
Farnesyl pyrophosphate
Encyclopedia
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway
used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpene
s, terpenoid
s, and sterol
s. It is sometimes also referred to as Farnesyl diphosphate (FDP).
It is the immediate precursor of squalene
(via the enzyme squalene synthase), dehydrodolichol diphosphate (a precursor of dolichol
), and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
(GGPP).
with 2 units of 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form farnesyl pyrophosphate.
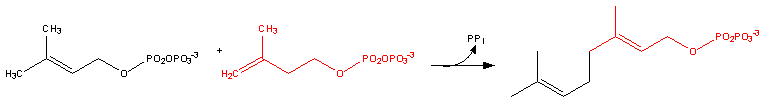
HMG-CoA reductase pathway
The mevalonate pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway or mevalonate-dependent route or isoprenoid pathway, is an important cellular metabolic pathway present in all higher eukaryotes and many bacteria...
used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpene
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
s, terpenoid
Terpenoid
The terpenoids , sometimes called isoprenoids, are a large and diverse class of naturally occurring organic chemicals similar to terpenes, derived from five-carbon isoprene units assembled and modified in thousands of ways. Most are multicyclic structures that differ from one another not only in...
s, and sterol
Sterol
Sterols, also known as steroid alcohols, are a subgroup of the steroids and an important class of organic molecules. They occur naturally in plants, animals, and fungi, with the most familiar type of animal sterol being cholesterol...
s. It is sometimes also referred to as Farnesyl diphosphate (FDP).
It is the immediate precursor of squalene
Squalene
Squalene is a natural organic compound originally obtained for commercial purposes primarily from shark liver oil, though plant sources are used as well, including amaranth seed, rice bran, wheat germ, and olives. All plants and animals produce squalene, including humans...
(via the enzyme squalene synthase), dehydrodolichol diphosphate (a precursor of dolichol
Dolichol
Dolichol refers to any of a group of long-chain mostly unsaturated organic compounds that are made up of varying numbers of isoprene units terminating in an α-saturated isoprenoid group, containing an alcohol functional group.-Functions:...
), and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. In plants it is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls....
(GGPP).
Biosynthesis
Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (a prenyl transferase) catalyzes sequential condensation reactions of dimethylallyl pyrophosphateDimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate product of both mevalonic acid pathway and DOXP/MEP pathway. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and exists in virtually all life forms...
with 2 units of 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form farnesyl pyrophosphate.
- Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate reacts with 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form geranyl pyrophosphateGeranyl pyrophosphateGeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, cholesterol, terpenes and terpenoids....
:
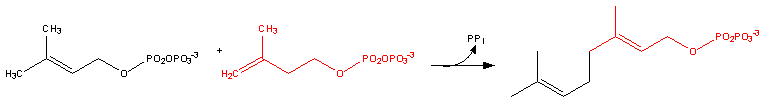
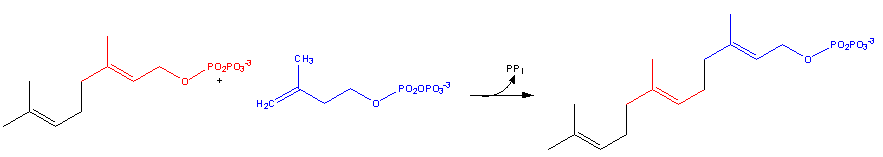
- Geranyl pyrophosphate itself reacts with 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate to form farnesyl pyrophosphate

Related compounds
- FarneseneFarneseneThe term farnesene refers to a set of six closely related chemical compounds which all are sesquiterpenes. α-Farnesene and β-farnesene are isomers, differing by the location of one double bond. α-Farnesene is 3,7,11-trimethyl-1,3,6,10-dodecatetraene and β-farnesene is...
- FarnesolFarnesolFarnesol is a natural organic compound which is an acyclic sesquiterpene alcohol found as a colorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, but miscible with oils...
- Geranyl pyrophosphateGeranyl pyrophosphateGeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of farnesyl pyrophosphate, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate, cholesterol, terpenes and terpenoids....
- Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphateGeranylgeranyl pyrophosphateGeranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. In plants it is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls....

