
Enstrophy
Encyclopedia
In fluid dynamics
, the enstrophy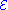 can be described as the integral of the square of the vorticity
can be described as the integral of the square of the vorticity  given a velocity field
given a velocity field 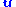 as,
as,
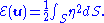
Here, since the curl gives a vector field
in 2-dimensions (vortex
) corresponding to the vector valued velocity
component in the Navier-Stokes equations
, we can integrate its square over a surface S to retrieve a continuous linear operator
, known as a current. This equation is however somewhat misleading. Here we have chosen a simplified version of the enstrophy derived from the incompressibility condition, which reduces to vanishing divergence,

More generally, when not restricted to the incompressible condition, the enstrophy may be computed by:
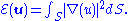
The enstrophy can be interpreted as another type of potential
density
(ie. see probability density
); or, more concretely, the quantity directly related to the kinetic energy
in the flow model that corresponds to dissipation
effects in the fluid. It is particularly useful in the study of turbulent flows
, and is often identified in the study of thruster
s as well as the field of flame theory.
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, the enstrophy
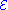 can be described as the integral of the square of the vorticity
can be described as the integral of the square of the vorticity  given a velocity field
given a velocity field  as,
as,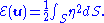
Here, since the curl gives a vector field
Vector field
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignmentof a vector to each point in a subset of Euclidean space. A vector field in the plane for instance can be visualized as an arrow, with a given magnitude and direction, attached to each point in the plane...
in 2-dimensions (vortex
Vortex
A vortex is a spinning, often turbulent,flow of fluid. Any spiral motion with closed streamlines is vortex flow. The motion of the fluid swirling rapidly around a center is called a vortex...
) corresponding to the vector valued velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
component in the Navier-Stokes equations
Navier-Stokes equations
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations, named after Claude-Louis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, describe the motion of fluid substances. These equations arise from applying Newton's second law to fluid motion, together with the assumption that the fluid stress is the sum of a diffusing viscous...
, we can integrate its square over a surface S to retrieve a continuous linear operator
Continuous linear operator
In functional analysis and related areas of mathematics, a continuous linear operator or continuous linear mapping is a continuous linear transformation between topological vector spaces....
, known as a current. This equation is however somewhat misleading. Here we have chosen a simplified version of the enstrophy derived from the incompressibility condition, which reduces to vanishing divergence,

More generally, when not restricted to the incompressible condition, the enstrophy may be computed by:
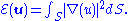
The enstrophy can be interpreted as another type of potential
Potential
*In linguistics, the potential mood*The mathematical study of potentials is known as potential theory; it is the study of harmonic functions on manifolds...
density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
(ie. see probability density
Probability density
Probability density may refer to:* Probability density function in probability theory* The product of the probability amplitude with its complex conjugate in quantum mechanics...
); or, more concretely, the quantity directly related to the kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
in the flow model that corresponds to dissipation
Dissipation
In physics, dissipation embodies the concept of a dynamical system where important mechanical models, such as waves or oscillations, lose energy over time, typically from friction or turbulence. The lost energy converts into heat, which raises the temperature of the system. Such systems are called...
effects in the fluid. It is particularly useful in the study of turbulent flows
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
, and is often identified in the study of thruster
Thruster
A thruster is a small propulsive device used by spacecraft and watercraft for station keeping, attitude control, in the reaction control system, or long duration low thrust acceleration.-Spacecraft thrusters:...
s as well as the field of flame theory.

