Emulsion polymerization
Overview
Radical polymerization
Free radical polymerization is a method of polymerization by which a polymer forms by the successive addition of free radical building blocks. Free radicals can be formed via a number of different mechanisms usually involving separate initiator molecules...
that usually starts with an emulsion
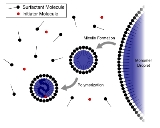
Emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible . Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms colloid and emulsion are sometimes used interchangeably, emulsion is used when both the dispersed and the...
incorporating water, monomer
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
, and surfactant
Surfactant
Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension of a liquid, the interfacial tension between two liquids, or that between a liquid and a solid...
. The most common type of emulsion polymerization is an oil-in-water emulsion, in which droplets of monomer (the oil) are emulsified (with surfactant
Surfactant
Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension of a liquid, the interfacial tension between two liquids, or that between a liquid and a solid...
s) in a continuous phase of water. Water-soluble polymers, such as certain polyvinyl alcohol
Polyvinyl alcohol
Polyvinyl alcohol is a water-soluble synthetic polymer .-Properties:...
s or hydroxyethyl cellulose
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
s, can also be used to act as emulsifiers/stabilizers. The name "emulsion polymerization" is a misnomer that arises from a historical misconception.

