
Forgery (Cryptography)
Encyclopedia
In a cryptographic
digital signature
or MAC
system, digital signature forgery is the ability to create a pair consisting of a message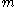 and a signature (or MAC)
and a signature (or MAC)  that is valid for
that is valid for 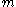 , where
, where  has not been signed in the past by the legitimate signer. There are three types of forgery: existential, selective, and universal.
has not been signed in the past by the legitimate signer. There are three types of forgery: existential, selective, and universal.
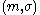 , where
, where  was not produced by the legitimate signer. The adversary need not have any control over
was not produced by the legitimate signer. The adversary need not have any control over 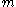 ;
; 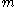 need not have any particular meaning; and indeed it may even be gibberish — as long as the pair
need not have any particular meaning; and indeed it may even be gibberish — as long as the pair 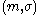 is valid, the adversary has succeeded in constructing an existential forgery.
is valid, the adversary has succeeded in constructing an existential forgery.
Existential forgery is essentially the weakest adversarial goal, therefore the strongest schemes are those that are "existentially unforgeable".
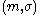 where
where 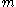 has been chosen by the adversary prior to the attack.
has been chosen by the adversary prior to the attack. 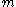 may be chosen to have interesting mathematical properties with respect to the signature algorithm; however, in selective forgery,
may be chosen to have interesting mathematical properties with respect to the signature algorithm; however, in selective forgery, 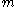 must be fixed before the start of the attack.
must be fixed before the start of the attack.
The ability to successfully conduct a selective forgery attack implies the ability to successfully conduct an existential forgery attack.
 for any given message
for any given message 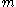 . An adversary capable of universal forgery is able to sign messages he chose himself (as in selective forgery), messages chosen at random, or even specific messages provided by an opponent.
. An adversary capable of universal forgery is able to sign messages he chose himself (as in selective forgery), messages chosen at random, or even specific messages provided by an opponent.
Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties...
digital signature
Digital signature
A digital signature or digital signature scheme is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit...
or MAC
Message authentication code
In cryptography, a message authentication code is a short piece of information used to authenticate a message.A MAC algorithm, sometimes called a keyed hash function, accepts as input a secret key and an arbitrary-length message to be authenticated, and outputs a MAC...
system, digital signature forgery is the ability to create a pair consisting of a message
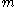 and a signature (or MAC)
and a signature (or MAC)  that is valid for
that is valid for 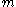 , where
, where  has not been signed in the past by the legitimate signer. There are three types of forgery: existential, selective, and universal.
has not been signed in the past by the legitimate signer. There are three types of forgery: existential, selective, and universal.Existential forgery
Existential forgery is the creation (by an adversary) of at least one message/signature pair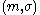 , where
, where  was not produced by the legitimate signer. The adversary need not have any control over
was not produced by the legitimate signer. The adversary need not have any control over 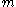 ;
; 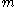 need not have any particular meaning; and indeed it may even be gibberish — as long as the pair
need not have any particular meaning; and indeed it may even be gibberish — as long as the pair 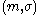 is valid, the adversary has succeeded in constructing an existential forgery.
is valid, the adversary has succeeded in constructing an existential forgery.Existential forgery is essentially the weakest adversarial goal, therefore the strongest schemes are those that are "existentially unforgeable".
Selective forgery
Selective forgery is the creation (by an adversary) of a message/signature pair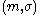 where
where 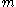 has been chosen by the adversary prior to the attack.
has been chosen by the adversary prior to the attack. 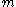 may be chosen to have interesting mathematical properties with respect to the signature algorithm; however, in selective forgery,
may be chosen to have interesting mathematical properties with respect to the signature algorithm; however, in selective forgery, 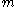 must be fixed before the start of the attack.
must be fixed before the start of the attack.The ability to successfully conduct a selective forgery attack implies the ability to successfully conduct an existential forgery attack.
Universal forgery
Universal forgery is the creation (by an adversary) of a valid signature for any given message
for any given message 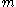 . An adversary capable of universal forgery is able to sign messages he chose himself (as in selective forgery), messages chosen at random, or even specific messages provided by an opponent.
. An adversary capable of universal forgery is able to sign messages he chose himself (as in selective forgery), messages chosen at random, or even specific messages provided by an opponent.

