
Egg-and-dart
Encyclopedia
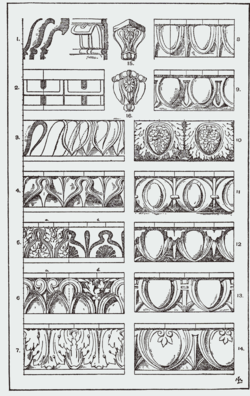
Ornament (architecture)
In architecture and decorative art, ornament is a decoration used to embellish parts of a building or object. Large figurative elements such as monumental sculpture and their equivalents in decorative art are excluded from the term; most ornament does not include human figures, and if present they...
device often carved in wood, stone, or plaster quarter-round ovolo
Ovolo
Ovolo in architecture, is a convex molding known also as the echinus, which in Classical architecture was invariably carved with the egg-and-dart ornament. The molding is called a quarter-round by woodworkers...
moulding
Molding (decorative)
Molding or moulding is a strip of material with various profiles used to cover transitions between surfaces or for decoration. It is traditionally made from solid milled wood or plaster but may be made from plastic or reformed wood...
s, consisting of an egg-shaped object alternating with an element shaped like an arrow
Arrow
An arrow is a shafted projectile that is shot with a bow. It predates recorded history and is common to most cultures.An arrow usually consists of a shaft with an arrowhead attached to the front end, with fletchings and a nock at the other.- History:...
, anchor
Anchor
An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, that is used to connect a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the vessel from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ancora, which itself comes from the Greek ἄγκυρα .Anchors can either be temporary or permanent...
or dart
Dart (missile)
Darts are missile weapons, designed to fly such that a sharp, often weighted point will strike first. They can be distinguished from javelins by fletching and a shaft that is shorter and/or more flexible, and from arrows by the fact that they are not of the right length to use with a normal...
. Egg-and-dart enrichment of the ovolo molding
Ovolo
Ovolo in architecture, is a convex molding known also as the echinus, which in Classical architecture was invariably carved with the egg-and-dart ornament. The molding is called a quarter-round by woodworkers...
of the Ionic capital
Ionic order
The Ionic order forms one of the three orders or organizational systems of classical architecture, the other two canonic orders being the Doric and the Corinthian...
is found in Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
architecture at the Erechtheion and was used by the Romans.

Motif (art)
In art, a motif is an element of a pattern, an image or part of one, or a theme. A motif may be repeated in a design or composition, often many times, or may just occur once in a work. A motif may be an element in the iconography of a particular subject or type of subject that is seen in other...
has been common in the classical architecture
Classical architecture
Classical architecture is a mode of architecture employing vocabulary derived in part from the Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity, enriched by classicizing architectural practice in Europe since the Renaissance...
of Europe since the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
.

