
Eddy diffusion
Encyclopedia
Eddy diffusion, eddy dispersion, or turbulent
diffusion
is any diffusion
process by which substances are mixed in the atmosphere
or in any fluid system due to eddy motion. In another definition it is mixing that is caused by eddies
that can vary in size from the small Kolmogorov microscales
to subtropical gyre
s.
Because the microscopic processes responsible for atmospheric mixing are too complex to model in detail, atmospheric modelers generally treat atmospheric mixing as a macroscopic "eddy" diffusion process. In this approach, the diffusion rate at each pressure level is parameterized by a quantity known as the eddy diffusion coefficient, K (also sometimes called eddy diffusivity, with units of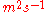 ).
).
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
is any diffusion
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
process by which substances are mixed in the atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
or in any fluid system due to eddy motion. In another definition it is mixing that is caused by eddies
Eddy (fluid dynamics)
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current created when the fluid flows past an obstacle. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object...
that can vary in size from the small Kolmogorov microscales
Kolmogorov microscales
Kolmogorov microscales are the smallest scales in turbulent flow. They are defined bywhere \epsilon is the average rate of energy dissipation per unit mass, and \nu is the kinematic viscosity of the fluid....
to subtropical gyre
Gyre
A gyre in oceanography is any large system of rotating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis Effect; planetary vorticity along with horizontal and vertical friction, which determine the circulation patterns from the wind curl...
s.
Because the microscopic processes responsible for atmospheric mixing are too complex to model in detail, atmospheric modelers generally treat atmospheric mixing as a macroscopic "eddy" diffusion process. In this approach, the diffusion rate at each pressure level is parameterized by a quantity known as the eddy diffusion coefficient, K (also sometimes called eddy diffusivity, with units of
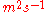 ).
).

