Essential fructosuria
Encyclopedia
Essential fructosuria, also known as hepatic fructokinase deficiency or ketohexokinase deficiency, is a hereditary metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency in hepatic fructokinase
, leading to fructose
being excreted in the urine
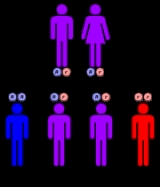
(-uria denotes "in the urine"). It is essentially a benign condition, as fructose cannot be broken down, so it is simply excreted in the urine. Inheritance is autosomal recessive
.
Essential fructosuria should not be confused with fructosemia, which denotes fructose in the blood (also known as hereditary fructose intolerance). Fructosemia is a very serious condition, as fructose is converted into fructose-1-phosphate, using up ATP and building up fructose-1-phosphate in the blood. This prevents proper release of glucose from glycogen, uses up free phosphate, and causes a rise in uric acid, leading to growth abnormalities and, in severe cases, coma.
Hepatic fructokinase
Hepatic fructokinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the phosphorylation of fructose to produce fructose-1-phosphate....
, leading to fructose
Fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a simple monosaccharide found in many plants. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. Fructose was discovered by French chemist Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut in 1847...
being excreted in the urine
Urine
Urine is a typically sterile liquid by-product of the body that is secreted by the kidneys through a process called urination and excreted through the urethra. Cellular metabolism generates numerous by-products, many rich in nitrogen, that require elimination from the bloodstream...
(-uria denotes "in the urine"). It is essentially a benign condition, as fructose cannot be broken down, so it is simply excreted in the urine. Inheritance is autosomal recessive
Recessive
In genetics, the term "recessive gene" refers to an allele that causes a phenotype that is only seen in a homozygous genotype and never in a heterozygous genotype. Every person has two copies of every gene on autosomal chromosomes, one from mother and one from father...
.
Essential fructosuria should not be confused with fructosemia, which denotes fructose in the blood (also known as hereditary fructose intolerance). Fructosemia is a very serious condition, as fructose is converted into fructose-1-phosphate, using up ATP and building up fructose-1-phosphate in the blood. This prevents proper release of glucose from glycogen, uses up free phosphate, and causes a rise in uric acid, leading to growth abnormalities and, in severe cases, coma.


