
FlexRay
Encyclopedia
FlexRay is an automotive network communications protocol
developed by the FlexRay Consortium. It is designed to be faster and more reliable than CAN
and TTP
, but is also more expensive. The FlexRay consortium disbanded in 2009, but the specifications are still available for download at the FlexRay website.
There were also Premium Associate and Associate members of FlexRay consortium. By September 2009, there were 28 premium associate members and more than 60 associate members. At the end of 2009, the consortium disbanded.
, enabling a new and fast adaptive damping system. Full use of FlexRay was introduced in 2008 in the new BMW 7 Series (F01), the world's first production vehicle to fully utilize the FlexRay system.
, or ECUs).
Each ECU has an independent clock. The clock drift
must be no more than 0.15% from the reference clock,
so the difference between the slowest and the fastest clock in the system is no greater than 0.3%.
This means that, if ECU-s is a sender and ECU-r is a receiver, then for every 300 cycles of the sender
there will be between 299 and 301 cycles of the receiver. The clocks are resynchronized frequently enough
to assure that this causes no problems.
The receiver keeps a buffer of the last 5 samples, and uses the majority of the last 5 samples as the input signal.
Single-cycle transmission errors may affect results near the boundary of the bits, but will not affect cycles in the middle of the 8-cycle region.
The errors are moved to the extreme cycles, and the clock is synchronized frequently enough for the drift to be small. (Drift is smaller than 1 cycle per 300 cycles, and during transmission the clock is synchronized more than once every 300 cycles).
 , packed in the following way:
, packed in the following way:
If nothing is being communicated, the bus is held in state 1 (high voltage), so every receiver knows that the communication started when the voltage drops to 0.
The receiver knows when the message is complete by checking whether BSS0 (1) or FES (0) was received.
Note that 8-cycle per bit has nothing to do with bytes. Each byte takes 80 cycles to transfer. 16 for BSS0 and BSS1 and 64 for its bits.
Also note that BSS0 has value 1, and BSS1 has value 0.
So the clock is synchronized when the transmission starts and between BSS0 and BSS1.
As synchronization is done on the voted signal, small transmission errors during synchronization that affect the boundary bits may skew the synchronization no more than 1 cycle. As there are at most 88 cycles between synchronization (BSS1, 8 bits of the last byte, FES and TES - 11 bits of 8 cycles each), and the clock drift is no larger than 1 per 300 cycles, the drift may skew the clock no more than 1 cycle. Small transmission errors during the receiving may affect only the boundary bits. So in the worst case the two middle bits are correct, and thus the sampled value is correct.
Here's an example of a particularly bad case - error during synchronization, a lost cycle due to clock drift and error in transmission.
Errors that happened in the example
Despite so many errors, the communication was received correctly.
The green cells are sampling points. All except the first are synchronized by the 1->0 edge in the transmission fragment shown.
are tools which collect, analyze, decode, store signals so people can view the high-speed waveforms at their leisure.
Vehicle bus
A vehicle bus is a specialized internal communications network that interconnects components inside a vehicle...
developed by the FlexRay Consortium. It is designed to be faster and more reliable than CAN
Controller Area Network
Controller–area network is a vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer....
and TTP
Time-Triggered Protocol
TTP is an open and modular control system platform technology that supports the design of upgradeable, reusable and easy-to-integrate systems...
, but is also more expensive. The FlexRay consortium disbanded in 2009, but the specifications are still available for download at the FlexRay website.
Features
FlexRay's prominent features are:- High data rates (up to )
- Time- and event-triggered behavior
- Redundancy
- Fault-tolerance
- Deterministic
Consortium
The FlexRay Consortium was made up of the following core members:- BMWBMWBayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
- VolkswagenVolkswagenVolkswagen is a German automobile manufacturer and is the original and biggest-selling marque of the Volkswagen Group, which now also owns the Audi, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, SEAT, and Škoda marques and the truck manufacturer Scania.Volkswagen means "people's car" in German, where it is...
- Daimler AG
- General MotorsGeneral MotorsGeneral Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
- Robert Bosch GmbHRobert Bosch GmbHRobert Bosch GmbH is a multinational engineering and electronics company headquartered in Gerlingen, near Stuttgart, Germany. It is the world's largest supplier of automotive components...
- NXP Semiconductors
- Freescale
There were also Premium Associate and Associate members of FlexRay consortium. By September 2009, there were 28 premium associate members and more than 60 associate members. At the end of 2009, the consortium disbanded.
Where used
The first series production vehicle with FlexRay was at the end of 2006 in the BMW X5BMW X5
The BMW X5 is a luxury crossover SUV introduced in 1999 as the first generation E53. It was BMW's first SUV also known as "Four-by-Four" in the UK. It features all-wheel drive which is branded as the "X" drive system and is available with either manual or automatic transmission...
, enabling a new and fast adaptive damping system. Full use of FlexRay was introduced in 2008 in the new BMW 7 Series (F01), the world's first production vehicle to fully utilize the FlexRay system.
Vehicles
- Audi A8Audi A8The Audi A8 is a four-door, full-size, luxury sedan car manufactured and marketed by the German automaker Audi since 1994. Succeeding the Audi V8, the A8 has been offered with front wheel drive or permanent four-wheel drive, with multitronic or tiptronic automatic transmissions — and in short- and...
- Bentley MulsanneBentley Mulsanne (2010)The new Bentley Mulsanne is a high-end luxury car produced by Bentley Motors Limited in the United Kingdom. The name is derived from Bentley's historical racing pedigree, which included five victories at the 24 Hours of Le Mans — the Mulsanne Straight being the stretch of the Le Mans racing...
- BMW X5BMW X5The BMW X5 is a luxury crossover SUV introduced in 1999 as the first generation E53. It was BMW's first SUV also known as "Four-by-Four" in the UK. It features all-wheel drive which is branded as the "X" drive system and is available with either manual or automatic transmission...
- BMW 7-SeriesBMW F01The BMW F01 is the current BMW 7 series that went into production in September 2008. The long-wheelbase model, codenamed BMW F02, is longer than the BMW F01.-Presentation:...
- BMW 5 Series Gran TurismoBMW 5 Series Gran TurismoThe BMW 5 Series Gran Turismo is an executive or mid-size car from German manufacturer BMW, which was first displayed at the 2009 Geneva Motor Show as a concept car...
- BMW 5-Series
- Rolls-Royce Ghost
Clock
FlexRay system consists of a bus and processors (Electronic control unitElectronic control unit
In automotive electronics, electronic control unit is a generic term for any embedded system that controls one or more of the electrical systems or subsystems in a motor vehicle....
, or ECUs).
Each ECU has an independent clock. The clock drift
Clock drift
Clock drift refers to several related phenomena where a clock does not run at the exact right speed compared to another clock. That is, after some time the clock "drifts apart" from the other clock. This phenomenon is also used for instance in computers to build random number generators...
must be no more than 0.15% from the reference clock,
so the difference between the slowest and the fastest clock in the system is no greater than 0.3%.
This means that, if ECU-s is a sender and ECU-r is a receiver, then for every 300 cycles of the sender
there will be between 299 and 301 cycles of the receiver. The clocks are resynchronized frequently enough
to assure that this causes no problems.
Bits on the bus
At each time, only one ECU writes to the bus. Each bit to be sent is held on the bus for 8 sample clock cycles.The receiver keeps a buffer of the last 5 samples, and uses the majority of the last 5 samples as the input signal.
Single-cycle transmission errors may affect results near the boundary of the bits, but will not affect cycles in the middle of the 8-cycle region.
Sampled bits
The value of the bit is sampled in the middle of the 8-bit region.The errors are moved to the extreme cycles, and the clock is synchronized frequently enough for the drift to be small. (Drift is smaller than 1 cycle per 300 cycles, and during transmission the clock is synchronized more than once every 300 cycles).
Frame
All the communication is sent in the form of frames. The message consists of bytes , packed in the following way:
, packed in the following way:
- Transmission Start Signal (TSS) - bit 0
- Frame Start Signal (FSS) - bit 1
-
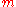 times:
times:
- Byte Start Signal 0 (BSS0) - bit 1
- Byte Start Signal 1 (BSS1) - bit 0
- 0-th bit of i-th byte
- 1-st bit of i-th byte
- 2-nd bit of i-th byte
- ...
- 7-th bit of i-th byte
- Frame End Signal (FES) - bit 0
- Transmission End Signal (TES) - bit 1
If nothing is being communicated, the bus is held in state 1 (high voltage), so every receiver knows that the communication started when the voltage drops to 0.
The receiver knows when the message is complete by checking whether BSS0 (1) or FES (0) was received.
Note that 8-cycle per bit has nothing to do with bytes. Each byte takes 80 cycles to transfer. 16 for BSS0 and BSS1 and 64 for its bits.
Also note that BSS0 has value 1, and BSS1 has value 0.
Clock synchronization
Clocks are resynchronized when the voted signal changes from 1 to 0, if the receiver was in either idle state or expecting BSS1.So the clock is synchronized when the transmission starts and between BSS0 and BSS1.
As synchronization is done on the voted signal, small transmission errors during synchronization that affect the boundary bits may skew the synchronization no more than 1 cycle. As there are at most 88 cycles between synchronization (BSS1, 8 bits of the last byte, FES and TES - 11 bits of 8 cycles each), and the clock drift is no larger than 1 per 300 cycles, the drift may skew the clock no more than 1 cycle. Small transmission errors during the receiving may affect only the boundary bits. So in the worst case the two middle bits are correct, and thus the sampled value is correct.
Here's an example of a particularly bad case - error during synchronization, a lost cycle due to clock drift and error in transmission.
Errors that happened in the example
- Because of a single-bit error during synchronization, the synchronization was delayed by 1 cycle
- Receiver clock was slower than sender clock, so receiver missed one cycle (marked X). This will not happen again before the next synchronization due to limits on maximum allowable clock drift.
- Because of a single-bit error during transmission, a bit was voted wrongly near the result.
Despite so many errors, the communication was received correctly.
The green cells are sampling points. All except the first are synchronized by the 1->0 edge in the transmission fragment shown.
| Signal to be sent | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal sent | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| On the bus | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Received | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | X | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 5-maj voted | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | X | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
Development tools
When developing and/or troubleshooting the FlexRay bus, examination of hardware signals can be very important. Logic analyzers and bus analyzersBus analyzer
A bus analyzer is a computer bus analysis tool, often a combination of hardware and software, used during development of hardware or device drivers for a specific bus, for diagnosing bus or device failures, or reverse engineering....
are tools which collect, analyze, decode, store signals so people can view the high-speed waveforms at their leisure.
The future of FlexRay
The bus has its own disadvantages like lower operating voltage levels and asymmetric of the edges, which leads to problems in extending the network length. FlexRay might soon be phased out with Ethernet taking over its place where high speed data transfers are required in vehicles.See also
- Controller Area NetworkController Area NetworkController–area network is a vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other within a vehicle without a host computer....
(CAN) - Local Interconnect NetworkLocal Interconnect NetworkThe LIN-Bus is a vehicle bus standard or computer networking bus-system used within current automotive network architectures....
(LIN) - lower cost and lower bandwidth than CAN
External links
- FlexRay FlexRay Consortium
- FlexRay Starter Kit Low cost FlexRay Starter Kit with the BOSCH E-Ray controller from DuxSolutions, also FlexRay Network Design tool available
- FlexRay Overview Technical Overview of FlexRay by National Instruments
- Flexray Products Samtec FlexRay product
- Flexray design tool Low cost network design tool for FlexRay

