
Flory-Huggins solution theory
Overview
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
of the thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
of polymer
Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
s which takes account of the great dissimilarity in molecular
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
sizes in adapting the usual expression
Expression (mathematics)
In mathematics, an expression is a finite combination of symbols that is well-formed according to rules that depend on the context. Symbols can designate numbers , variables, operations, functions, and other mathematical symbols, as well as punctuation, symbols of grouping, and other syntactic...
for the entropy of mixing
Entropy of mixing
In thermodynamics the entropy of mixing is the increase in the total entropy of a compound system, when different and chemically non-reacting chemical substances or material components are mixed by removing partition between the system's initially separate volumes...
. The result is an equation for the Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
change
 for mixing a polymer with a solvent
for mixing a polymer with a solventSolvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
. Although it makes simplifying assumptions, it generates useful results for interpreting experiments.
The thermodynamic equation
Thermodynamic potentials
A thermodynamic potential is a scalar function used to represent the thermodynamic state of a system. The concept of thermodynamic potentials was introduced by Pierre Duhem in 1886. Josiah Willard Gibbs in his papers used the term fundamental functions. One main thermodynamic potential that has a...
for the Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy
In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that measures the "useful" or process-initiating work obtainable from a thermodynamic system at a constant temperature and pressure...
change accompanying mixing at constant temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and (external) pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
is
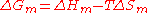
A change, denoted by
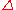 , is the value
, is the valueNumber
A number is a mathematical object used to count and measure. In mathematics, the definition of number has been extended over the years to include such numbers as zero, negative numbers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and complex numbers....
of a variable
Variable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
for a solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
or mixture
Mixture
In chemistry, a mixture is a material system made up by two or more different substances which are mixed together but are not combined chemically...
minus the values for the pure components
Component (thermodynamics)
In thermodynamics, a component is a chemically distinct constituent ofa system. Calculating the number of components in a system is necessary, for example, when applying Gibbs phase rule in determination of the number of degrees of freedom of a system....
considered separately.

