
Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis
Encyclopedia
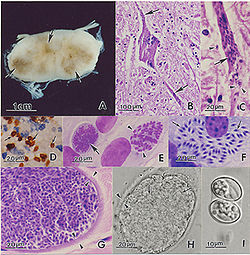
Protozoa
Protozoa are a diverse group of single-cells eukaryotic organisms, many of which are motile. Throughout history, protozoa have been defined as single-cell protists with animal-like behavior, e.g., movement...
l infection of the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
of horse
Horse
The horse is one of two extant subspecies of Equus ferus, or the wild horse. It is a single-hooved mammal belonging to the taxonomic family Equidae. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million years from a small multi-toed creature into the large, single-toed animal of today...
s.
History
EPM was discovered in the 1960s by Dr. Jim Rooney. The disease is considered rare, though recently, an increasing number of cases have been reported. Research at the University of KentuckyUniversity of Kentucky
The University of Kentucky, also known as UK, is a public co-educational university and is one of the state's two land-grant universities, located in Lexington, Kentucky...
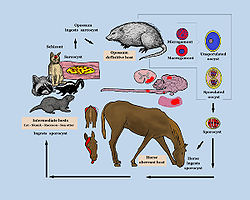
has labeled the opossum as the definitive host
Host (biology)
In biology, a host is an organism that harbors a parasite, or a mutual or commensal symbiont, typically providing nourishment and shelter. In botany, a host plant is one that supplies food resources and substrate for certain insects or other fauna...
of the disease.
Causes
Sarcocystis
Sarcocystis is a genus of protozoa. Species in this genus infect reptiles, birds and mammals. The name is dervived from Greek: sarx = flesh and kystis = bladder.There are about 130 recognised species in this genus...
neurona. In order to complete its life cycle this parasite needs two hosts, a definitive and an intermediate. In the laboratory, raccoon
Raccoon
Procyon is a genus of nocturnal mammals, comprising three species commonly known as raccoons, in the family Procyonidae. The most familiar species, the common raccoon , is often known simply as "the" raccoon, as the two other raccoon species in the genus are native only to the tropics and are...
s, cat
Cat
The cat , also known as the domestic cat or housecat to distinguish it from other felids and felines, is a small, usually furry, domesticated, carnivorous mammal that is valued by humans for its companionship and for its ability to hunt vermin and household pests...
s, armadillo
Armadillo
Armadillos are New World placental mammals, known for having a leathery armor shell. Dasypodidae is the only surviving family in the order Cingulata, part of the superorder Xenarthra along with the anteaters and sloths. The word armadillo is Spanish for "little armored one"...
s, skunk
Skunk
Skunks are mammals best known for their ability to secrete a liquid with a strong, foul odor. General appearance varies from species to species, from black-and-white to brown or cream colored. Skunks belong to the family Mephitidae and to the order Carnivora...
s, and sea otter
Sea Otter
The sea otter is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between 14 and 45 kg , making them the heaviest members of the weasel family, but among the smallest marine mammals...
s have been shown to be intermediate hosts. The opossum is the definitive host of the disease. Horses most commonly contract EPM from grazing or watering in areas where an opossum has recently defecated. However, horses cannot pass the disease among themselves. That is, one horse cannot contract the disease from another infected horse. The horse is the dead-end, or aberrant, host of the disease.
Symptoms
The neurologic signs that EPM causes are most commonly asymmetric incoordination (ataxiaAtaxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign and symptom that consists of gross lack of coordination of muscle movements. Ataxia is a non-specific clinical manifestation implying dysfunction of the parts of the nervous system that coordinate movement, such as the cerebellum...
), weakness and spasticity
Spasticity
Spasticity is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance in muscle tone involving hypertonia, which is also referred to as an unusual "tightness" of muscles...
, although they may mimic almost any neurologic disorder. Clinical signs among horses with EPM include a wide array of symptoms that may result from primary or secondary problems. Some of the signs cannot be distinguished from other problems, such as lameness, which can be attributed to many different causes. Airway abnormalities, such as laryngeal hemiplegia (paralyzed flaps), dorsal displacement of the soft palate
Soft palate
The soft palate is the soft tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone....
(snoring), or airway noise of undetermined origin may result from protozoa infecting the nerves which innervate the throat. Apparent lameness, particularly atypical lameness or slight gait asymmetry of the rear limbs are commonly caused by EPM. Focal muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy, or disuse atrophy, is defined as a decrease in the mass of the muscle; it can be a partial or complete wasting away of muscle. When a muscle atrophies, this leads to muscle weakness, since the ability to exert force is related to mass...
, or even generalized muscle atrophy or loss of condition may result. Secondary signs also occur with neurologic disease. Upward fixation of the patella (locking up of the stifle joint
Stifle joint
The stifle joint is a complex joint in the hind limbs of quadruped mammals such as the sheep, horse or dog. It is the equivalent joint to the human knee...
) is among the most common findings among horses with neurologic disease. Another common side effect of EPM is back soreness, which can be severe. The actual method by which the Sarcocystis neurona infects a horse is still unknown, however it is thought to preferentially infect leukocytes (white blood cells) in order to cross the blood brain barrier.
Treatment and prevention
This disease is curable if caught soon enough and treated with antiprotozoal drugs. There are currently three antiprotozoal treatments available: potentiated sulfonamide medications such as ReBalance, Marquis (ponazurilPonazuril
Ponazuril , sold by the Bayer Corporation under the trade name Marquis, is a drug currently approved for the treatment of equine protozoal myeloencephalitis in horses, caused by Sarcocystis neurona. More recently, veterinarians have been preparing a formulary version of the medication for use in...
), and Navigator.
Control of this disease includes a recently released vaccine
Vaccine
A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins...
against the parasite and control of opossums in an area. The vaccine, however, has only been conditionally approved by the USDA until efficacy tests are available.

