Facial artery
Encyclopedia
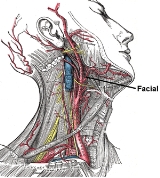
The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery
that supplies structures of the superficial face.
a little above the lingual artery
and, sheltered by the ramus of the mandible, passes obliquely up beneath the digastric and stylohyoid muscles, over which it arches to enter a groove on the posterior surface of the submandibular gland
.
It then curves upward over the body of the mandible at the antero-inferior angle of the masseter; passes forward and upward across the cheek to the angle of the mouth, then ascends along the side of the nose, and ends at the medial commissure of the eye, under the name of the angular artery
.
This vessel, both in the neck and on the face, is remarkably tortuous: in the former situation, to accommodate itself to the movements of the pharynx
in deglutition; and in the latter, to the movements of the mandible, lips
, and cheeks.
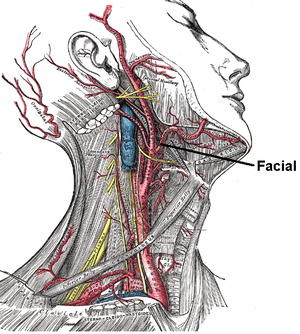
, but superficial to the hypoglossal nerve
.
It lies upon the middle pharyngeal constrictor and the superior pharyngeal constrictor, the latter of which separates it, at the summit of its arch, from the lower and back part of the tonsil.
On the face, where it passes over the body of the mandible, it is comparatively superficial, lying immediately beneath the dilators of the mouth. In its course over the face, it is covered by the integument, the fat of the cheek, and, near the angle of the mouth, by the platysma, risorius
, and zygomaticus major. It rests on the buccinator
and levator anguli oris
, and passes either over or under the infraorbital head of the levator labii superioris
.
The anterior facial vein
lies lateral/posterior to the artery, and takes a more direct course across the face, where it is separated from the artery by a considerable interval. In the neck it lies superficial to the artery.
The branches of the facial nerve
cross the artery from behind forward.
The facial artery anastomoses with (among others) the dorsal nasal artery
of the internal carotid artery
.
External carotid artery
In human anatomy, the external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it bifurcates into the external and internal carotid artery.-Course:...
that supplies structures of the superficial face.
Structure
The facial artery arises in the carotid triangle from the external carotid arteryExternal carotid artery
In human anatomy, the external carotid artery is a major artery of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery when it bifurcates into the external and internal carotid artery.-Course:...
a little above the lingual artery
Lingual artery
The lingual artery arises from the external carotid between the superior thyroid and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue.-Path:It first runs obliquely upward and medialward to the greater cornu of the hyoid bone....
and, sheltered by the ramus of the mandible, passes obliquely up beneath the digastric and stylohyoid muscles, over which it arches to enter a groove on the posterior surface of the submandibular gland
Submandibular gland
The paired submandibular glands are salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In humans, they account for 70% of the salivary volume and weigh about 15 grams. Unstimulated in humans, the percentage contribution to whole saliva; ~25% Parotid, Submandibular and Sublingual ~ 67% and...
.
It then curves upward over the body of the mandible at the antero-inferior angle of the masseter; passes forward and upward across the cheek to the angle of the mouth, then ascends along the side of the nose, and ends at the medial commissure of the eye, under the name of the angular artery
Angular artery
The angular artery is the terminal part of the facial artery; it ascends to the medial angle of the eye's orbit, imbedded in the fibers of the angular head of the Quadratus labii superioris, and accompanied by the angular vein....
.
This vessel, both in the neck and on the face, is remarkably tortuous: in the former situation, to accommodate itself to the movements of the pharynx
Pharynx
The human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately posterior to the mouth and nasal cavity, and anterior to the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx , the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx...
in deglutition; and in the latter, to the movements of the mandible, lips
Lip
Lips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans and many animals. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech...
, and cheeks.

Relations
In the neck, its origin is superficial, being covered by the integument, platysma, and fascia; it then passes beneath the digastric and stylohyoid muscles and part of the submandibular glandSubmandibular gland
The paired submandibular glands are salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In humans, they account for 70% of the salivary volume and weigh about 15 grams. Unstimulated in humans, the percentage contribution to whole saliva; ~25% Parotid, Submandibular and Sublingual ~ 67% and...
, but superficial to the hypoglossal nerve
Hypoglossal nerve
The hypoglossal nerve is the twelfth cranial nerve , leading to the tongue. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus and emerges from the medulla oblongata in the preolivary sulcus separating the olive and the pyramid. It then passes through the hypoglossal canal...
.
It lies upon the middle pharyngeal constrictor and the superior pharyngeal constrictor, the latter of which separates it, at the summit of its arch, from the lower and back part of the tonsil.
On the face, where it passes over the body of the mandible, it is comparatively superficial, lying immediately beneath the dilators of the mouth. In its course over the face, it is covered by the integument, the fat of the cheek, and, near the angle of the mouth, by the platysma, risorius
Risorius
The risorius is a muscle of facial expression which arises in the fascia over the parotid gland and, passing horizontally forward, superficial to the platysma, inserts onto the skin at the angle of the mouth...
, and zygomaticus major. It rests on the buccinator
Buccinator
The buccinator muscle is a muscle at the side of the face.Buccinator may also refer to:* Buccinator artery * Buccinator lymph node* Buccinator nerve * An ancient Roman buccina player...
and levator anguli oris
Levator anguli oris
The levator anguli oris is a facial muscle of the mouth arising from the canine fossa, immediately below the infraorbital foramen....
, and passes either over or under the infraorbital head of the levator labii superioris
Levator labii superioris
The levator labii superioris is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone....
.
The anterior facial vein
Anterior facial vein
The anterior facial vein commences at the side of the root of the nose and is a direct continuation of the angular vein where it also receives a small nasal branch. It lies behind the facial artery and follows a less tortuous course...
lies lateral/posterior to the artery, and takes a more direct course across the face, where it is separated from the artery by a considerable interval. In the neck it lies superficial to the artery.
The branches of the facial nerve
Facial nerve
The facial nerve is the seventh of twelve paired cranial nerves. It emerges from the brainstem between the pons and the medulla, and controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue and oral cavity...
cross the artery from behind forward.
The facial artery anastomoses with (among others) the dorsal nasal artery
Dorsal nasal artery
The dorsal nasal artery is an artery of the head. It is one of the two terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery.-Course:...
of the internal carotid artery
Internal carotid artery
In human anatomy, the internal carotid arteries are two major arteries, one on each side of the head and neck. They arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid artery, and they supply the brain....
.
Branches
The branches of the facial artery are:- cervical
- Ascending palatine arteryAscending palatine arteryThe ascending palatine artery is an artery in the head that branches off the facial artery and runs up the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle.-Structure:...
- Tonsillar branch
- Submental arterySubmental arteryThe submental artery is a branch of the facial artery that runs on the underside of the chin.-Course:The submental artery is the largest of the cervical branches of the facial artery, given off just as that vessel leaves the submandibular gland: it runs forward upon the mylohyoid, just below the...
- Glandular branchesGlandular branches of facial arteryThe glandular branches of the facial artery consist of three or four large vessels, which supply the submaxillary gland, some being prolonged to the neighboring muscles, lymph glands, and integument....
- Ascending palatine artery
- facial
- Inferior labial arteryInferior labial arteryThe Iinferior labial artery arises near the angle of the mouth; it passes upward and forward beneath the Triangularis and, penetrating the Orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane.It supplies the labial glands, the...
- Superior labial arterySuperior labial arteryThe superior labial artery is larger and more egregious than the inferior labial artery.It follows a similar course along the edge of the upper lip, lying between the mucous membrane and the Orbicularis oris, and anastomoses with the artery of the opposite side.It supplies the upper lip, and gives...
- Lateral nasal branchLateral nasal branch of facial arteryThe lateral nasal branch of facial artery is derived from the facial artery as that vessel ascends along the side of the nose.-Supplies:...
to nasalis muscleNasalis muscleThe nasalis is a sphincter-like muscle of the nose whose function is to compress the nasal cartilage.It consists of two parts, transverse and alar:... - Angular arteryAngular arteryThe angular artery is the terminal part of the facial artery; it ascends to the medial angle of the eye's orbit, imbedded in the fibers of the angular head of the Quadratus labii superioris, and accompanied by the angular vein....
- the terminal branch
- Inferior labial artery
Muscles
Muscles supplied by the facial artery include:- buccinatorBuccinatorThe buccinator muscle is a muscle at the side of the face.Buccinator may also refer to:* Buccinator artery * Buccinator lymph node* Buccinator nerve * An ancient Roman buccina player...
- levator anguli orisLevator anguli orisThe levator anguli oris is a facial muscle of the mouth arising from the canine fossa, immediately below the infraorbital foramen....
- levator labii superiorisLevator labii superiorisThe levator labii superioris is a muscle of the human body used in facial expression. It is a broad sheet, the origin of which extends from the side of the nose to the zygomatic bone....
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
- levator veli palatiniLevator veli palatiniThe levator veli palatini is the elevator muscle of the soft palate in the human body. During swallowing, it contracts, elevating the soft palate to help prevent food from entering the nasopharynx...
- masseter
- mentalisMentalisThe Mentalis is a paired central muscle of the lower lip, situated at the tip of the chin. It raises and pushes up the lower lip, causing wrinkling of the chin, as in doubt or displeasure...
- mylohyoidMylohyoidMylohyoid can refer to:* Mylohyoid muscle* Mylohyoid line* Mylohyoid nerve* Mylohyoid branch of inferior alveolar artery* Mylohyoid groove...
- nasalisNasalis muscleThe nasalis is a sphincter-like muscle of the nose whose function is to compress the nasal cartilage.It consists of two parts, transverse and alar:...
- palatoglossus
- palatopharyngeus
- platysma
- procerus
- risoriusRisoriusThe risorius is a muscle of facial expression which arises in the fascia over the parotid gland and, passing horizontally forward, superficial to the platysma, inserts onto the skin at the angle of the mouth...
- styloglossusStyloglossusThe Styloglossus, the shortest and smallest of the three styloid muscles, arises from the anterior and lateral surfaces of the styloid process, near its apex, and from the stylomandibular ligament....
- transverseTransverse planeThe transverse plane is an imaginary plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts. It is perpendicular to the coronal and sagittal planes....
portion of the nasalisNasalisNasalis may refer to:* Proboscis Monkey , the only monkey in the genus Nasalis* Nasalis muscle...

