
Factorization lemma
Encyclopedia
In measure theory, the factorization lemma allows us to express a function f with another function T if f is measurable with respect to T. An application of this is regression analysis
.
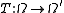 be a function of a set
be a function of a set 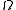 in a measure space
in a measure space 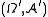 and let
and let 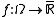 be a scalar function on
be a scalar function on 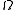 . Then
. Then 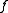 is measurable with respect to the σ-algebra
is measurable with respect to the σ-algebra 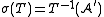 generated by
generated by 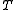 in
in 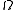 if and only if there exists a measurable function
if and only if there exists a measurable function 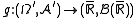 such that
such that 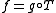 , where
, where 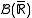 denotes the Borel set
denotes the Borel set
of the real numbers. If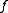 only takes finite values, then
only takes finite values, then 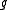 also only takes finite values.
also only takes finite values.
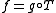 , then f is
, then f is 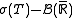 measurable because it is the composition of a
measurable because it is the composition of a 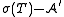 and of a
and of a 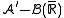 measurable function. The proof of the converse falls into four parts: (1)f is a step function
measurable function. The proof of the converse falls into four parts: (1)f is a step function
, (2)f is a positive function, (3) f is any scalar function, (4) f only takes finite values.
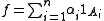 is a step function, i.e.
is a step function, i.e. 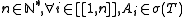 and
and 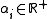 . As T is a measurable function, for all i, there exists
. As T is a measurable function, for all i, there exists 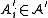 such that
such that 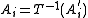 .
. 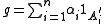 fulfills the requirements.
fulfills the requirements.
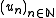 of step functions. For each of these, by (1), there exists
of step functions. For each of these, by (1), there exists 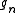 such that
such that 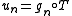 . The function
. The function 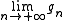 fulfils the requirements.
fulfils the requirements.
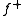 and a negative part
and a negative part 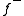 . We can then find
. We can then find 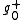 and
and 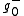 such that
such that 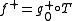 and
and 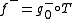 . The problem is that the difference
. The problem is that the difference 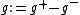 is not defined on the set
is not defined on the set 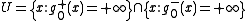 . Fortunately,
. Fortunately, 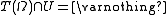 because
because 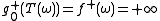 always implies
always implies 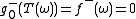
We define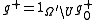 and
and 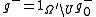 .
. 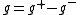 fulfils the requirements.
fulfils the requirements.
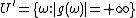 . Then
. Then 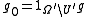 fulfils the requirements because
fulfils the requirements because 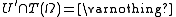 .
.
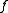 is not scalar, but takes values in a different measurable space, such as
is not scalar, but takes values in a different measurable space, such as 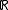 with its trivial σ-algebra (the empty set, and the whole real line) instead of
with its trivial σ-algebra (the empty set, and the whole real line) instead of 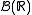 , then the lemma becomes false (as the restrictions on
, then the lemma becomes false (as the restrictions on 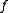 are much weaker).
are much weaker).
Regression analysis
In statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
.
Theorem
Let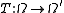 be a function of a set
be a function of a set 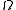 in a measure space
in a measure space 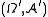 and let
and let 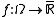 be a scalar function on
be a scalar function on 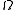 . Then
. Then 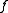 is measurable with respect to the σ-algebra
is measurable with respect to the σ-algebra 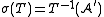 generated by
generated by 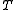 in
in 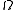 if and only if there exists a measurable function
if and only if there exists a measurable function 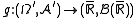 such that
such that 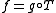 , where
, where 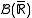 denotes the Borel set
denotes the Borel setBorel set
In mathematics, a Borel set is any set in a topological space that can be formed from open sets through the operations of countable union, countable intersection, and relative complement...
of the real numbers. If
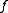 only takes finite values, then
only takes finite values, then 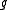 also only takes finite values.
also only takes finite values.Proof
First, if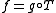 , then f is
, then f is 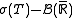 measurable because it is the composition of a
measurable because it is the composition of a 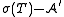 and of a
and of a 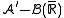 measurable function. The proof of the converse falls into four parts: (1)f is a step function
measurable function. The proof of the converse falls into four parts: (1)f is a step functionStep function
In mathematics, a function on the real numbers is called a step function if it can be written as a finite linear combination of indicator functions of intervals...
, (2)f is a positive function, (3) f is any scalar function, (4) f only takes finite values.
f is a step function
Suppose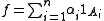 is a step function, i.e.
is a step function, i.e. 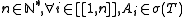 and
and 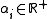 . As T is a measurable function, for all i, there exists
. As T is a measurable function, for all i, there exists 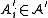 such that
such that 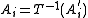 .
. 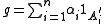 fulfills the requirements.
fulfills the requirements.f takes only positive values
If f takes only positive values, it is the limit of a sequence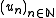 of step functions. For each of these, by (1), there exists
of step functions. For each of these, by (1), there exists 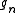 such that
such that 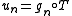 . The function
. The function 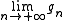 fulfils the requirements.
fulfils the requirements.General case
We can decompose f in a positive part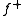 and a negative part
and a negative part 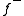 . We can then find
. We can then find 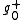 and
and 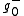 such that
such that 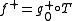 and
and 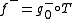 . The problem is that the difference
. The problem is that the difference 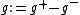 is not defined on the set
is not defined on the set 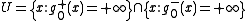 . Fortunately,
. Fortunately, 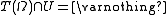 because
because 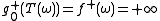 always implies
always implies 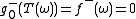
We define
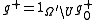 and
and 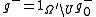 .
. 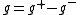 fulfils the requirements.
fulfils the requirements.f takes finite values only
If f takes finite values only, we will show that g also only takes finite values. Let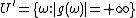 . Then
. Then 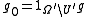 fulfils the requirements because
fulfils the requirements because 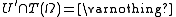 .
.Importance of the measure space
If the function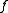 is not scalar, but takes values in a different measurable space, such as
is not scalar, but takes values in a different measurable space, such as  with its trivial σ-algebra (the empty set, and the whole real line) instead of
with its trivial σ-algebra (the empty set, and the whole real line) instead of 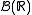 , then the lemma becomes false (as the restrictions on
, then the lemma becomes false (as the restrictions on 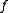 are much weaker).
are much weaker).

