
EF-Tu
Encyclopedia
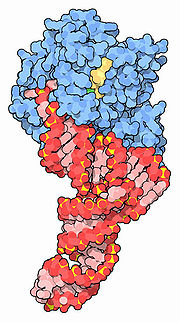
Prokaryotic elongation factors
In prokaryotes, three elongation factors are required for translation: EF-Tu, EF-Ts, and EF-G.*EF-Tu mediates the entry of the aminoacyl tRNA into a free site of the ribosome....
.
The prokaryotic factor EF-Tu mediates the entry of the aminoacyl-tRNA
Aminoacyl-tRNA
Aminoacyl-tRNA is tRNA to which its cognated amino acid is adhered. Its role is to deliver the amino acid to the ribosome where it will be incorporated into the polypeptide chain that is being produced...
into a free site of the ribosome
Ribosome
A ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
. EF-Tu functions by binding an aminoacylated, or charged, tRNA molecule in the cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
. This complex transiently enters the ribosome, with the tRNA anticodon domain associating with the mRNA codon in the ribosomal A site. If the codon-anticodon pairing is correct, EF-Tu hydrolyzes guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It can act as a substrate for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process...
(GTP) into guanosine diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate
Guanosine diphosphate, abbreviated GDP, is a nucleoside diphosphate. It is an ester of pyrophosphoric acid with the nucleoside guanosine. GDP consists of the pyrophosphate group, the pentose sugar ribose, and the nucleobase guanine....
(GDP) and inorganic phosphate, and changes in conformation to dissociate from the tRNA molecule. The aminoacyl-tRNA then fully enters the A site, where its amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
is brought near the P site's polypeptide and the ribosome catalyzes the covalent transfer of the amino acid onto the polypeptide.
EF-Tu contributes to translational accuracy in three ways. It delays GTP hydrolysis if the tRNA in the ribosome’s A site does not match the mRNA codon, thus preferentially increasing the likelihood for the incorrect tRNA to leave the ribosome. It also adds a second delay (regardless of tRNA matching) after freeing itself from tRNA, before the aminoacyl-tRNA fully enters the A site. This delay period is a second opportunity for incorrectly paired tRNA (and their bound amino acids) to move out of the A site before the incorrect amino acid is irreversibly added to the polypeptidic chain. A third mechanism is the less well understood function of EF-Tu to crudely check aminoacyl-tRNA associations and reject complexes where the amino acid is not bound to the correct tRNA coding for it.

