cross out all the digits of the divisor. We write the divisor again one space to the right Dividing 5884 by 594 yields 9 which is written as the new digit of the quotient. 58 − 5×9 = 13 so cross out the 5 and 8 and above them write 1 and 3. Cross out the 5 of the divisor. The resulting divident is now 1384. 138 − 9×9 = 57. Cross out 1,3, and 8 of the dividend and write 5 and 7 above. Cross out the 9 of the divisor. The resulting dividend is 574. 574 − 4×9 = 538. Cross out the 7 and 4 of the dividend and write 3 and 8 above them. Cross out the 4 of the divisor. The resulting dividend is 538. The process is done, the quotient is 109 and the remainder is 538.
and other parts of the Middle East
.
traced the origin of Galley method of division to Sunzi Mathematical Classis written about 400AD. The division described by Al-Khwarizmi in 825 was identical to the Sunzi algorithm for
division.
Arithmetic
Arithmetic or arithmetics is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics, used by almost everyone, for tasks ranging from simple day-to-day counting to advanced science and business calculations. It involves the study of quantity, especially as the result of combining numbers...
, the galley method, also known as the batello or the scratch method, was the most widely used method of division
Division (mathematics)
right|thumb|200px|20 \div 4=5In mathematics, especially in elementary arithmetic, division is an arithmetic operation.Specifically, if c times b equals a, written:c \times b = a\,...
in use prior to 1600. The names galea and batello refer to a boat which the outline of the work was thought to resemble.
An earlier version of this method was used as early as 825 by Al-Khwarizmi. The Galley method is thought to be of Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
origin and is most effective when used on a sand abacus
Abacus
The abacus, also called a counting frame, is a calculating tool used primarily in parts of Asia for performing arithmetic processes. Today, abaci are often constructed as a bamboo frame with beads sliding on wires, but originally they were beans or stones moved in grooves in sand or on tablets of...
.However, Lam Lay Yong
Lam Lay Yong
Lam Lay Yong , granddaughter of Tan Kah Kee, niece of Lee Kong Chian, is Professor in Mathematics at the Department of Mathematics, National University of Singapore. She graduated from the National University of Singapore in 1957 and pursued graduate study in Cambridge University, obtaining her Ph.D...
's research pointed out that the Galley method of
division was originated in ancient China
The galley method writes fewer figures than long division
Long division
In arithmetic, long division is a standard procedure suitable for dividing simple or complex multidigit numbers. It breaks down a division problem into a series of easier steps. As in all division problems, one number, called the dividend, is divided by another, called the divisor, producing a...
, and results in interesting shapes and pictures as it expands both above and below the initial lines. It was the preferred method of division for 17 centuries longer than long division's 4 centuries.
How it works



Now multiply each digit of the divisor by the new digit of the quotient and subtract that from the left-hand segment of the dividend. Where the subtrahend and the dividend segment differ, cross out the dividend digit and write if necessary the subtrahend digit and next vertical empty space. Cross out the divisor digit used. Compute 6 − 5×1 = 1. Cross out the 6 of the divident and above it write a 1. Cross out the 5 of the divisor. The resulting dividend is now read off as the topmost un-crossed digits: 15284. Using the left-hand segment of the resulting dividend we get 15 − 9×1 = 6. Cross out the 1 and 5 and write 6 above. Cross out the 9. The resulting dividend is 6284. Compute 62 − 4×1 = 58. Cross out the 6 and 2 and write 5 and 8 above. Cross out the 4. The resulting dividend is 5884. Write the divisor one step to the right of where it was originally written using empty spaces below existing crossed out digits. Dividing 588 by 594 yields 0 which is written as the new digit of the quotient. As 0 times any digit of the divisor is 0, the dividend will remain unchanged. We therefore can cross out all the digits of the divisor. We write the divisor again one space to the right Dividing 5884 by 594 yields 9 which is written as the new digit of the quotient. 58 − 5×9 = 13 so cross out the 5 and 8 and above them write 1 and 3. Cross out the 5 of the divisor. The resulting divident is now 1384. 138 − 9×9 = 57. Cross out 1,3, and 8 of the dividend and write 5 and 7 above. Cross out the 9 of the divisor. The resulting dividend is 574. 574 − 4×9 = 538. Cross out the 7 and 4 of the dividend and write 3 and 8 above them. Cross out the 4 of the divisor. The resulting dividend is 538. The process is done, the quotient is 109 and the remainder is 538.
Other versions
The above is called the cross-out version and is the most common. An erasure version exists for situations where erasure is acceptable and there is not need to keep track of the intermediate steps. This is the method used with a sand abacus. Finally, there is a printers method that uses neither erasure or crossouts. Only the top digit in each column of the dividend is active with a zero used to denote an entirely inactive column.Modern usage
Galley division was the favorite method of division with arithmeticians through the 18th century and it is thought that it fell out of use due to the lack of cancelled types in printing. It is still taught in the Moorish schools of North AfricaNorth Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
and other parts of the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
.
Origin
Lam Lay Yong, mathematics professor of National University of SingaporeNational University of Singapore
The National University of Singapore is Singapore's oldest university. It is the largest university in the country in terms of student enrollment and curriculum offered....
traced the origin of Galley method of division to Sunzi Mathematical Classis written about 400AD. The division described by Al-Khwarizmi in 825 was identical to the Sunzi algorithm for
division.
See also
- GroupGroup (mathematics)In mathematics, a group is an algebraic structure consisting of a set together with an operation that combines any two of its elements to form a third element. To qualify as a group, the set and the operation must satisfy a few conditions called group axioms, namely closure, associativity, identity...
- Field (algebra)
- Division algebraDivision algebraIn the field of mathematics called abstract algebra, a division algebra is, roughly speaking, an algebra over a field, in which division is possible.- Definitions :...
- Division ringDivision ringIn abstract algebra, a division ring, also called a skew field, is a ring in which division is possible. Specifically, it is a non-trivial ring in which every non-zero element a has a multiplicative inverse, i.e., an element x with...
- Long divisionLong divisionIn arithmetic, long division is a standard procedure suitable for dividing simple or complex multidigit numbers. It breaks down a division problem into a series of easier steps. As in all division problems, one number, called the dividend, is divided by another, called the divisor, producing a...
- Vinculum

