
Dynamization
Encyclopedia
In computer science
, Dynamization is the process of transforming a static data structure into a dynamic one. Although static data structures may provide very good functionality and fast queries, their utility is limited because of their inability to grow/shrink fast, thus making them inapplicable for the solution of dynamic problem
s, where the amount of the input data changes. Dynamization techniques provide uniform ways of creating dynamic data structures.
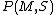 . Problem P is decomposable if the set S can be decomposed into subsets
. Problem P is decomposable if the set S can be decomposed into subsets  and there exist an operation
and there exist an operation 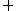 of result unification such that
of result unification such that 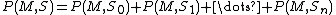 .
.
. For simplicity, binary system will be used in this article but any other base (as well as other possibilities such as Fibonacci number
s) can also be utilized.
If using the binary system, a set of elements is broken down into subsets of sizes with
elements is broken down into subsets of sizes with
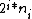
elements where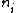 is the
is the  -th bit of
-th bit of  in binary. This means that if
in binary. This means that if  has
has 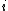 -th bit equal to 0, the corresponding set does not contain any elements. Each of the subset has the same property as the original static data structure. Operations performed on the new dynamic data structure may involve traversing
-th bit equal to 0, the corresponding set does not contain any elements. Each of the subset has the same property as the original static data structure. Operations performed on the new dynamic data structure may involve traversing 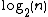 sets formed by decomposition. As a result, this will add
sets formed by decomposition. As a result, this will add 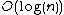 factor as opposed to the static data structure operations but will allow Insert/Delete operation to be added.
factor as opposed to the static data structure operations but will allow Insert/Delete operation to be added.
Kurt Mehlhorn
proved several equations for time complexity of operations on data structures dynamized according to this idea. Some of these equalities are listed.
If
 = time to build the static data structure
= time to build the static data structure
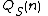 = time to query the static data structure
= time to query the static data structure
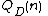 = time to query the dynamic data structure formed by decomposition
= time to query the dynamic data structure formed by decomposition
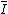 = amortized insertion time
= amortized insertion time
Then
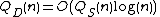

If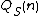 is at least polynomial
is at least polynomial
, then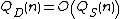 .
.
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, Dynamization is the process of transforming a static data structure into a dynamic one. Although static data structures may provide very good functionality and fast queries, their utility is limited because of their inability to grow/shrink fast, thus making them inapplicable for the solution of dynamic problem
Dynamic problem (algorithms)
Dynamic problems in computational complexity theory are problems stated in terms of the changing input data. In the most general form a problem in this category is usually stated as follows:...
s, where the amount of the input data changes. Dynamization techniques provide uniform ways of creating dynamic data structures.
Decomposable search problems
We define problem P of searching for the predicate M match in the set S as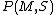 . Problem P is decomposable if the set S can be decomposed into subsets
. Problem P is decomposable if the set S can be decomposed into subsets  and there exist an operation
and there exist an operation 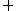 of result unification such that
of result unification such that 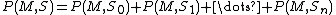 .
.Decomposition
Decomposition is a term used in computer science to break static data structures into smaller units of unequal size. The basic principle is the idea that any decimal number can be translated into a representation in any other base. For more details about the topic see Decomposition (computer science)Decomposition (computer science)
Decomposition in computer science, also known as factoring, refers to the process by which a complex problem or system is broken down into parts that are easier to conceive, understand, program, and maintain.- Overview :...
. For simplicity, binary system will be used in this article but any other base (as well as other possibilities such as Fibonacci number
Fibonacci number
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers are the numbers in the following integer sequence:0,\;1,\;1,\;2,\;3,\;5,\;8,\;13,\;21,\;34,\;55,\;89,\;144,\; \ldots\; ....
s) can also be utilized.
If using the binary system, a set of
 elements is broken down into subsets of sizes with
elements is broken down into subsets of sizes with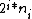
elements where
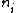 is the
is the  -th bit of
-th bit of  in binary. This means that if
in binary. This means that if  has
has 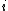 -th bit equal to 0, the corresponding set does not contain any elements. Each of the subset has the same property as the original static data structure. Operations performed on the new dynamic data structure may involve traversing
-th bit equal to 0, the corresponding set does not contain any elements. Each of the subset has the same property as the original static data structure. Operations performed on the new dynamic data structure may involve traversing 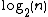 sets formed by decomposition. As a result, this will add
sets formed by decomposition. As a result, this will add 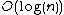 factor as opposed to the static data structure operations but will allow Insert/Delete operation to be added.
factor as opposed to the static data structure operations but will allow Insert/Delete operation to be added.Kurt Mehlhorn
Kurt Mehlhorn
Kurt Mehlhorn is a German computer scientist. He has been a vice president of the Max Planck Society and is director of the Max Planck Institute for Computer Science.-Education:...
proved several equations for time complexity of operations on data structures dynamized according to this idea. Some of these equalities are listed.
If
 = time to build the static data structure
= time to build the static data structure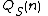 = time to query the static data structure
= time to query the static data structure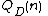 = time to query the dynamic data structure formed by decomposition
= time to query the dynamic data structure formed by decomposition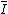 = amortized insertion time
= amortized insertion timeThen
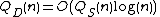

If
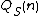 is at least polynomial
is at least polynomialPolynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is an expression of finite length constructed from variables and constants, using only the operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and non-negative integer exponents...
, then
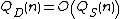 .
.
