
Dynamic structure factor
Encyclopedia
In condensed matter physics
, the dynamic structure factor is a mathematical function that contains information about inter-particle correlations and their time evolution. Experimentally, it can be accessed most directly by inelastic neutron scattering
.
The dynamic structure factor is most often denoted S(q,ω), where q (also k) is a wave vector (a wave number for isotropic materials), and ω a frequency (sometimes stated as energy,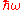 ). It is the spatial and temporal Fourier transform
). It is the spatial and temporal Fourier transform
of van Hove
's time-dependent pair correlation function G(r,t), whose Fourier transform
with respect to r, F(Q,t), is called the intermediate scattering function and can be measured by neutron spin echo
spectroscopy.
In an isotropic sample (with scalar r), G(r,t) is a time dependent radial distribution function
.
Condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics deals with the physical properties of condensed phases of matter. These properties appear when a number of atoms at the supramolecular and macromolecular scale interact strongly and adhere to each other or are otherwise highly concentrated in a system. The most familiar...
, the dynamic structure factor is a mathematical function that contains information about inter-particle correlations and their time evolution. Experimentally, it can be accessed most directly by inelastic neutron scattering
Inelastic neutron scattering
Inelastic neutron scattering is an experimental technique commonly used in condensed matter research to study atomic and molecular motion as well as magnetic and crystal field excitations....
.
The dynamic structure factor is most often denoted S(q,ω), where q (also k) is a wave vector (a wave number for isotropic materials), and ω a frequency (sometimes stated as energy,
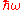 ). It is the spatial and temporal Fourier transform
). It is the spatial and temporal Fourier transformFourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
of van Hove
Léon Van Hove
Léon Van Hove was a Belgian physicist and a former Director General of CERN. He developed a scientific career spanning mathematics, solid state physics, elementary particle and nuclear physics to cosmology.-Biography:...
's time-dependent pair correlation function G(r,t), whose Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
with respect to r, F(Q,t), is called the intermediate scattering function and can be measured by neutron spin echo
Neutron spin echo
Neutron spin echo spectroscopy is an inelastic neutron scattering technique invented by Ferenc Mezei in the 1970's, and developed in collaboration with John Hayter.In recognition of his work and in other areas, Mezei was awarded the first in 1999....
spectroscopy.
In an isotropic sample (with scalar r), G(r,t) is a time dependent radial distribution function
Radial distribution function
In statistical mechanics, a radial distribution function , g, describes how the atomic density varies as a function of the distance from one particular atom....
.

