
Eta Andromedae
Encyclopedia
Eta Andromedae is a spectroscopic binary star
in the constellation
of Andromeda
. It consists of two G-type subgiant or giant star
s orbiting each other with a period of 115.7 days and has an overall apparent visual magnitude of approximately 4.403.
 Eta Andromedae was discovered to be a double-lined spectroscopic binary in a series of spectra taken in 1899 and 1900. Its orbit was computed in 1946 from spectroscopic observations. Because spectroscopy only reveals the radial velocity
Eta Andromedae was discovered to be a double-lined spectroscopic binary in a series of spectra taken in 1899 and 1900. Its orbit was computed in 1946 from spectroscopic observations. Because spectroscopy only reveals the radial velocity
of a star towards or away from the viewer, such a computation does not determine all orbital elements
. In observations made from 1990 to 1992, Eta Andromedae was resolved interferometrically by the Mark III Stellar Interferometer
at Mount Wilson Observatory
, California
, United States
. This allowed a more complete orbit to be computed and, in 1993, published.
of apparent visual magnitude 11.5, BD+22°153B, visible 129.2 arcseconds away.
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
in the constellation
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
of Andromeda
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Andromeda, the princess in the Greek legend of Perseus who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus...
. It consists of two G-type subgiant or giant star
Giant star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main sequence star of the same surface temperature. Typically, giant stars have radii between 10 and 100 solar radii and luminosities between 10 and 1,000 times that of the Sun. Stars still more luminous than giants are...
s orbiting each other with a period of 115.7 days and has an overall apparent visual magnitude of approximately 4.403.
History

Radial velocity
Radial velocity is the velocity of an object in the direction of the line of sight . In astronomy, radial velocity most commonly refers to the spectroscopic radial velocity...
of a star towards or away from the viewer, such a computation does not determine all orbital elements
Orbital elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are generally considered in classical two-body systems, where a Kepler orbit is used...
. In observations made from 1990 to 1992, Eta Andromedae was resolved interferometrically by the Mark III Stellar Interferometer
Mark III Stellar Interferometer
The Mark III Stellar Interferometer was a long-baseline optical astronomical interferometer, located at the Mount Wilson Observatory, California, United States. It had a maximum baseline of 32 meters and operated in wavelengths between 450 and 800 nm...
at Mount Wilson Observatory
Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a 5,715 foot peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles...
, California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. This allowed a more complete orbit to be computed and, in 1993, published.
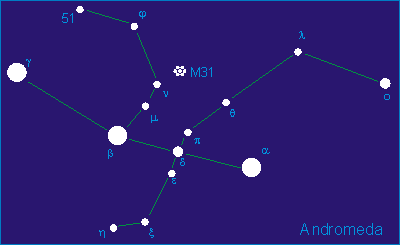
Location
This star's location in the constellation Andromeda can be seen in the following diagram:
Visual companion
The star has a visual companion starDouble star
In observational astronomy, a double star is a pair of stars that appear close to each other in the sky as seen from Earth when viewed through an optical telescope. This can happen either because the pair forms a binary star, i.e...
of apparent visual magnitude 11.5, BD+22°153B, visible 129.2 arcseconds away.

