
Enol ether
Encyclopedia
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
with an alkoxy substituent
Substituent
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a substituent is an atom or group of atoms substituted in place of a hydrogen atom on the parent chain of a hydrocarbon...
. The general structure is
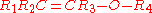 with R an alkyl or an aryl
with R an alkyl or an arylAryl
In the context of organic molecules, aryl refers to any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, be it phenyl, naphthyl, thienyl, indolyl, etc....
group. Enol ethers and enamine
Enamine
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine followed by loss of H2O.The word "enamine" is derived from the affix en-, used as the suffix of alkene, and the root amine. This can be compared with enol, which is a functional group...
s are so-called activated alkenes or electron rich alkenes because the oxygen atom donates electrons to the double bond by forming a resonance structure with the corresponding oxonium ion
Oxonium ion
The oxonium ion in chemistry is any oxygen cation with three bonds. The simplest oxonium ion is the hydronium ion H3O+. Another oxonium ion frequently encountered in organic chemistry is obtained by protonation or alkylation of a carbonyl group e.g...
. This property makes them reactive substrates in certain organic reaction
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
s such as the Diels-Alder reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. The reaction can proceed even if some of the atoms in the newly formed ring are not carbon...
. An enol ether can be considered the ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
of the corresponding enolate, hence the name. Two simple enol ethers are methyl vinyl ether
Methyl vinyl ether
Methyl vinyl ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula C3H6O. It is the simplest chemical that contains both an alkene group and an alkyl group with an ether linkage. The compound can be made by reaction of acetylene and methanol in presence of a base. The alkene portion of the...
and 2,3-dihydrofuran
2,3-Dihydrofuran
2,3-Dihydrofuran is a heterocyclic compound. It is one of the simplest enol ethers....
.

