
Flory convention
Encyclopedia
The Flory convention for defining the variables involved on modeling the position vectors of atoms in macromolecules it is often necessary to convert from Cartesian coordinates (x,y,z) to generalized coordinates
. It is named after nobel prize
-winning Paul Flory
.
As an example of its use, a peptide bond
can be described by the x,y,z positions of every atom in this bond or the Flory convention can be used. Here one must know the bond length
s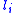 , bond angles
, bond angles 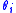 , and the dihedral angle
, and the dihedral angle
s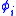 (note that the sequence of dihedral angles is specified using angle 0 as trans). Applying a vector conversion from the Cartesian coordinates to the generalized coordinates will describe the same three-dimensional structure using the Flory convention.
(note that the sequence of dihedral angles is specified using angle 0 as trans). Applying a vector conversion from the Cartesian coordinates to the generalized coordinates will describe the same three-dimensional structure using the Flory convention.
Generalized coordinates
In the study of multibody systems, generalized coordinates are a set of coordinates used to describe the configuration of a system relative to some reference configuration....
. It is named after nobel prize
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
-winning Paul Flory
Paul Flory
Paul John Flory was an American chemist and Nobel laureate who was known for his prodigious volume of work in the field of polymers, or macromolecules...
.
As an example of its use, a peptide bond
Peptide bond
This article is about the peptide link found within biological molecules, such as proteins. A similar article for synthetic molecules is being created...
can be described by the x,y,z positions of every atom in this bond or the Flory convention can be used. Here one must know the bond length
Bond length
- Explanation :Bond length is related to bond order, when more electrons participate in bond formation the bond will get shorter. Bond length is also inversely related to bond strength and the bond dissociation energy, as a stronger bond will be shorter...
s
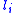 , bond angles
, bond angles 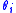 , and the dihedral angle
, and the dihedral angleDihedral angle
In geometry, a dihedral or torsion angle is the angle between two planes.The dihedral angle of two planes can be seen by looking at the planes "edge on", i.e., along their line of intersection...
s
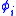 (note that the sequence of dihedral angles is specified using angle 0 as trans). Applying a vector conversion from the Cartesian coordinates to the generalized coordinates will describe the same three-dimensional structure using the Flory convention.
(note that the sequence of dihedral angles is specified using angle 0 as trans). Applying a vector conversion from the Cartesian coordinates to the generalized coordinates will describe the same three-dimensional structure using the Flory convention.

