
GSI3D
Encyclopedia
British Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research. The BGS headquarters are in Keyworth, Nottinghamshire, but other centres...
has been acting as a test bed for the accelerated development of the system. Since its roll-out throughout the Survey GSI3D has started to revolutionise the working practices, data standards and products of a geological survey
Geological survey
The term geological survey can be used to describe both the conduct of a survey for geological purposes and an institution holding geological information....
as a whole. The software is written in Java
Java (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
and data is stored in extensible mark-up language XML
XML
Extensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
.
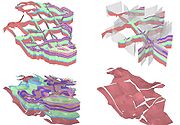
The BGS has just completed a 3 year research and development project to further extend the GSI3D methodology to deal with faulted bedrock terrain.
A brief outline of the methodology
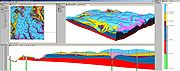
GSI3D utilizes a digital elevation modelDigital elevation model
A digital elevation model is a digital model or 3-D representation of a terrain's surface — commonly for a planet , moon, or asteroid — created from terrain elevation data....
, surface geological linework and downhole borehole
Borehole
A borehole is the generalized term for any narrow shaft bored in the ground, either vertically or horizontally. A borehole may be constructed for many different purposes, including the extraction of water or other liquid or gases , as part of a geotechnical investigation, environmental site...
data to enable the geologist to construct cross sections by correlating boreholes and the outcrops to produce a geological fence diagram. Mathematical interpolation between the nodes along the drawn sections and the limits of the units produces a solid model comprising a stack of triangulated objects each corresponding to one of the geological units present. Scientists draw their sections based on facts such as borehole logs correlated by intuition - the shape 'looks right' to a geologist. This 'looks right' element pulls on the geologists' wealth of understanding of earth processes, examination of exposures and theoretical knowledge gathered over a career in geology. GSI3D enables the efficient capture of tacit and implicit knowledge which was until now trapped in geologist's heads.
Application of Models
The biggest single user of geological models at present is the Environment AgencyEnvironment Agency
The Environment Agency is a British non-departmental public body of the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs and an Assembly Government Sponsored Body of the Welsh Assembly Government that serves England and Wales.-Purpose:...
of England and Wales. The models are used in groundwater resource management and aquifer vulnerability assessments. The BGS is responding to the increasing need of reliable groundwater models by creating direct links between GSI3D and the groundwater modelling software ZOOMQ3D
ZOOMQ3D
ZOOMQ3D is a numerical finite-difference model, which simulates groundwater flow in aquifers. The program is used by hydrogeologists to investigate groundwater resources and to make predictions about possible future changes in their quantity and quality...
.
External links
- GSI3D Research Consortium website
- GSI3D in the British Geological Survey
- Modelling soils at the British Geological Survey
- 2nd International GSI3D conference, 2008
- 3D geological model featured on the BBC
- Report on the 2nd International GSI3D conference in the oilIT journal
- Report on the 2nd International GSI3D conference in Geoconnexion
- A GSI3D model of the City of Halle, Germany
- http://www.lithosphere-east.de
- A downloadable model from the British Geological Survey
- Hydrogeological GSI3D Models in NW Germany
- Halle Model on YouTube
- 3D Geological model on YouTube

