
Effect of taxes and subsidies on price
Encyclopedia
Tax
es and subsidies
change the price of goods and, as a result, the quantity consumed.
paid by the consumers (which is equal to the new market price), and decrease the price received by the sellers.
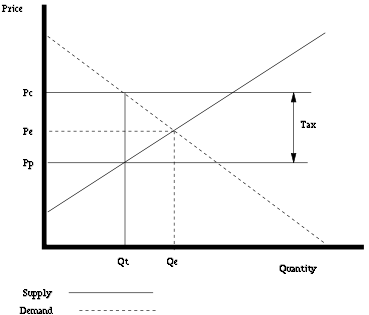
diagram. Without a tax, the equilibrium
price will be at Pe and the equilibrium quantity will be at Qe.
After a tax is imposed, the price consumers pay will shift to Pc and the price producers receive will shift to Pp. The consumers' price will be equal to the producers' price plus the cost of the tax. Since consumers will buy less at the higher consumer price (Pc) and producers will sell less at a lower producer price (Pp), the quantity sold will fall from Qe to Qt.
Tax
To tax is to impose a financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or the functional equivalent of a state such that failure to pay is punishable by law. Taxes are also imposed by many subnational entities...
es and subsidies
Subsidy
A subsidy is an assistance paid to a business or economic sector. Most subsidies are made by the government to producers or distributors in an industry to prevent the decline of that industry or an increase in the prices of its products or simply to encourage it to hire more labor A subsidy (also...
change the price of goods and, as a result, the quantity consumed.
Tax impact
A marginal tax on the sellers of a good will shift the supply curve to the left until the vertical distance between the two supply curves is equal to the per unit tax; when other things remain equal, this will increase the pricePrice
-Definition:In ordinary usage, price is the quantity of payment or compensation given by one party to another in return for goods or services.In modern economies, prices are generally expressed in units of some form of currency...
paid by the consumers (which is equal to the new market price), and decrease the price received by the sellers.
Subsidy impact
Marginal subsidies on production will shift the supply curve to the right until the vertical distance between the two supply curves is equal to the per unit subsidy; when other things remain equal, this will decrease price paid by the consumers (which is equal to the new market price) and increase the price received by the producers. Similarly, a marginal subsidy on consumption will shift the demand curve to the right; when other things remain equal, this will decrease the price paid by consumers and increase the price received by producers by the same amount as if the subsidy had been granted to producers. However, in this case, the new market price will be the price received by producers. The end result is that the lower price that consumers pay and the higher price that producers receive will be the same, regardless of how the subsidy is administered.Effect of elasticity
Depending on the price elasticities of demand and supply, who bears more of the tax or who receives more of the subsidy may differ. Where the supply curve is more inelastic than the demand curve, producers bear more of the tax and receive more of the subsidy than consumers as the difference between the price producers receive and the initial market price is greater than the difference borne by consumers. Where the demand curve is more inelastic than the supply curve, the consumers bear more of the tax and receive more of the subsidy as the difference between the price consumers pay and the initial market price is greater than the difference borne by producers.An illustration
The effect of this type of tax can be illustrated on a standard supply and demandSupply and demand
Supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers will equal the quantity supplied by producers , resulting in an...
diagram. Without a tax, the equilibrium
Economic equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a state of the world where economic forces are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. It is the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal...
price will be at Pe and the equilibrium quantity will be at Qe.
After a tax is imposed, the price consumers pay will shift to Pc and the price producers receive will shift to Pp. The consumers' price will be equal to the producers' price plus the cost of the tax. Since consumers will buy less at the higher consumer price (Pc) and producers will sell less at a lower producer price (Pp), the quantity sold will fall from Qe to Qt.


