
Dynamic modulus
Encyclopedia
Dynamic modulus is the ratio of stress to strain under vibratory conditions (calculated from data obtained from either free or forced vibration tests, in shear, compression, or elongation). It is a property of viscoelastic materials.
where an oscillatory force (stress) is applied to a material and the resulting displacement (strain) is measured. http://las.perkinelmer.com/content/ApplicationNotes/APP_FilmsandCoatings.pdf
Stress and strain in a viscoelastic material can be represented using the following expressions:
where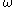 is frequency of strain oscillation,
is frequency of strain oscillation, is time,
is time,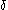 is phase lag between stress and strain.
is phase lag between stress and strain.
Similarly we also define shear storage and shear loss moduli,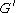 and
and 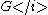 .
.
Complex variables can be used to express the moduli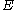 and
and 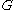 as follows:
as follows: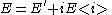
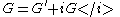
where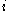 is the imaginary unit
is the imaginary unit
.
Viscoelastic stress-strain phase-lag
Viscoelasticity is studied using dynamic mechanical analysisDynamic mechanical analysis
Dynamic mechanical analysis is a technique used to study and characterize materials. It is most useful for studying the viscoelastic behavior of polymers. A sinusoidal stress is applied and the strain in the material is measured, allowing one to determine the complex modulus...
where an oscillatory force (stress) is applied to a material and the resulting displacement (strain) is measured. http://las.perkinelmer.com/content/ApplicationNotes/APP_FilmsandCoatings.pdf
- In purely elastic materials the stress and strain occur in phasePhase (waves)Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
, so that the response of one occurs simultaneously with the other. - In purely viscous materials, there is a phase difference between stress and strain, where strain lags stress by a 90 degree (
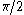 radianRadianRadian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
radianRadianRadian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius. The radian is the standard unit of angular measure, used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly a SI supplementary unit, but this category was abolished in 1995 and the radian is now considered a SI derived unit...
) phase lag. - Viscoelastic materials exhibit behavior somewhere in between that of purely viscous and purely elastic materials, exhibiting some phase lag in strain.
Stress and strain in a viscoelastic material can be represented using the following expressions:
- Strain:
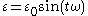
- Stress:
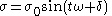
where
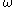 is frequency of strain oscillation,
is frequency of strain oscillation, is time,
is time,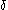 is phase lag between stress and strain.
is phase lag between stress and strain.Storage and loss modulus
The storage and loss modulus in viscoelastic solids measure the stored energy, representing the elastic portion, and the energy dissipated as heat, representing the viscous portion . The tensile storage and loss moduli are defined as follows:- Storage:
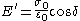
- Loss:
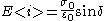
Similarly we also define shear storage and shear loss moduli,
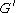 and
and 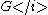 .
.Complex variables can be used to express the moduli
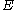 and
and 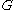 as follows:
as follows: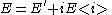
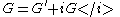
where
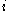 is the imaginary unit
is the imaginary unitImaginary unit
In mathematics, the imaginary unit allows the real number system ℝ to be extended to the complex number system ℂ, which in turn provides at least one root for every polynomial . The imaginary unit is denoted by , , or the Greek...
.

