
Exaltation (astrology)
Encyclopedia
Astrology
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
, exaltation is one of the five essential dignities
Essential dignity
In astrology, essential dignity is the strength of a planet or point's zodiac position, judged only by its position by sign and degree, or its essence--what the pre-eminent 17th-century astrologer William Lilly called "the strength, fortitude or debility of the Planets [or] significators." In other...
of a planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
. Each of the seven traditional planets has its exaltation in one zodiac
Zodiac
In astronomy, the zodiac is a circle of twelve 30° divisions of celestial longitude which are centred upon the ecliptic: the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year...
sign
Astrological sign
Astrological signs represent twelve equal segments or divisions of the zodiac. According to astrology, celestial phenomena reflect or govern human activity on the principle of "as above, so below", so that the twelve signs are held to represent twelve basic personality types or characteristic modes...
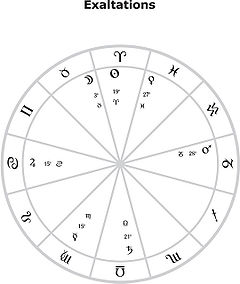
. The positions are:
- SunSun (astrology)The sun is considered a very important part of astrology. It, as well as the Moon, are the most important of the astrological planets, and the two of them are often referred to as the luminaries. In Greek mythology the sun was represented by Apollo, the god of light, and Helios, the god of the sun...
: 19th degree of AriesAries (astrology)Aries is the first astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the zero degree and the 29th degree of celestial longitude. The Sun enters Aries when it reaches the northern vernal equinox, which is usually on March 21 each year, and remains in this sign until around April 20...
(i.e., 18°00' - 18°59') - MoonMoon (astrology)The Moon is the Earth's companion satellite. The Moon is large enough for its gravity to affect the Earth, stabilising its orbit and producing the regular ebb and flow of the tides. The Moon is also familiar to us for its different phases, waxing and waning in appearance in an unchanging cycle...
: 3rd degree of TaurusTaurus (astrology)Taurus is the second astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the 30th and 59th degree of celestial longitude. Generally, the Sun transits this area of the zodiac between April 21 to May 21 each year... - Mercury: 15th degee of VirgoVirgo (astrology)Virgo is the sixth astrological sign in the Zodiac, which spans the zodiac between the 150th and 179th degree of celestial longitude. Generally, the Sun transits this area of the zodiac between August 23 to September 22 each year...
- Venus: 27th degree of Pisces
- Mars: 28th degree of Capricorn
- Jupiter: 15th degree of CancerCancer (astrology)Cancer is the fourth astrological sign in the Zodiac. It is considered a water sign and one of four cardinal signs. Cancer is ruled by the Moon. Individuals born when the Sun is in this sign are considered Cancerian individuals...
- Saturn: 21st degree of LibraLibra (astrology)Libra is the seventh astrological sign in the Zodiac, originating from the constellation of Libra. In astrology, Libra is considered a "masculine", positive sign. It is also considered an air sign and is one of four cardinal signs...
Exaltations have also been attributed to the north node
Lunar node
The lunar nodes are the orbital nodes of the Moon, that is, the points where the orbit of the Moon crosses the ecliptic . The ascending node is where the moon crosses to the north of the ecliptic...
(3rd degree of Gemini) and the south node
Lunar node
The lunar nodes are the orbital nodes of the Moon, that is, the points where the orbit of the Moon crosses the ecliptic . The ascending node is where the moon crosses to the north of the ecliptic...
(3rd degree of Sagittarius). These positions are listed in astrological texts of the early medieval Arabic period, such as Albiruni's
Al-Biruni
Abū al-Rayḥān Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad al-BīrūnīArabic spelling. . The intermediate form Abū Rayḥān al-Bīrūnī is often used in academic literature...
11th century Book of Instruction in the elements of the art of astrology. Whilst modern Vedic astrologers place significance on the exaltation positions of the nodes, the western astrological tradition transmitted through medieval Europe demonstrates little use of them in practice traditionally and currently. Albiruni also points out that, in contradiction to the Greeks and Persians, the Hindu astrologers of his period disagreed upon the degree positions of the Sun, Jupiter and Saturn, and did not recognize the exaltations of the nodes - a principle he described himself as being "quite proper".
The exaltations are one of the most ancient astrological factors still in use. They are used in ancient Mesopotamian astrology
Babylonian astrology
In Babylon as well as in Assyria as a direct offshoot of Babylonian culture, astrology takes its place in theofficial cult as one of the two chief means at the disposal of the priests for ascertaining the will and intention of the gods, the other being through the inspection of the liver of the...
from an era which pre-dates the known use of the zodiac (using reference to constellation positions which shows correspondence with those later attributed to zodiac degrees). Francesca Rochberg
Francesca Rochberg
Francesca Rochberg is an American Assyriologist, historian of science, and Catherine and William L. Magistretti Distinguished Professor of Near Eastern Studies at University of California, Berkeley....
has pointed out that since the system is found in the tradition of Enuma anu enlil
Enuma anu enlil
Enuma Anu Enlil is a major series of 68 or 70 tablets dealing with Babylonian astrology...
, its roots may extend into the second millennium BCE.
Why the Babylonians considered these placements to be dignified is not known. Although many speculations concerning the reasoning behind it have been put forth over the centuries, there are, as Robert Hand has said, still anomalies that are almost impossible to explain with any consistency, such as the exaltation of vigorous Mars in cold Capricorn. The Western sidereal astrologer
Sidereal astrology
Sidereal and tropical are astronomical terms used to describe two different definitions of a "year". They are also used as terms for two systems of ecliptic coordinates used in astrology....
, Cyril Fagan
Cyril Fagan
Cyril Fagan was an astrologer, who claimed historical use of sidereal astrology in the west and established it as a separate field from tropical astrology....
, has speculated that the planets all rose heliacally
Heliacal rising
The heliacal rising of a star occurs when it first becomes visible above the eastern horizon for a brief moment just before sunrise, after a period of time when it had not been visible....
at these degrees in the year of the erection of an important temple to the Babylonian god Nabu
Nabu
Nabu is the Assyrian and Babylonian god of wisdom and writing, worshipped by Babylonians as the son of Marduk and his consort, Sarpanitum, and as the grandson of Ea. Nabu's consort was Tashmetum....
in the year 786 BC, but this is still very speculative.
Since in Hellenistic astrology and in its cognate Vedic astrology aspects were generally recognised from sign to sign, it is uncertain whether the distance of a planet from the exact degree of exaltation had much significance. However, the degree itself was used by ancient astrologers; for example, the exact degree of exaltation of each of the luminaries
Luminary
The luminaries were what traditional astrologers called the two astrological "planets" which were the brightest and most important objects in the heavens, that is, the Sun and the Moon.- Origins :...
(the Sun and Moon) was used in the formula for the Hellenistic Lot of Exaltation
Arabian Parts
In astrology, the Arabian/Arabic parts or lots are constructed points based on mathematical calculations of three horoscopic entities such as planets or angles...
.
In later Medieval astrology, influenced by the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
and Byzantine
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
, a hierarchy of all five essential dignities was favored, in which the most important dignity was that of the domicile ruler, followed in importance by exaltation. Medieval astrologers assigned numerical values to each dignity in the hierarchy, and these were tabulated to provide a rough statistical mode of comparison (see Essential dignity
Essential dignity
In astrology, essential dignity is the strength of a planet or point's zodiac position, judged only by its position by sign and degree, or its essence--what the pre-eminent 17th-century astrologer William Lilly called "the strength, fortitude or debility of the Planets [or] significators." In other...
.) These weighted valuations are still in use today by astrologers.
After the discovery of the three outer planets--Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto--modern astrologers speculated on possible domicile and exaltation rulerships for these planets. It was suggested, for example, that Neptune was the "true" domicile ruler of Pisces (usurping one of Jupiter's two domicile rulerships). The ancient system was complex and symmetrical, making no allowance for additional, unseen planets, and it is difficult to include them in traditional techniques. Most modern astrologers have therefore abandoned attempts to assign exaltations to these newer planets.
The sign position directly opposite a planet's sign of exaltation is considered to be its fall
Astrological fall
In astrology, the fall of a planet is the sign which is opposite that planet's sign of exaltation. Originally, in Greek, the sign of a planet's "fall" were called tapeinoma, which means "humbled" or "dejected" or "depressed," whereas "exalted," in Greek was hyposoma, which means "risen in...
. As the exaltation is a place of strength and for the planet, the fall is a position of weakness.

