
Encephalization
Encyclopedia
Encephalization is defined as the amount of brain
mass exceeding that related to an animal's total body mass
. Quantifying an animal's encephalization has been argued to be directly related to that animal's level of intelligence
. Aristotle wrote in 335 B.C. "Of all the animals, man has the brain largest in proportion to his size." Also, in 1871, Charles Darwin
wrote in his book The Descent of Man: "No one, I presume, doubts that the large proportion which the size of man's brain bears to his body, compared to the same proportion in the gorilla or orang, is closely connected with his mental powers."
In 2004, Dennis Bramble and Daniel Lieberman proposed that early Homo
were scavengers that used stone tools to harvest meat off carcasses and to open bones. They proposed that humans specialized in long-distance running to compete with other scavengers in reaching carcasses. It has been suggested that such an adaptation ensured a food supply that made large brains
possible.
More encephalized species tend to have longer spinal shock
duration.
Encephalization may also refer to the tendency for a species toward larger brains through evolutionary time. Anthropological studies indicate that bipedalism preceded encephalization in the human evolutionary lineage after divergence from the chimpanzee
lineage. Compared to the chimpanzee brain, the human brain is larger and certain brain regions have been particularly altered during human evolution. Most brain growth of chimpanzees happens before birth while most human brain growth happens after birth.
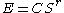
In Snell's equation of simple allometry "E" is the weight of the brain, "C" is the cephalization factor and "S" is body weight and "r" is the exponential constant. The exponential constant for primates is 0.28 and either 0.56 or 0.66 for mammals in general.
The "Encephalization Quotient" (EQ) is the ratio of "C" over the expected value for "C" of an animal of given weight "S".
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
mass exceeding that related to an animal's total body mass
Brain to body mass ratio
Brain-to-body mass ratio, also known as the brain to body weight ratio, is the ratio of brain weight to body weight, which is hypothesised to be a rough estimate of the intelligence of an animal. A more complex measurement, encephalization quotient, takes into account allometric effects of widely...
. Quantifying an animal's encephalization has been argued to be directly related to that animal's level of intelligence
Intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in different ways, including the abilities for abstract thought, understanding, communication, reasoning, learning, planning, emotional intelligence and problem solving....
. Aristotle wrote in 335 B.C. "Of all the animals, man has the brain largest in proportion to his size." Also, in 1871, Charles Darwin
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
wrote in his book The Descent of Man: "No one, I presume, doubts that the large proportion which the size of man's brain bears to his body, compared to the same proportion in the gorilla or orang, is closely connected with his mental powers."
In 2004, Dennis Bramble and Daniel Lieberman proposed that early Homo
Homo (genus)
Homo is the genus that includes modern humans and species closely related to them. The genus is estimated to be about 2.3 to 2.4 million years old, evolving from australopithecine ancestors with the appearance of Homo habilis....
were scavengers that used stone tools to harvest meat off carcasses and to open bones. They proposed that humans specialized in long-distance running to compete with other scavengers in reaching carcasses. It has been suggested that such an adaptation ensured a food supply that made large brains
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
possible.
More encephalized species tend to have longer spinal shock
Spinal shock
Spinal shock was first defined by Whytt in 1750 as a loss of sensation accompanied by motor paralysis with initial loss but gradual recovery of reflexes, following a spinal cord injury – most often a complete transection. Reflexes in the spinal cord caudal to the SCI are depressed or absent ,...
duration.
Encephalization may also refer to the tendency for a species toward larger brains through evolutionary time. Anthropological studies indicate that bipedalism preceded encephalization in the human evolutionary lineage after divergence from the chimpanzee
Chimpanzee
Chimpanzee, sometimes colloquially chimp, is the common name for the two extant species of ape in the genus Pan. The Congo River forms the boundary between the native habitat of the two species:...
lineage. Compared to the chimpanzee brain, the human brain is larger and certain brain regions have been particularly altered during human evolution. Most brain growth of chimpanzees happens before birth while most human brain growth happens after birth.
Encephalization quotient
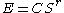
In Snell's equation of simple allometry "E" is the weight of the brain, "C" is the cephalization factor and "S" is body weight and "r" is the exponential constant. The exponential constant for primates is 0.28 and either 0.56 or 0.66 for mammals in general.
The "Encephalization Quotient" (EQ) is the ratio of "C" over the expected value for "C" of an animal of given weight "S".
| Species | EQ | Species | EQ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 7.44 | Cat | 1.00 |
| Dolphin | 5.31 | Horse | 0.86 |
| Chimpanzee | 2.49 | Sheep | 0.81 |
| Rhesus Monkey | 2.09 | Mouse | 0.50 |
| Elephant | 1.87 | Rat | 0.40 |
| Whale | 1.76 | Rabbit | 0.40 |
| Dog | 1.17 | ||
See also
- Evolutionary biology
- CephalizationCephalizationCephalization is considered an evolutionary trend, whereby nervous tissue, over many generations, becomes concentrated toward one end of an organism. This process eventually produces a head region with sensory organs....
- Human evolutionHuman evolutionHuman evolution refers to the evolutionary history of the genus Homo, including the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species and as a unique category of hominids and mammals...
- Human brainHuman brainThe human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
- Aquatic ape

