Fundic gland polyposis
Encyclopedia
Fundic gland polyposis is a medical syndrome where the fundus
of the stomach
develops many polyps
. The condition has been described both in patients with polyposis conditions of the colon (including familial adenomatous polyposis
), and in patients in whom it occurs sporadically.
 Most patients with fundic gland polyposis do not have any symptoms, and the diagnosis is made on gastroscopy done for other reasons. Retrospective analysis of patients with sporadic fundic gland polyposis shows that a high percentage do have symptoms, but that this is more likely to be related to the underlying disease responsible for the polyposis. These symptoms include:
Most patients with fundic gland polyposis do not have any symptoms, and the diagnosis is made on gastroscopy done for other reasons. Retrospective analysis of patients with sporadic fundic gland polyposis shows that a high percentage do have symptoms, but that this is more likely to be related to the underlying disease responsible for the polyposis. These symptoms include:
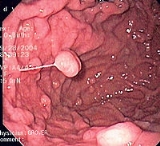
The polyps on endoscopy are usually tiny, numerous and sessile
, and usually scattered throughout the fundus of the stomach, where parietal cells are more numerous. They have the same colour as the gastric mucosa, and never have a stalk. When the polyps are biopsied
, the pathology typically shows shortened gastric pits
, and both superficial and deep cystic lesions in the fundic glands. As sometimes parietal cell hyperplasia may develop deep dilations of gland, one should be really strict in the diagnosis of FGPs (i.e. the presence of deep and superficial dilations). Infrequently, the two lesions may coexist. Foci of dysplasia can sometimes be seen.
, and are more common in middle aged women.
The most important consideration in evaluating patients with fundic gland polyposis is determining whether there is an underlying congenital cause for the condition, or whether the condition was acquired. This is to ascertain the risk of development of gastric cancer, and to ascertain the risk of concomitant colon cancer.
Fundic gland polyposis can be found in association with the following congenital conditions :
The following are acquired causes for fundic gland polyposis :
Helicobacter pylori
infection does not correlate with fundic gland polyposis, and may cause polyp regression.
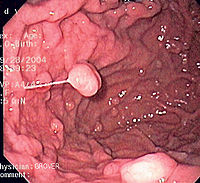
.jpg) The development of polyps depends on the underlying disorder.
The development of polyps depends on the underlying disorder.
In sporadic cases of fundic gland polyposis, there is usually a driving force for parietal cell hypertrophy; for example in chronic proton pump inhibitor use, the cause is up-regulation of gastrin
from acid suppression. Mutations in the β-catenin gene are associated as a risk for polyp development
In familial adenomatous polyposis
, the abnormality is a mutation in the APC gene, resulting in its inactivity. Attenuated FAP can occur from other mutations in the APC gene, and causes a phenotype
wherein colonic
polyps may be few in number
Both the β-catenin gene and the APC gene are involved in the same cell growth signalling pathway, but the APC gene is known to have a significantly higher association with the development of colorectal tumors.
to evaluate the colon. If there are polyps seen on colonoscopy, genetic testing and testing of family members is recommended.
It is still unclear which patients would benefit with surveillance gastroscopy, but most physicians recommend endoscopy every one to three years to survey polyps for dysplasia or cancer. In the event of high grade dysplasia, polypectomy, which is done through the endoscopy, or partial gastrectomy
may be recommended. One study showed the benefit of NSAID therapy in regression of gastric polyps, but the efficacy of this strategy (given the side effects of NSAIDs) is still dubious.
Fundus (stomach)
The fundus of the stomach is the left portion of the stomach's body, and is marked off from the remainder of the body by a plane passing horizontally through the cardiac orifice....
of the stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
develops many polyps
Polyp (medicine)
A polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated. If no stalk is present, it is said to be sessile. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, sinus, urinary bladder...
. The condition has been described both in patients with polyposis conditions of the colon (including familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
), and in patients in whom it occurs sporadically.
Clinical presentation

- epigastric pain
- nauseaNauseaNausea , is a sensation of unease and discomfort in the upper stomach with an involuntary urge to vomit. It often, but not always, precedes vomiting...
- vomitingVomitingVomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
- weight lossWeight lossWeight loss, in the context of medicine, health or physical fitness, is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon and other connective tissue...
The polyps on endoscopy are usually tiny, numerous and sessile
Sessility (medicine)
In medicine, sessility is a characteristic of tumors and polyps that lack a stalk, as opposed to those that are pedunculated....
, and usually scattered throughout the fundus of the stomach, where parietal cells are more numerous. They have the same colour as the gastric mucosa, and never have a stalk. When the polyps are biopsied
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
, the pathology typically shows shortened gastric pits
Gastric pits
Gastric pits are indentations in the stomach which denote entrances to the tubular shaped gastric glands. They are deeper in the pylorus than they are in the other parts of the stomach. The human stomach has several million of these pits which dot the surface of the lining epithelium...
, and both superficial and deep cystic lesions in the fundic glands. As sometimes parietal cell hyperplasia may develop deep dilations of gland, one should be really strict in the diagnosis of FGPs (i.e. the presence of deep and superficial dilations). Infrequently, the two lesions may coexist. Foci of dysplasia can sometimes be seen.
Epidemiology and disease associations
Fundic gland polyposis is found in 0.8 to 1.9% of patients who undergo esophagogastroduodenoscopyEsophagogastroduodenoscopy
For other expansions of the initialism "OGD", see the disambiguation page.In medicine , esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract up to the duodenum...
, and are more common in middle aged women.
The most important consideration in evaluating patients with fundic gland polyposis is determining whether there is an underlying congenital cause for the condition, or whether the condition was acquired. This is to ascertain the risk of development of gastric cancer, and to ascertain the risk of concomitant colon cancer.
Fundic gland polyposis can be found in association with the following congenital conditions :
- familial adenomatous polyposisFamilial adenomatous polyposisFamilial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
- attenuated familial adenomatous polyposis syndromes
- Cowden's syndrome
The following are acquired causes for fundic gland polyposis :
- chronic use of proton pump inhibitors (proposed by some authors, denied by others)
- Zollinger-Ellison syndromeZollinger-Ellison syndromeZollinger–Ellison syndrome is a triad of gastric acid hypersecretion, severe peptic ulceration, and non-beta cell islet tumor of pancreas . In this syndrome increased levels of the hormone gastrin are produced, causing the stomach to produce excess hydrochloric acid. Often the cause is a tumor of...
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
infection does not correlate with fundic gland polyposis, and may cause polyp regression.
Pathophysiology
.jpg)
In sporadic cases of fundic gland polyposis, there is usually a driving force for parietal cell hypertrophy; for example in chronic proton pump inhibitor use, the cause is up-regulation of gastrin
Gastrin
In humans, gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas...
from acid suppression. Mutations in the β-catenin gene are associated as a risk for polyp development
In familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
, the abnormality is a mutation in the APC gene, resulting in its inactivity. Attenuated FAP can occur from other mutations in the APC gene, and causes a phenotype
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
wherein colonic
Colon (anatomy)
The colon is the last part of the digestive system in most vertebrates; it extracts water and salt from solid wastes before they are eliminated from the body, and is the site in which flora-aided fermentation of unabsorbed material occurs. Unlike the small intestine, the colon does not play a...
polyps may be few in number
Both the β-catenin gene and the APC gene are involved in the same cell growth signalling pathway, but the APC gene is known to have a significantly higher association with the development of colorectal tumors.
Cancer risk and the need for screening
There is a risk of development of cancer with fundic gland polyposis, but it varies based on the underlying cause of the polyposis. The risk is highest with congenital polyposis syndromes, and is lowest in acquired causes. As a result, it is recommend that patients with multiple fundic polyps have a colonoscopyColonoscopy
Colonoscopy is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It may provide a visual diagnosis and grants the opportunity for biopsy or removal of suspected...
to evaluate the colon. If there are polyps seen on colonoscopy, genetic testing and testing of family members is recommended.
It is still unclear which patients would benefit with surveillance gastroscopy, but most physicians recommend endoscopy every one to three years to survey polyps for dysplasia or cancer. In the event of high grade dysplasia, polypectomy, which is done through the endoscopy, or partial gastrectomy
Gastrectomy
A gastrectomy is a partial or full surgical removal of the stomach.-Indications:Gastrectomies are performed to treat cancer and perforations of the stomach wall....
may be recommended. One study showed the benefit of NSAID therapy in regression of gastric polyps, but the efficacy of this strategy (given the side effects of NSAIDs) is still dubious.

