
Fick principle
Encyclopedia
Developed by Adolf Eugen Fick
(1829 - 1901), the Fick principle was first devised as a technique for measuring cardiac output
. However, its underlying principles may be applied in a variety of clinical situations.
The essence of the Fick principle is that blood flow to an organ can be calculated using a marker substance if the following information is known:
In Fick's original method, the "organ" was the entire human body and the marker substance was oxygen.
The principle may be applied in different ways. For example, if the blood flow to an organ is known, together with the arterial and venous concentrations of the marker substance, then the uptake of marker substance by the organ may then be calculated.
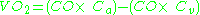
where CO = Cardiac Output, Ca = Oxygen concentration of arterial blood and Cv = Oxygen concentration of mixed venous blood.
This allows us to say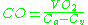
and hence calculate cardiac output.
Note that (Ca – Cv) is also known as the arteriovenous oxygen difference
.
A commonly-used value for O2 consumption at rest is 125ml O2 per minute per square meter of body surface area
.
content of blood
thus giving the arteriovenous oxygen difference, and the flow calculated is the flow across the pulmonary system. This gives a simple way to calculate the cardiac output:

Assuming there is no intracardiac shunt, the pulmonary blood flow equals the systemic blood flow. Measurement of the arterial and venous oxygen content of blood involves the sampling of blood from the pulmonary artery (low oxygen content) and from the pulmonary vein (high oxygen content). In practice, sampling of peripheral arterial blood is a surrogate for pulmonary venous blood. Determination of the oxygen consumption of the peripheral tissues is more complex.
The calculation of the arterial and venous oxygen concentration of the blood is a straightforward process. Almost all oxygen in the blood is bound to hemoglobin
molecule
s in the red blood cell
s. Measuring the content of hemoglobin in the blood and the percentage of saturation of hemoglobin (the oxygen saturation of the blood) is a simple process and is readily available to physicians. Using the fact that each gram
of hemoglobin can carry 1.36 ml of O2
, the oxygen content of the blood (either arterial or venous) can be estimated by the following formula:
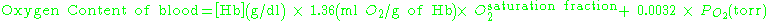
Assuming a hemoglobin concentration of 15g/dl and an oxygen saturation of 99%, the oxygen concentration of arterial blood is approximately 200ml of O2 per litre.
The saturation of mixed venous blood is approximately 75% in health. Using this value in the above equation, the oxygen concentration of mixed venous blood is approximately 150ml of O2 per litre.
Cardiac output may also be estimated with the Fick principle using production of carbon dioxide
as a marker substance.
to calculate renal blood flow
.
In this context, it is not oxygen which is measured, but a marker such as para-aminohippurate. However, the principles are essentially the same.
Adolf Eugen Fick
Adolf Eugen Fick was a German physiologist. He started to study mathematics and physics, but then realized he was more interested in medicine. He earned his doctorate in medicine at Marburg in 1851...
(1829 - 1901), the Fick principle was first devised as a technique for measuring cardiac output
Cardiac output
Cardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min...
. However, its underlying principles may be applied in a variety of clinical situations.
The essence of the Fick principle is that blood flow to an organ can be calculated using a marker substance if the following information is known:
- Amount of marker substance taken up by the organ per unit time
- Concentration of marker substance in arterial blood supplying the organ
- Concentration of marker substance in venous blood leaving the organ
In Fick's original method, the "organ" was the entire human body and the marker substance was oxygen.
The principle may be applied in different ways. For example, if the blood flow to an organ is known, together with the arterial and venous concentrations of the marker substance, then the uptake of marker substance by the organ may then be calculated.
Variables
In Fick's original method, the following variables are measured:- VO2, oxygen consumption in ml of pure gaseous oxygen per minute. This may be measured using a spirometerSpirometerA spirometer is an apparatus for measuring the volume of air inspired and expired by the lungs. It is a precision differential pressure transducer for the measurements of respiration flow rates. The spirometer records the amount of air and the rate of air that is breathed in and out over a...
within a closed rebreathing circuit incorporating a CO2Carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
absorber - Cv, the oxygen concentration of blood taken from the pulmonary arteryPulmonary arteryThe pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood....
(representing deoxygenated blood) - Ca, the oxygen concentration of blood from a cannula in a peripheral artery (representing oxygenated blood)
Equation
From these values, we know that: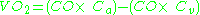
where CO = Cardiac Output, Ca = Oxygen concentration of arterial blood and Cv = Oxygen concentration of mixed venous blood.
This allows us to say
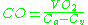
and hence calculate cardiac output.
Note that (Ca – Cv) is also known as the arteriovenous oxygen difference
Arteriovenous oxygen difference
The arteriovenous oxygen difference, or a-vO2 diff, is the difference in the oxygen content of the blood between the arterial blood and the venous blood. It is an indication of how much oxygen is removed from the blood in capillaries as the blood circulates in the body...
.
Assumed Fick determination
In reality, this method is rarely used due to the difficulty of collecting and analysing the gas concentrations. However, by using an assumed value for oxygen consumption, cardiac output can be closely approximated without the cumbersome and time-consuming oxygen consumption measurement. This is sometimes called an assumed Fick determination.A commonly-used value for O2 consumption at rest is 125ml O2 per minute per square meter of body surface area
Body surface area
In physiology and medicine, the body surface area is the measured or calculated surface of a human body. For many clinical purposes BSA is a better indicator of metabolic mass than body weight because it is less affected by abnormal adipose mass...
.
Underlying principles
The Fick principle relies on the observation that the total uptake of (or release of) a substance by the peripheral tissues is equal to the product of the blood flow to the peripheral tissues and the arterial-venous concentration difference (gradient) of the substance. In the determination of cardiac output, the substance most commonly measured is the oxygenOxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
content of blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
thus giving the arteriovenous oxygen difference, and the flow calculated is the flow across the pulmonary system. This gives a simple way to calculate the cardiac output:

Assuming there is no intracardiac shunt, the pulmonary blood flow equals the systemic blood flow. Measurement of the arterial and venous oxygen content of blood involves the sampling of blood from the pulmonary artery (low oxygen content) and from the pulmonary vein (high oxygen content). In practice, sampling of peripheral arterial blood is a surrogate for pulmonary venous blood. Determination of the oxygen consumption of the peripheral tissues is more complex.
The calculation of the arterial and venous oxygen concentration of the blood is a straightforward process. Almost all oxygen in the blood is bound to hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s in the red blood cell
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
s. Measuring the content of hemoglobin in the blood and the percentage of saturation of hemoglobin (the oxygen saturation of the blood) is a simple process and is readily available to physicians. Using the fact that each gram
Gram
The gram is a metric system unit of mass....
of hemoglobin can carry 1.36 ml of O2
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, the oxygen content of the blood (either arterial or venous) can be estimated by the following formula:
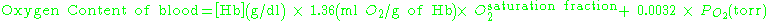
Assuming a hemoglobin concentration of 15g/dl and an oxygen saturation of 99%, the oxygen concentration of arterial blood is approximately 200ml of O2 per litre.
The saturation of mixed venous blood is approximately 75% in health. Using this value in the above equation, the oxygen concentration of mixed venous blood is approximately 150ml of O2 per litre.
Cardiac output may also be estimated with the Fick principle using production of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
as a marker substance.
Use in renal physiology
The principle can also be used in renal physiologyRenal physiology
Renal physiology is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including reabsorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; regulation of fluid balance and blood pressure;...
to calculate renal blood flow
Renal blood flow
In the physiology of the kidney, renal blood flow is the volume of blood delivered to the kidneys per unit time. In humans, the kidneys together receive roughly 22% of cardiac output, amounting to 1.1 L/min in a 70-kg adult male...
.
In this context, it is not oxygen which is measured, but a marker such as para-aminohippurate. However, the principles are essentially the same.

