Familial dysautonomia
Encyclopedia
Familial dysautonomia is a disorder of the autonomic nervous system
which affects the development and survival of sensory, sympathetic and some parasympathetic neurons in the autonomic and sensory nervous system
resulting in variable symptoms including: insensitivity to pain, inability to produce tears, poor growth, and labile blood pressure (episodic hypertension and postural hypotension). People with FD have frequent vomiting crises, pneumonia, problems with speech and movement, difficulty swallowing, inappropriate perception of heat, pain, and taste, as well as unstable blood pressure and gastrointestinal dysmotility. FD does not affect intelligence. Originally reported by Conrad Milton Riley and Richard Lawrence Day in 1949, FD is one example of a group of disorders known as hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies HSAN. All HSAN are characterized by widespread sensory dysfunction and variable autonomic dysfunction caused by incomplete development of sensory and autonomic neurons. The disorders are believed to be genetically distinct from each other.
fashion. Both parents must be carriers in order for a child to be affected. The carrier frequency in Jewish individuals of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) ancestry is about 1/30, while the carrier frequency in non-Jewish individuals is about 1/3000. If both parents are carriers, there is a one in four, or 25%, chance with each pregnancy for an affected child. Genetic counseling
and genetic testing
is recommended for families who may be carriers of familial dysautonomia.
Worldwide, there have been approximately 600 diagnoses recorded since discovery of the disease, with approximately 350 of them still living.
gene on chromosome 9, which encodes for the IKAP protein (IkB kinase complex associated protein). There have been three mutations in IKBKAP identified in individuals with FD. The most common FD-causing mutation occurs in intron
20 of the donor gene. Conversion of T-->C in intron 20 of the donor gene resulted in shift splicing that generates an IKAP transcript lacking exon
20. Translation of this mRNA results in a truncated protein lacking all of the amino acids encoded in exons 20-37. Another less common mutation is a G-->C conversion resulting in one amino acid mutation in 696, where Proline
substitutes normal Arginine
. The decreased amount of functional IKAP protein in cells causes Familial Dysautonomia.
Symptoms in an older child with FD might include:
 A clinical diagnosis of FD is supported by a constellation of criteria:
A clinical diagnosis of FD is supported by a constellation of criteria:
is examined with a designed probe specific to the known mutations. The accuracy of the test is above 99%. Dr. Anat Blumenfeld
of the Hadasah Medical center in Jerusalem identified chromosome number 9 as the responsible chromosome.
pattern, which means 2 copies of the gene in each cell are altered. If both parents are shown to be carriers by genetic testing, there is a 25% chance that the child will produce FD. Prenatal diagnosis for pregnancies at increased risk for FD by amniocentesis
(for 14–17 weeks) or chorionic villus sampling
(for 10–11 weeks) is possible.
one at New York University Hospital and one at the Hadassah Hospital in Israel
.
One is being planned for the San Francisco area.
The survival rate and quality of life has increased since the mid 80's mostly due to greater understanding of the most dangerous symptoms.
At present, FD patients can be expected to function independently if treatment is begun early and major disabilities avoided.
A major issue has been Aspiration Pneumonias, where food or regurgitated stomach content would be aspirated into the lungs causing infections. Fundoplications
(by preventing regurgitation) and gastrostomy tubes (to provide non oral nutrition) have reduced the frequency of hospitalization.
Other issues which can be treated include FD Crises, Scoliosis
, and various eye conditions due to limited or no tears.
An FD crisis is the body's loss of control of various Autonomic nervous system
functions including blood pressure, heartrate, and body temperature. Both short term and chronic periodic high or low blood pressure have consequences and medication is used to stabilize blood pressure.
 Although the FD-causing gene has been identified and it seems to have tissue specific expression, there is no definitive treatment at present.
Although the FD-causing gene has been identified and it seems to have tissue specific expression, there is no definitive treatment at present.
Treatment of FD remains preventative, symptomatic and supportive. FD does not express itself in a consistent manner. The type and severity of symptoms displayed vary among patients and even at different ages on the same patients. So patients should have specialized individual treatment plans. Medications are used to control vomiting, eye dryness, and blood pressure
. There are some commonly needed treatments including:
There is no cure for this genetic disorder.
in the setting of central nervous system degeneration have a generally poor long-term prognosis
. Death can occur from pneumonia
, acute respiratory failure, or sudden cardiopulmonary arrest in such patients.
Educate parents and patients regarding daily eye care and early warning signs of corneal problems as well as use of punctual cautery. This education has resulted in decreased corneal scarring and need for more aggressive surgical measures such as tarsorrhaphy
, conjunctival flaps, and corneal transplants.
and Massachusetts General Hospital
simultaneously reported finding the genetic mutation that causes FD, a discovery that opens the door to many diagnostic and treatment possibilities.
Despite that it probably would not happen in the near future, some expect that stem-cell therapy will result. Eventually, treatment could be given in utero.
While that may be years ahead, genetic screening became available around April 2001, enabling Ashkenazi Jews to find out if they are carriers. Screening organization Dor Yeshorim
offers testing as part of its panel, which also includes Tay-Sachs disease
and cystic fibrosis
.
In the meantime more research into treatments are being funded by the foundations that exist. These foundations are organized and run by parents of those with FD. There is no governmental support beyond recognizing those diagnosed with FD as eligible for certain programs.
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
which affects the development and survival of sensory, sympathetic and some parasympathetic neurons in the autonomic and sensory nervous system
Nervous system
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
resulting in variable symptoms including: insensitivity to pain, inability to produce tears, poor growth, and labile blood pressure (episodic hypertension and postural hypotension). People with FD have frequent vomiting crises, pneumonia, problems with speech and movement, difficulty swallowing, inappropriate perception of heat, pain, and taste, as well as unstable blood pressure and gastrointestinal dysmotility. FD does not affect intelligence. Originally reported by Conrad Milton Riley and Richard Lawrence Day in 1949, FD is one example of a group of disorders known as hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies HSAN. All HSAN are characterized by widespread sensory dysfunction and variable autonomic dysfunction caused by incomplete development of sensory and autonomic neurons. The disorders are believed to be genetically distinct from each other.
Incidence
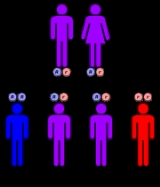
Familial dysautonomia is seen almost exclusively in Ashkenazi Jews and is inherited in an autosomal recessiveRecessive
In genetics, the term "recessive gene" refers to an allele that causes a phenotype that is only seen in a homozygous genotype and never in a heterozygous genotype. Every person has two copies of every gene on autosomal chromosomes, one from mother and one from father...
fashion. Both parents must be carriers in order for a child to be affected. The carrier frequency in Jewish individuals of Eastern European (Ashkenazi) ancestry is about 1/30, while the carrier frequency in non-Jewish individuals is about 1/3000. If both parents are carriers, there is a one in four, or 25%, chance with each pregnancy for an affected child. Genetic counseling
Genetic counseling
Genetic counseling or traveling is the process by which patients or relatives, at risk of an inherited disorder, are advised of the consequences and nature of the disorder, the probability of developing or transmitting it, and the options open to them in management and family planning...
and genetic testing
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is among the newest and most sophisticated of techniques used to test for genetic disorders which involves direct examination of the DNA molecule itself. Other genetic tests include biochemical tests for such gene products as enzymes and other proteins and for microscopic...
is recommended for families who may be carriers of familial dysautonomia.
Worldwide, there have been approximately 600 diagnoses recorded since discovery of the disease, with approximately 350 of them still living.
Etiology
Familial Dysautonomia, is the result of mutations in IKBKAPIKBKAP
IKBKAP is a human gene that provides instructions to make the IKAP protein, which is found in a variety of cells throughout the body, including brain cells...
gene on chromosome 9, which encodes for the IKAP protein (IkB kinase complex associated protein). There have been three mutations in IKBKAP identified in individuals with FD. The most common FD-causing mutation occurs in intron
Intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is removed by RNA splicing to generate the final mature RNA product of a gene. The term intron refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene, and the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. Sequences that are joined together in the final...
20 of the donor gene. Conversion of T-->C in intron 20 of the donor gene resulted in shift splicing that generates an IKAP transcript lacking exon
Exon
An exon is a nucleic acid sequence that is represented in the mature form of an RNA molecule either after portions of a precursor RNA have been removed by cis-splicing or when two or more precursor RNA molecules have been ligated by trans-splicing. The mature RNA molecule can be a messenger RNA...
20. Translation of this mRNA results in a truncated protein lacking all of the amino acids encoded in exons 20-37. Another less common mutation is a G-->C conversion resulting in one amino acid mutation in 696, where Proline
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
substitutes normal Arginine
Arginine
Arginine is an α-amino acid. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that codify for arginine during...
. The decreased amount of functional IKAP protein in cells causes Familial Dysautonomia.
Symptoms
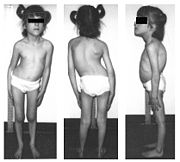
Symptoms displayed by a baby with FD might include:- The most distinctive clinical feature is absence of overflow tears with emotional crying after age 7 months. This symptom can manifest less dramatically as persistent bilateral eye irritation.
- High prevalence of breech presentation
- Weak or absent suck and poor tone
- Poor suck and misdirected swallowing
- Red blotching of skin
Symptoms in an older child with FD might include:
- Delayed speech and walking
- Unsteady gait
- Spinal curvature
- Corneal abrasionCorneal abrasionCorneal abrasion is a medical condition involving the loss of the surface epithelial layer of the eye's cornea.-Symptoms and signs:Symptoms of corneal abrasion include pain, photophobia, a foreign-body sensation, excessive squinting, and a reflex production of tears...
- Less perception in pain or temperature with nervous systemNervous systemThe nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
. - Poor growth
- Erratic or unstable blood pressureBlood pressureBlood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
. - Red puffy hands
- Dysautonomia crisis: constellation of symptoms response to physical and emotional stress; usually accompanied by vomitingVomitingVomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
, increased heart rate, increase in blood pressureBlood pressureBlood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
, sweatingSweatingPerspiration is the production of a fluid consisting primarily of water as well as various dissolved solids , that is excreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals...
, droolingDroolingDrooling is when saliva flows outside the mouth...
, blotching of the skin and a negative change in personality.
Clinical Diagnosis

- Parents of Ashkenazi Jewish Background
- No fungiform papillae on the tongue
- Decreased deep tendon reflexes
- Lack of an axon flare following intradermal histamine
- No overflow tears with emotional crying
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing is performed on a small sample of blood from the tested individual. The DNADNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
is examined with a designed probe specific to the known mutations. The accuracy of the test is above 99%. Dr. Anat Blumenfeld
Anat Blumenfeld
Dr. Anat Blumenfeld is an Israeli research biochemist at Hadassah Medical Center in Jerusalem. She discovered a chromosome responsible for the serious disease Familial dysautonomia which affects the nerves of fetuses...
of the Hadasah Medical center in Jerusalem identified chromosome number 9 as the responsible chromosome.
Prenatal Testing
Familial Dysautonomia is inherited in an autosomal recessiveRecessive
In genetics, the term "recessive gene" refers to an allele that causes a phenotype that is only seen in a homozygous genotype and never in a heterozygous genotype. Every person has two copies of every gene on autosomal chromosomes, one from mother and one from father...
pattern, which means 2 copies of the gene in each cell are altered. If both parents are shown to be carriers by genetic testing, there is a 25% chance that the child will produce FD. Prenatal diagnosis for pregnancies at increased risk for FD by amniocentesis
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections, in which a small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is sampled from the amnion or amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus, and the fetal DNA is examined for...
(for 14–17 weeks) or chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling
Chorionic villus sampling , sometimes misspelled "chorionic villous sampling", is a form of prenatal diagnosis to determine chromosomal or genetic disorders in the fetus. It entails sampling of the chorionic villus and testing it...
(for 10–11 weeks) is possible.
Treatment and treatment locations
There currently is no cure for FD and death occurs in 50% of affected individuals by age 30. There are only two treatment centers,one at New York University Hospital and one at the Hadassah Hospital in Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
.
One is being planned for the San Francisco area.
The survival rate and quality of life has increased since the mid 80's mostly due to greater understanding of the most dangerous symptoms.
At present, FD patients can be expected to function independently if treatment is begun early and major disabilities avoided.
A major issue has been Aspiration Pneumonias, where food or regurgitated stomach content would be aspirated into the lungs causing infections. Fundoplications
Nissen fundoplication
Nissen fundoplication is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and hiatus hernia. In GERD it is usually performed when medical therapy has failed, but with paraesophageal hiatus hernia, it is the first-line procedure...
(by preventing regurgitation) and gastrostomy tubes (to provide non oral nutrition) have reduced the frequency of hospitalization.
Other issues which can be treated include FD Crises, Scoliosis
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition in which a person's spine is curved from side to side. Although it is a complex three-dimensional deformity, on an X-ray, viewed from the rear, the spine of an individual with scoliosis may look more like an "S" or a "C" than a straight line...
, and various eye conditions due to limited or no tears.
An FD crisis is the body's loss of control of various Autonomic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system functioning largely below the level of consciousness, and controls visceral functions. The ANS affects heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils,...
functions including blood pressure, heartrate, and body temperature. Both short term and chronic periodic high or low blood pressure have consequences and medication is used to stabilize blood pressure.
Treatment of Manifestations

Treatment of FD remains preventative, symptomatic and supportive. FD does not express itself in a consistent manner. The type and severity of symptoms displayed vary among patients and even at different ages on the same patients. So patients should have specialized individual treatment plans. Medications are used to control vomiting, eye dryness, and blood pressure
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
. There are some commonly needed treatments including:
- Artificial tears: using eye drop containing artificial tear solutions (methylcellulose)
- Feeding: Maintenance of adequate nutrition, avoidance of aspiration; thickened formula and different shaped nipples are used for baby.
- Daily chest physiotherapy (nebulization, bronchodilators, and postural drainage): for Chronic lung disease from recurrent aspiration pneumoniaPneumoniaPneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
- Special drug management of autonomic manifestations such as vomiting: intravenous or rectal diazepamDiazepamDiazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
(0.2 mg/kg q3h) and rectal chloral hydrate (30 mg/kg q6h) - Protecting the child from injury (coping with decreased taste, temperature and pain perception)
- Combating orthostatic hypotensionOrthostatic hypotensionOrthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, orthostasis, and colloquially as head rush or dizzy spell, is a form of hypotension in which a person's blood pressure suddenly falls when the person stands up or stretches. The decrease is typically greater than 20/10 mm Hg, and may be...
: hydration, leg exercise, frequent small meals, a high-salt diet, and drugs such as fludrocortisoneFludrocortisoneFludrocortisone is a synthetic corticosteroid with moderate glucocorticoid potency and much greater mineralocorticoid potency. The brand name in the U.S. and Canada is Florinef.-Uses:...
. - Treatment of orthopedic problems (tibial torsion and spinal curvature)
- Compensating for labile blood pressures
There is no cure for this genetic disorder.
Therapies under investigation
It is noted that in cell lines derived from heterozygous carriers of FD who display a normal phenotype, there are decreased levels of the wild-type IKAP transcript and also functional IKAP protein respectively. This would suggest that increasing the amount of the wild-type IKAP transcript may improve the manifestation in patients with FD.Prognosis
The outlook for patients with FD depends on the particular diagnostic category. Patients with chronic, progressive, generalized dysautonomiaDysautonomia
Dysautonomia is a broad term that describes any disease or malfunction of the autonomic nervous system. This includes postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome , inappropriate sinus tachycardia , vasovagal syncope, mitral valve prolapse dysautonomia, pure autonomic failure, neurocardiogenic...
in the setting of central nervous system degeneration have a generally poor long-term prognosis
Prognosis
Prognosis is a medical term to describe the likely outcome of an illness.When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock will die within 28 days" can be made with some confidence, because...
. Death can occur from pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
, acute respiratory failure, or sudden cardiopulmonary arrest in such patients.
Educate parents and patients regarding daily eye care and early warning signs of corneal problems as well as use of punctual cautery. This education has resulted in decreased corneal scarring and need for more aggressive surgical measures such as tarsorrhaphy
Tarsorrhaphy
Tarsorrhaphy is a surgical procedure in which the eyelids are partially sewn together to narrow the opening .It may be done to protect the cornea in cases of corneal exposure or after corneal graft surgery.-External links:*...
, conjunctival flaps, and corneal transplants.
Future
In January 2001, researchers at Fordham UniversityFordham University
Fordham University is a private, nonprofit, coeducational research university in the United States, with three campuses in and around New York City. It was founded by the Roman Catholic Diocese of New York in 1841 as St...
and Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital is a teaching hospital and biomedical research facility in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts...
simultaneously reported finding the genetic mutation that causes FD, a discovery that opens the door to many diagnostic and treatment possibilities.
Despite that it probably would not happen in the near future, some expect that stem-cell therapy will result. Eventually, treatment could be given in utero.
While that may be years ahead, genetic screening became available around April 2001, enabling Ashkenazi Jews to find out if they are carriers. Screening organization Dor Yeshorim
Dor Yeshorim
Dor Yeshorim , also called Committee for Prevention of Genetic Diseases, is an organization that offers genetic screening to members of the worldwide Jewish community...
offers testing as part of its panel, which also includes Tay-Sachs disease
Tay-Sachs disease
Tay–Sachs disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder...
and cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a recessive genetic disease affecting most critically the lungs, and also the pancreas, liver, and intestine...
.
In the meantime more research into treatments are being funded by the foundations that exist. These foundations are organized and run by parents of those with FD. There is no governmental support beyond recognizing those diagnosed with FD as eligible for certain programs.
See also
- Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathyHereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathyHereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy or hereditary sensory neuropathy is a condition used to describe any of the types of this disease which inhibit sensation.They are less common than Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease....
(HSAN)- Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosisCongenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosisCongenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis is an extremely rare inherited disorder of the nervous system which prevents the sensation of pain, heat, cold, or any real nerve-related sensations ; however, patients can still feel pressure. CIPA is the fourth type of hereditary sensory and...
(CIPA), HSAN Type IV
- Congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis
- Congenital insensitivity to painCongenital insensitivity to painCongenital insensitivity to pain , also known as congenital analgesia, is one or more rare conditions where a person cannot feel physical pain...
- DysautonomiaDysautonomiaDysautonomia is a broad term that describes any disease or malfunction of the autonomic nervous system. This includes postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome , inappropriate sinus tachycardia , vasovagal syncope, mitral valve prolapse dysautonomia, pure autonomic failure, neurocardiogenic...
- Medical genetics of Ashkenazi Jews
External links
Support organizations
- Cure FD Foundation; a non profit organization supporting research at Fordham University for a cure for Familial Dysautonomia
- Dysautonomia Foundation, Inc.— a non-profit organization supporting medical research and treatment for those afflicted with Familial Dysautonomia
- Familial Dysautonomia Hope Foundation
- Familial Dysautonomia NOW FDNOW.org
- National Dysautonomia Research Foundation
- Kids of Courage — a non-profit organizing trips and camps with special facilities for children with Familial Dysautonomia (see Kids of CourageKids of CourageKids of Courage is a non-profit charity based in the United States. The organization specializes in medically supervised trips for children and young adults with serious medical diagnoses....
)

