
Equivalent temperature
Encyclopedia
Equivalent temperature is the temperature of an air parcel from which all the water vapor has been extracted by an adiabatic process.
Air contains water vapor that has been evaporated into it from liquid sources (lakes, sea, etc...). The energy needed to do that has been taken from the air. Taking a volume of air at temperature
T and mixing ratio
of r , drying it by condensation will restitute energy to the airmass. This will depend on the latent heat
release as:
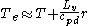
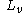 : latent heat
: latent heat
of evaporation
(2400 kJ/kg {at 25C} to 2600 kJ/kg {at -40C})
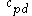 : specific heat at constant pressure for air (
: specific heat at constant pressure for air (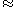 1004 J/(kg·K))
1004 J/(kg·K))
Tables exist for exact values of the last two coefficients.
Air contains water vapor that has been evaporated into it from liquid sources (lakes, sea, etc...). The energy needed to do that has been taken from the air. Taking a volume of air at temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
T and mixing ratio
Mixing ratio
In chemistry and physics, the dimensionless mixing ratio is defined as the abundance of one component of a mixture relative to that of all other components...
of r , drying it by condensation will restitute energy to the airmass. This will depend on the latent heat
Latent heat
Latent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a chemical substance or a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature. A typical example is a change of state of matter, meaning a phase transition such as the melting of ice or the boiling of water. The term was...
release as:
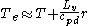
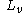 : latent heat
: latent heatLatent heat
Latent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a chemical substance or a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature. A typical example is a change of state of matter, meaning a phase transition such as the melting of ice or the boiling of water. The term was...
of evaporation
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
(2400 kJ/kg {at 25C} to 2600 kJ/kg {at -40C})
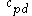 : specific heat at constant pressure for air (
: specific heat at constant pressure for air (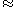 1004 J/(kg·K))
1004 J/(kg·K))Tables exist for exact values of the last two coefficients.

