
Euler force
Encyclopedia
In classical mechanics
, the Euler acceleration (named for Leonhard Euler
), also known as azimuthal acceleration or transverse acceleration is an acceleration
that appears when a non-uniformly rotating reference frame
is used for analysis of motion and there is variation in the angular velocity
of the reference frame
's axes. This article is restricted to a frame of reference that rotates about a fixed axis.
The Euler force is a fictitious force
on a body that is related to the Euler acceleration by F = m a , where a is the Euler acceleration and m is the mass of the body.
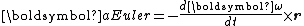
where:
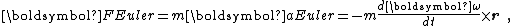
where:
Classical mechanics
In physics, classical mechanics is one of the two major sub-fields of mechanics, which is concerned with the set of physical laws describing the motion of bodies under the action of a system of forces...
, the Euler acceleration (named for Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler was a pioneering Swiss mathematician and physicist. He made important discoveries in fields as diverse as infinitesimal calculus and graph theory. He also introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, particularly for mathematical analysis, such as the notion...
), also known as azimuthal acceleration or transverse acceleration is an acceleration
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
that appears when a non-uniformly rotating reference frame
Rotating reference frame
A rotating frame of reference is a special case of a non-inertial reference frame that is rotating relative to an inertial reference frame. An everyday example of a rotating reference frame is the surface of the Earth. A rotating frame of reference is a special case of a non-inertial reference...
is used for analysis of motion and there is variation in the angular velocity
Angular velocity
In physics, the angular velocity is a vector quantity which specifies the angular speed of an object and the axis about which the object is rotating. The SI unit of angular velocity is radians per second, although it may be measured in other units such as degrees per second, revolutions per...
of the reference frame
Frame of reference
A frame of reference in physics, may refer to a coordinate system or set of axes within which to measure the position, orientation, and other properties of objects in it, or it may refer to an observational reference frame tied to the state of motion of an observer.It may also refer to both an...
's axes. This article is restricted to a frame of reference that rotates about a fixed axis.
The Euler force is a fictitious force
Fictitious force
A fictitious force, also called a pseudo force, d'Alembert force or inertial force, is an apparent force that acts on all masses in a non-inertial frame of reference, such as a rotating reference frame....
on a body that is related to the Euler acceleration by F = m a , where a is the Euler acceleration and m is the mass of the body.
Euler acceleration
The direction and magnitude of the Euler acceleration is given by: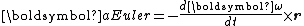
where:
- ω is the angular velocity of rotation of the reference frame;
- r is the vector position of the point where the acceleration is measured relative to the axis of the rotation.
Euler force
Using the above acceleration, the Euler force is: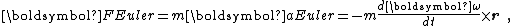
where:
- m is the massMassMass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of the object upon which this fictitious forceFictitious forceA fictitious force, also called a pseudo force, d'Alembert force or inertial force, is an apparent force that acts on all masses in a non-inertial frame of reference, such as a rotating reference frame....
is exerted.
See also
- Fictitious forceFictitious forceA fictitious force, also called a pseudo force, d'Alembert force or inertial force, is an apparent force that acts on all masses in a non-inertial frame of reference, such as a rotating reference frame....
- Coriolis effectCoriolis effectIn physics, the Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the left of the motion of the object; in one with counter-clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the right...
- Centrifugal forceCentrifugal forceCentrifugal force can generally be any force directed outward relative to some origin. More particularly, in classical mechanics, the centrifugal force is an outward force which arises when describing the motion of objects in a rotating reference frame...
- Rotating reference frameRotating reference frameA rotating frame of reference is a special case of a non-inertial reference frame that is rotating relative to an inertial reference frame. An everyday example of a rotating reference frame is the surface of the Earth. A rotating frame of reference is a special case of a non-inertial reference...

