
FAD-AMP lyase (cyclizing)
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, a FAD-AMP lyase (cyclizing) is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Hence, this enzyme has one substrate
, FAD
, and two products
, AMP
and riboflavin cyclic-4',5'-phosphate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyase
s, specifically the class of phosphorus-oxygen lyases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is FAD AMP-lyase (riboflavin-cyclic-4',5'-phosphate-forming). Other names in common use include FMN cyclase, and FAD AMP-lyase (cyclic-FMN-forming).
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- FAD
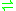 AMP + riboflavin cyclic-4',5'-phosphate
AMP + riboflavin cyclic-4',5'-phosphate
Hence, this enzyme has one substrate
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
, FAD
FAD
In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide is a redox cofactor involved in several important reactions in metabolism. FAD can exist in two different redox states, which it converts between by accepting or donating electrons. The molecule consists of a riboflavin moiety bound to the phosphate...
, and two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
, AMP
Adenosine monophosphate
Adenosine monophosphate , also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide that is used as a monomer in RNA. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine...
and riboflavin cyclic-4',5'-phosphate.
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyase
Lyase
In biochemistry, a lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis and oxidation, often forming a new double bond or a new ring structure...
s, specifically the class of phosphorus-oxygen lyases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is FAD AMP-lyase (riboflavin-cyclic-4',5'-phosphate-forming). Other names in common use include FMN cyclase, and FAD AMP-lyase (cyclic-FMN-forming).

